- Gather all needed supplies.
- Explain the procedure to the patient.
- Answer the patient's questions.
- Ask the patient to lie in a supine position in the center of the bed with his arms at his sides.
- If the patient can't tolerate lying flat, raise the head of the bed to semi-Fowler position.
- Ensure privacy.
- Expose the patient's arms, legs, and chest.
- Drape the patient for comfort.
Selecting lead sites
- Choose areas that are flat and fleshy, not muscular or bony.
- As needed, take steps to enhance electrode contact with the skin:
- Clip excessively hairy areas.
- Remove excess oil and other substances from the skin.
- To ensure an accurate recording, be sure to apply the electrodes correctly.
- Keep in mind that inaccurate placement of an electrode may lead to inaccurate waveforms and incorrect ECG interpretation.

Placing the leads
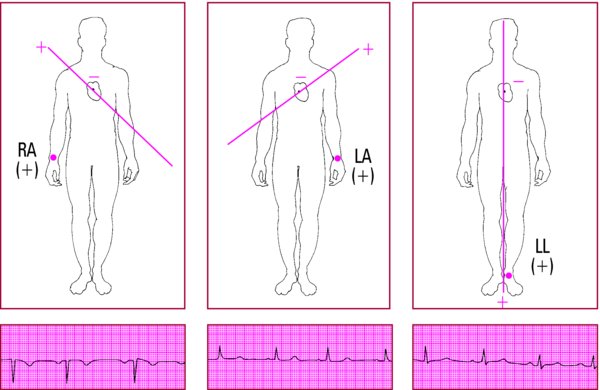
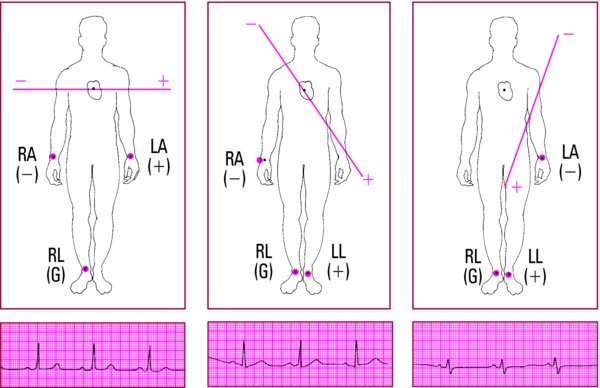
- Place electrodes on both of the patient's arms and on the left leg.
- Place an electrode on the right leg. (This is a ground that doesn't contribute to the waveform.)
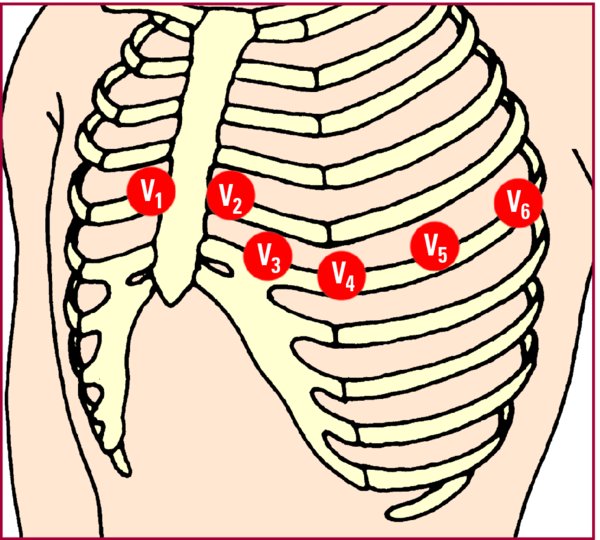
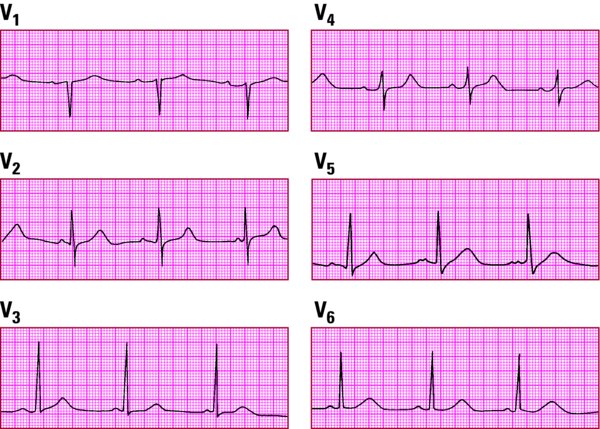
- Place the six unipolar precordial leads (V1 through V6) in sequence across the chest.