Cause:(Peds 2004;114:e130; Nejm 2001;344:581)
Indirect bilirubin elevations:
- Glucuronyl transferase deficiency
- Normal in premature infant, esp if increased enterohepatic circulation
- Congenital deficiency (Crigler-Najjar syndrome) rarely; rx w phototherapy, perhaps hepatocyte transplantation (Nejm 1998;338:1422)
- ABO and Rh (see above) incompatibility
- Breast milk (pregnane-3
 , 20
, 20 -diol)-induced jaundice, never needs rx no matter how high (Peds 1993;91:470)
-diol)-induced jaundice, never needs rx no matter how high (Peds 1993;91:470) - Hypothyroidism (cretin)
- Drug induced, eg, by excess vitamin K, or chloramphenicol (gray baby syndrome)
Direct bilirubin elevations:
- Infections
- Bacterial sepsis
- Intrauterine infections like syphilis, and TORCH (TOxoplasma, Rubella, CMV, Herpes) infections, which typically elevate LFTs and direct bilirubin
- Perinatally acquired infections like herpes, enteroviruses, hepatitis B
- Biliary obstruction
Pathophys:More bilirubin production from incr rbc turnover and limited amounts of glucuronyl transferase, which attaches glucuronic acid to unconjugated, poorly water-soluble bilirubin so it can be excreted
Exaggerated physiologic jaundice more common in Asians, males, borderline preterm, poor feeders
Usually benign, no neurologic damage in 36+-wk-old term infants w bilirubin over 25 mg % in 1st mo of life (Nejm 2006;354:1889); Crigler-Najjar rapidly fatal, though some variants can survive
Kernicterus (brain damage): 10% mortality, and 70% morbidity with retardation and basal ganglia degeneration
Lab:
Chem:Elevated bilirubin, either by blood measurement of transcutaneous bilirubinometry; indirect elevation > direct; up to 17 mg % in term infants in 1st wk of life can be normal.
Fig.13.1 Algorithm for the Management of Jaundice in the Newborn Nursery
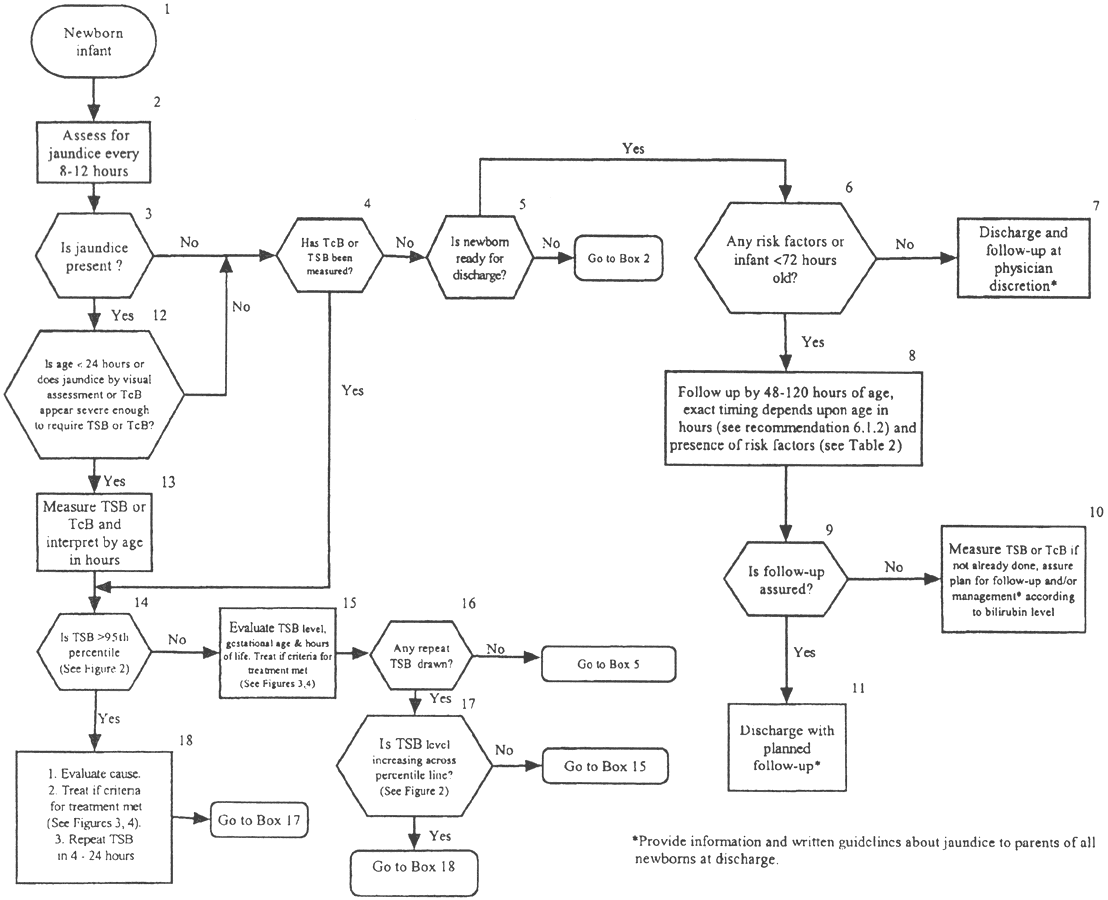
Subcommittee on hyperbilirubinemia. Management of hyperbilrubinemia in newborn infants 35 or more weeks of gestation. Reproduced with permission from Peds 2004:114:297; copyright 2004 by Am Acad Pediatrics
Of transcutaneous biliometry:
better than visual assessment; not appropriate to track progress of (light) therapy; only measures total biliruben; measurement at forehead better than at sternum; decreases need for serum biliruben measurements (Pediatr 1997; 99:599, Pediatr 2001;107:1264)
Rx:
None at term if under 25 mg % unless prematurity, sick child where should rx >20 mg % (Peds 1992;89:809; 1983;71:660); rx guidelines vary depending on weight and hours of life (Peds 1994;94:558)
Feeding on demand, breast or bottle, including Pedialyte supplementation, decr the enterohepatic recirculation of bilirubin
Bilirubin lights (fluorescent white, blue, or green) isomerize bilirubin to hepatically excretable benign products (Med Let 1971;13:11)
Exchange transfusions if lights not enough
 , 20
, 20 -diol)-induced jaundice, never needs rx no matter how high (Peds 1993;91:470)
-diol)-induced jaundice, never needs rx no matter how high (Peds 1993;91:470)
