Nitrogen (N2) content of inspired air prevents alveolar collapse.
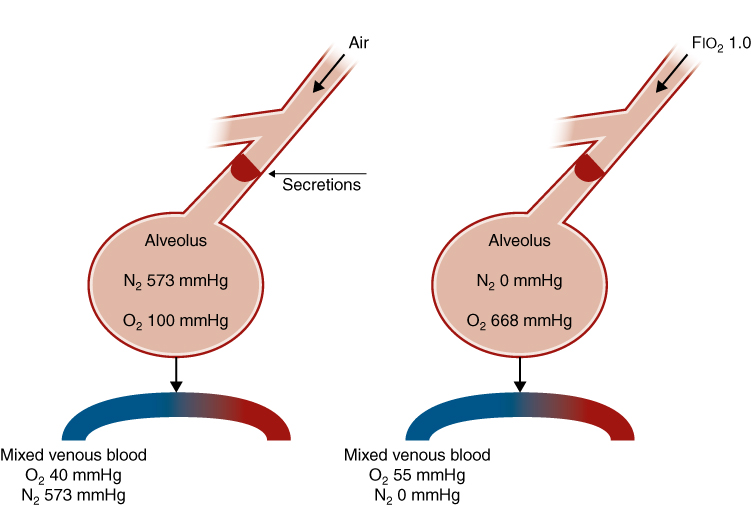
On the left, secretions obstruct the airway while the patient was breathing room air. There is a small oxygen (O2) gradient between the alveolus and mixed venous blood. On the right, secretions obstruct the airway after denitrogenation. As a result, the mixed venous blood is very hypobaric compared with the alveolus. The alveolus will tend to collapse as O2 rapidly flows down its pressure gradient. CO2 and H2O have been omitted for simplicity.
(Adapted with permission from WestJB. Respiratory Physiology. 4th ed. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins; 1990.)