ECG effects of hypokalemia 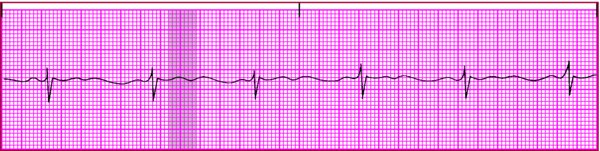
P wave - Normal size
- Normal configuration
- May be peaked in severe hypokalemia
QRS complex - Within normal limits
- Possibly widened
- Prolonged in severe hypokalemia
T wave - Has decreased amplitude
- Becomes flat as potassium level drops, and U wave appears (the key finding, as shown in shaded area on strip)
- Flattens completely in severe hypokalemia and may become inverted
- May fuse with increasingly prominent U wave
QT interval - Usually indiscernible as T wave flattens
Other - Depressed ST segment
- Increased amplitude and prominence of U wave as hypokalemia worsens; may fuse with T wave
|