Am Rv Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161:S221
Cause:Mycobacterium tuberculosis andbovis
Pathophys:
Primary infection by inhalation to lower lungs leading to local node involvement and asx bacteremia causing gradual hypersensitization via lymphocytic response and eventual calcification and scar = sterile Ghon complex
Secondary disease is a reactivation and hypersensitivity reaction to bacteria spread by asx bacteremia to lung apices and upper kidneys where high O2 concentrations prevent Ghon complex-type sterilization
Inhalation of respiratory droplets, of infected persons; but once on drugs probably little infectivity despite positive smears (Nejm 1974;290:459). Reinfection may be as important as reactivation, at least in homeless. Epidemic description at Bath Iron Works (Ann IM 1996;125:114)
Incidence, 25000 new US cases/yr; these rates are increased in the 1990s from HIV patients, prisons, homeless populations (Nejm 1992;326:703) and the foreign born (Jama 1997;278:304). 3/4 cases from patients with previous positive PPD. 25 million positive PPDs in US, only 5-10% ever result in active disease whereas HIV pos pts who contract tbc become active cases at 5-10%/yr. In elderly and foreign born, 90% of cases are reactivation, whereas only 60% are in younger pts and the homeless (Jama 1996;275:305), and 1/3 are recent infections (Nejm 1994;330:1692, 1703, 1750); 3/4 are now due to exogenous reinfection (Nejm 1999;341:1174)
Incidence higher (Mmwr 5/18/90) in diabetics, institutionalized, household contacts, HIV-infected (Nejm 1992;326:231; 1991;324:289, 1644), alcoholics, gastrectomy, silicosis, immunosuppressed including pts on TNF agents (Nejm 2001;345:1098), postpartum (Ann IM 1971;74:764)
Bovis now very rare due to pasteurization of milk
Worldwide 33% prevalence and causes 6% of all deaths (Jama 1995;273:220, Mmwr 1993;42:961)
MDR (multiple drug resistant) type: resistant to rifampin isoniazide
XDR (extensively drug resistant) type (Nejm 2008;359:563): MDR resistance pattern, plus resistant to any fluoroquinolone and at least 1 of the 3 following injectable drugs: capreomycin, kanamycin, and amikacin. Emerged in 2005 in S. Africa in HIV+ patients; now on the rise worldwide. Thought due to inappropriate use of 2nd-line rx (see below) when 1st-line rx failing
Sx: Fever, weight loss, night sweats, cough, sputum production, hemoptysis
Si:Same as sx
Mortality 6%/yr, 12% at 2 yr, but 50% at 2 yr if HIV positive and 80% if have AIDS (Jama 1996;276:1223)
Apical lung abscess; peritonitis (Nejm 1969;281:1091); meningitis; epididymitis; PID; endometritis; splenic and hepatic abscesses; nontender, scarring skin sores/abscesses; arthritis (esp bovis); pericarditis (Nejm 1964;270:327); osteomyelitis, esp of spine (POTT'S DISEASE); pleuritis (Am Rev Tbc 1955;71:616); laryngitis, very infectious (Ann IM 1974;80:708); hypercalcemia (25%) from vitamin D sensitivity (Ann IM 1979;90:324)
Antibiotic resistance (see above, MDR and XDR emergence), geographically variable, 25% of cases resistant to INH and/or rifampin (Nejm 1993;328:521, 527); multiple drug resistance epidemics in AIDS patients now (Nejm 1992;326:1514), esp in New York City (Jama 1996;276:1229)
Lab:
Bact:Sputum or urine AFB smears; cultures of sputum, gastric aspirate, urine, peritoneal fluid (1 L spun down—Nejm 1969;281:1091)
Path:Biopsy of liver pos in high % of miliary, or of peritoneum if ascites protein >2.5 gm %
Serol:Interferon gamma release assays (Ann IM 2007;146:340) like QuantiFERON-Tb Gold test: interferon-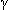
 0.35 IU/cc (Med Let 2007;49:83; Jama 2005;293:2746, 2756; 2001;286:1740) used just like but more specif (>90%) and sens (80%) than skin test even in BCG immunized and all done on one visit; cost $35-100
0.35 IU/cc (Med Let 2007;49:83; Jama 2005;293:2746, 2756; 2001;286:1740) used just like but more specif (>90%) and sens (80%) than skin test even in BCG immunized and all done on one visit; cost $35-100
Skin tests:Intermediate strength (IPPD, 5 U), positive if  5 mm in HIV pts (Ann IM 1997;126:123) or pts w pulmonary scars or recent contacts, >10 mm in others or perhaps even >15 mm in very low risk; repeat in 2-3 wk to get booster effect, 1/3 more become positive (>10 mm) in elderly but of questionable significance in the young and elderly (Ann IM 1994;120:190; Jags 2007;55:1592). Ignore old BCG immunization in interpreting, esp if >5-10 yr ago. False negs with overwhelming infection, sarcoid, or other anergy.
