Sx:H/o OD >10 gm (>140 mg/kg), usually  15 gm (4 gm/d is maximal therapeutic dose) within 24 h but can occur at just 4 gm/d in alcoholics (Med Let 1996;38:55). May have no sx for 72 h
15 gm (4 gm/d is maximal therapeutic dose) within 24 h but can occur at just 4 gm/d in alcoholics (Med Let 1996;38:55). May have no sx for 72 h
Si:None
Cause:Acetaminophen po
Pathophys:Toxic metabolite causes liver failure; can occur at "nontoxic" levels in alcoholics (Ann IM 1986;104:398) and be inadvertant (Nejm 1997;337:1112)
Sx:H/o OD >10 gm (>140 mg/kg), usually  15 gm (4 gm/d is maximal therapeutic dose) within 24 h but can occur at just 4 gm/d in alcoholics (Med Let 1996;38:55). May have no sx for 72 h
15 gm (4 gm/d is maximal therapeutic dose) within 24 h but can occur at just 4 gm/d in alcoholics (Med Let 1996;38:55). May have no sx for 72 h
Si:None
Hepatitis more commonly if fasting and/or concomitant ethanol ingestion (Jama 1994;272:1845), and/or hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs like seizure medications
Lab: Chem:Acetaminophen level initially on all drug ODs and, if positive, at 4, 8, and 12 h after OD and plot on nomogram (Nejm 1988;319:1557); if 4-h level >200 µgm/mL or 12-h level >50, hepatic toxicity likely; if half-life >4 h then hepatitis likely, if >12 h then encephalopathy likely
Rx:Acetylcysteine 140 mg/kg load, 70 mg/kg × 17 doses q4h po or via NG tube; or 300 mg iv over 20 h. Treat levels of >150 µgm/mL at 4 h, >50 at 8 h (see nomogram). Works regardless of level, probably by increasing tissue O2 delivery (Nejm 1991;324:1852). Best result if start within 4-8 h but still worth doing up to 24 h postingestion. Activated charcoal binds acetylcysteine, but 1 dose ok since have 12 h to start acetylcysteine and one 1 dose may help adsorb some of the acetaminophen and other drugs taken concomitantly; if did get charcoal, consider increasing initial acetylcysteine dose by 20-40%. Ondansetron 4 mg iv can help nauseated pts tolerate
Figure 1.2 Acetaminophen overdose nomogram
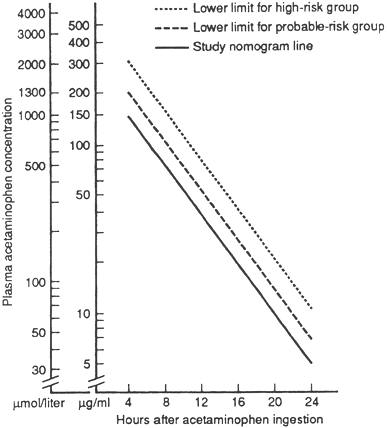
Reproduced with permission from Smilkstein MJ, et al. Efficacy of oral N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose. New Eng J Med 1988;319:1558. Copyright 1988, Mass. Medical Society, all rights reserved.