Nejm 2005;353:2477; Jama 2004;292:97
Cause:Neoplasia, some are genetic and familial (Ann IM 1993;118:106) from change in chromsome 3p: von Hippel-Lindau disease, hereditary papillary renal carcinoma, familial oncocytoma, and hereditary renal carcinoma
Pathophys:Frequent vascular metastases
4 (women) to 10 (men)/100 000/yr incidence (Jama 1999;281:1628); peak incidence age 60-80 yr; increased incidence in von Hippel-Lindau disease (40%), smokers, obesity, and HT (Nejm 2000;343:1305). 31 000 new cases/yr in US
Male/female = 3:1
Sx:Hematuria (70%); renal colic due to clots (50%); costovertebral angle pain. Asx in 25-40%
Si:Flank mass (30-60% on presentation); anemia (41%); fever (17%); polycythemia (4%); hypertension; accessory nipples (20%) (Ann IM 1981;95:182); IVC obstruction if on right; left varicocele due to left spermatic vein obstruction (2%) if on left.
Without metastases, 88% 5-yr survival if >7 cm (stage 2), 95% if <7 cm (stage 1); with single resected met, 35% 5-yr survival; with multiple mets, 4% 5-yr survival
Hypercalcemia due to increased parathormone, amyloidosis
Lab:
Chem:Alkaline phosphatase increased (produced in tumor)
Path:Clear cell (75%), papillary (15%), chromophobic (5%), collecting duct (2%) types
Xray:IVP or CT. Occasionally ultrasound with diagnostic tap if complex cystic lesion.
Rx:
Surgical partial or total resection; resection of multiple mets doesn’t improve survival; no chemotherapy or radiation rx helpful.
of metastatic disease: after resection of primary, cytokines: interleukin- 2a or -
2a or - 2b (Nejm 1998;338:1272; 2001;345:1655), or interferon-
2b (Nejm 1998;338:1272; 2001;345:1655), or interferon-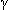 1b; perhaps as 2nd-line rx, sunitinib (Jama 2006;295:2516) and sorafenib (Urolo 2008;179:326)
1b; perhaps as 2nd-line rx, sunitinib (Jama 2006;295:2516) and sorafenib (Urolo 2008;179:326)
 2a or -
2a or - 2b (Nejm 1998;338:1272; 2001;345:1655), or interferon-
2b (Nejm 1998;338:1272; 2001;345:1655), or interferon-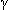 1b; perhaps as 2nd-line rx, sunitinib (Jama 2006;295:2516) and sorafenib (Urolo 2008;179:326)
1b; perhaps as 2nd-line rx, sunitinib (Jama 2006;295:2516) and sorafenib (Urolo 2008;179:326)