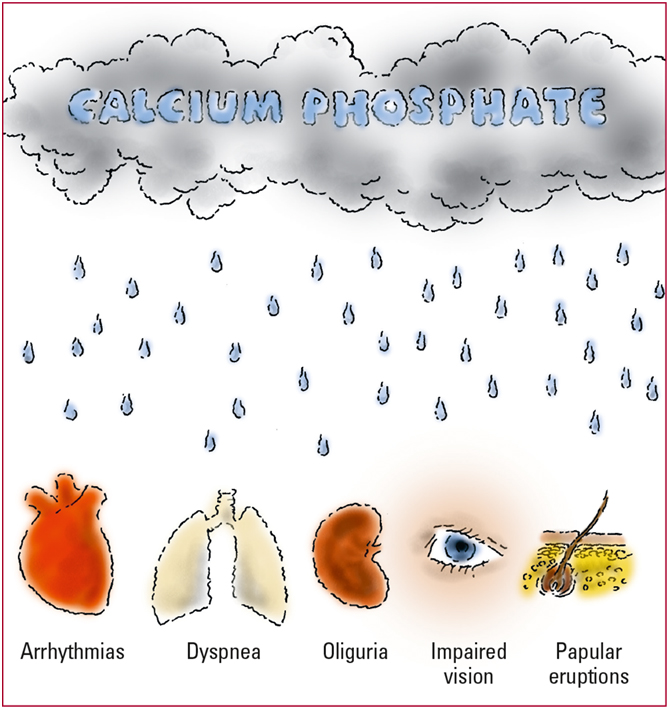
When serum phosphorus levels are high, phosphorus binds with calcium to form an insoluble compound called calcium phosphate. The compound is deposited in the heart, lungs, kidneys, eyes, skin, and other soft tissues where it interferes with normal organ and tissue function. This illustration shows some of the organs affected and the effect calcification has on these organs.