Nejm 1999;340:1021; 1997;337:762
Cause:Genetic, autosomal
Pathophys:
Val substituted for Glut in ß chain leading to hemoglobin (Hgb) S, unstable at low O2, which causes polymer precipitation, which in turn sickles cells. These sickled cells stick to vessel walls, thus causing clots and infarctions. Splenic infarcts produce diminished antibody formation, which leads to increased infections. Hgb F ( 2
2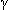 2) may persist as survival mechanism into adult life. Heterozygous cells sickle only in severe hypoxia or if Hgb C or D present. Renal damage to medulla causes decreased concentrating ability, K+ loss, papillary necrosis, etc.
2) may persist as survival mechanism into adult life. Heterozygous cells sickle only in severe hypoxia or if Hgb C or D present. Renal damage to medulla causes decreased concentrating ability, K+ loss, papillary necrosis, etc.  -Thalassemia trait protects and vice versa (Nejm 1982;307:1441)
-Thalassemia trait protects and vice versa (Nejm 1982;307:1441)
In US blacks, 7% have trait, 0.5% homozygous. Genetic distribution in world correlates with history, geography, and malaria (Ann IM 1973;79:258)
Sx:Painful crises in 60%; frequency correlates w worse prognosis (Nejm 1991;325:11)
Si:Retarded growth and sexual maturation (Nejm 1984;311:7); frontal bossing; skin ulcers, esp lower legs; angioid streaking of fundi indicates neovascularization (r/o Paget's, pseudoxanthoma elasticum)
50% live to age 45 yr, longer if fetal Hgb >8.6% (Nejm 1994;330:1639); heterozygotes have no clinical disease
Lab:
Hem:ESR low, sickled cells in peripheral smear; hemoglobin electrophoresis shows Hgb S + increased Hgb F (Nejm 1978;299:1428)
Urine:UA w hematuria, low specific gravity due to inability to concentrate even in heterozygotes
Xray:Long bone infarcts/necrosis, "hair on end" skull, step fractures of vertebrae
Rx:
Preventive maneuvers:
- Amniocentesis and abortion of affected fetuses (Nejm 1983;309:831)
- Penicillin (or Tm/S, or macrolide) prophylactically until age 5 yr (Jama 2003;290:1057)
- Pneumococcal vaccine (Nejm 1977;297:897); or phenoxymethyl penicillin 125 mg bid works age 4 mo-3 yr? (Nejm 1986;314:1593)
- Preop exchange transfusion helps (Nejm 1990;322:1666), but prophylactic transfusion in pregnancy does not work (Nejm 1988;319:1447)
- Hydroxyurea (Nejm 2008;358:1362; Ann IM 2008;148:932, 939; Jama 2002;289:1645) 10-25 mg/kg/d gradually increased to just start suppressing polys; stimulates fetal hemoglobin production (Nejm 1990;322:1037); improves survival over 8 yr
Butyrate (short-chain FA) is ineffective (Nejm 1995;332:1606)
of surgical crisis: transfuse to normal hematocrit (Nejm 1995;333:206)
of anemia
- Transfusions, but rx limited by sensitization, less with black blood donors (Nejm 1990;322:1617)
- Marrow or stem cell transplant perhaps if HLA compatible donor, 90% survive (Nejm 2009;361:2309)
of nephropathy: ACE inhibitors to prevent progression (Nejm 1992;326:910)
of sepsis: ceftriaxone im in children as outpts (Nejm 1993;329:472)
of crisis: iv fluids, NSAIDs, narcotics; possibly steroids (Nejm 1994;330:733); possibly poloxamer 188 (Jama 2001;286;2099), inhaled nitric oxide/O2, 80%/20% not helpful (Jama 2011;305:893)
of stroke: transcranial Doppler ultrasound and transfusions (plain or exchange) (Nejm 1998;339:5)
 2
2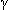 2) may persist as survival mechanism into adult life. Heterozygous cells sickle only in severe hypoxia or if Hgb C or D present. Renal damage to medulla causes decreased concentrating ability, K+ loss, papillary necrosis, etc.
2) may persist as survival mechanism into adult life. Heterozygous cells sickle only in severe hypoxia or if Hgb C or D present. Renal damage to medulla causes decreased concentrating ability, K+ loss, papillary necrosis, etc.  -Thalassemia trait protects and vice versa (Nejm 1982;307:1441)
-Thalassemia trait protects and vice versa (Nejm 1982;307:1441)