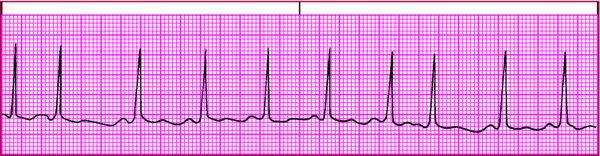
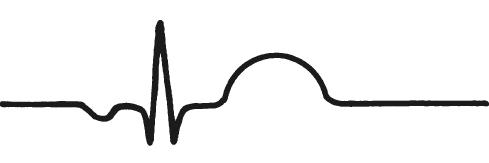
This rhythm strip illustrates PJC. Look for these distinguishing characteristics:
P wave inversion
Look for an inverted P wave in leads II, III, and aVF. Depending on when the impulse occurs, the P wave may fall before, during, or after the QRS complex. (See Identifying a PJC.) If it falls during the QRS complex, it's hidden. If it comes before the QRS complex, the PR interval is less than 0.12 second.
Because the ventricles are usually depolarized normally, the QRS complex has a normal configuration and a normal duration of less than 0.12 second. The T wave and the QT interval are usually normal.