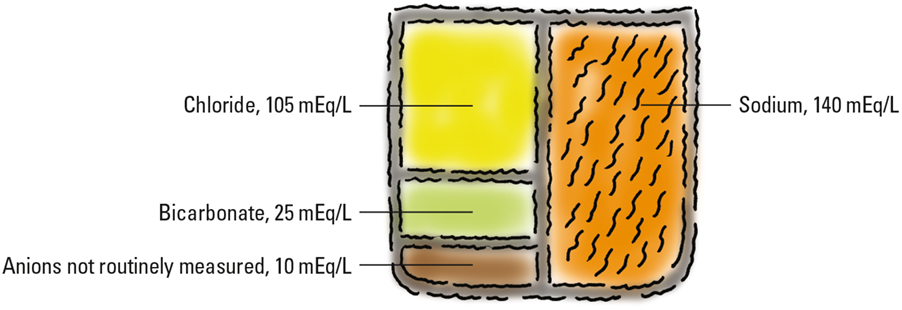
This illustration represents the normal anion gap. The gap is calculated by adding the chloride level and the bicarbonate level and then subtracting that total from the sodium level. The value normally ranges from 8 to 14 mEq/L and represents the level of unmeasured anions in extracellular fluid.
In the example below, the chloride level is 105 mEq/L, the bicarbonate level is 25 mEq/L, and the sodium level is 140 mEq/L. To find the anion gap, first add the chloride and bicarbonate levels to get a total of 130 mEq/L. Then subtract that total from the sodium level of 140 mEq/L, which leaves 10 mEq/L—the anion gap.