5 mm in HIV pts (Ann IM 1997;126:123) or pts w pulmonary scars or recent contacts, >10 mm in others or perhaps even >15 mm in very low risk; repeat in 2-3 wk to get booster effect, 1/3 more become positive (>10 mm) in elderly but of questionable significance in the young and elderly (Ann IM 1994;120:190; Jags 2007;55:1592). Ignore old BCG immunization in interpreting, esp if >5-10 yr ago. False negs with overwhelming infection, sarcoid, or other anergy.
Urine:Acid, sterile, wbc's and rbc's, protein
Xray:
Chest shows apical or superior segment of lower lobe scarring and/or Ghon complex
IVP characteristically shows beaded ureters
Rx:
Prevent w
- Hospital preventive policies (Nejm 1995;332:92) respiratory isolation in negative pressure rooms (debatably—Ann IM 2000;133:779) until 3 negative smears of HIV pts w abnormal chest xray, plus regular skin testing programs (Nejm 1995;332:92; Ann IM 1995;122:658)
- BCG vaccination X1 to entire at-risk population, 50% effective over 60 yr (Jama 2004;291:2086; 1994;271:698)
- Rx of latent, PPD-positive tbc, w:
- INH 300 mg po qd × 9 mo for PPD reactors (10-20% lifetime risk—Nejm 2004;350:2060) and household contacts; hepatitis risk is small (<1/1000 under age 35 yr, 2/1000 age 35-65 yr, 3/1000 >65 yr—Jama 1999;281:1014), <1/50 000 die (Ann IM 1997;127:1058); supplement w pyridoxine only if alcoholic and/or malnourished, not for asthmatics on steroids (Ann IM 1976;84:261); in pts on immusuppressives (infliximab, et al) or HIV-pos pts w pos PPD or anergy, 300 mg po qd w B6 (pyridoxine) 50 mg po qd forever decr incid by 2/3 at 2 yr (Nejm 1997;337:801)
- Rifampin 600 mg alone × 4 mos
- Rifabutin alone if on some protease inhibitors
of active disease (Guidelines—Med Let 2007;50:15): contact local health dept; use 4 drugs initially in all and continuing in AIDS (Nejm 1999;340:367); use tiw directly observed rx for all cases to prevent further drug resistance (Jama 1995;274:945; Nejm 1994;330:1179) or biw rx after 2 wk of qd rx; prevalence of drug resistance incr from 10% to 36% if take meds for <1 mo (Nejm 1998;338:1641)
- 1st line; use 1st 4 together until sensitivities studies back:
- INH 300 mg qd × 6 mo or biw-tiw × 9 mo, with pyridoxine only if >300 mg qd to prevent neuropathy; adverse effect: hepatitis
- Rifampin 600 mg qd or biw-tiw × 9 mo, less toxic than streptomycin or INH or as Rifamate (INH + rifampin), or as longer-acting form, rifapentine (Priftin) (Med Let 1999;41:21) biw × 2 mos then q wk thereafter; adv reactions: drug interactions, red body fluids, incr urate; $90/mo
- Pyrazinamide 0.5-40 mg/kg/d or biw-tiw × 2 mo, with above allows 6-mo cure courses (Am Rev Respir Dis 1991;143:700, 707). Or as "Rifater," a combination pill of all 3 (preferable—Ann IM 1995;122:951). Cure rates ~98% (Am Rev Respir Dis 1982;126:460). Adv effects: hepatitis, arthralgias, pruritis, rash, gi intolerance, elevated uric acid
- Ethambutol 15 mg/kg pos qd, use as 4th drug until know sensitivities (Med Let 1995;37-67); adverse effects: retrobulbar neuritis, check visual acuity regularly, rarely reversible
- Mycobutin (Rifabutin) 5 mg/kg (300 mg max) po qd, or biw-tiw; adv effects: hepatitis, flu syndrome, uveitis, neutropenia, drug interactions
- 2nd-line drugs:
of antibiotic-resistant tbc: 3 drugs to which organism test susceptible × 12-24 mo; frequent now in AIDS pts (Nejm 1993;328:1137; 1992;326:1514; Ann IM 1992;117:177, 191), must use 4 drugs
of meniningitis: dexamethasone 0.15-0.3 mg/kg × 8 wk (Nejm 2004;351:1741) for adults and children, HIV positive or negative
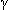
 0.35 IU/cc (Med Let 2007;49:83; Jama 2005;293:2746, 2756; 2001;286:1740) used just like but more specif (>90%) and sens (80%) than skin test even in BCG immunized and all done on one visit; cost $35-100
0.35 IU/cc (Med Let 2007;49:83; Jama 2005;293:2746, 2756; 2001;286:1740) used just like but more specif (>90%) and sens (80%) than skin test even in BCG immunized and all done on one visit; cost $35-100 5 mm in HIV pts (Ann IM 1997;126:123) or pts w pulmonary scars or recent contacts, >10 mm in others or perhaps even >15 mm in very low risk; repeat in 2-3 wk to get booster effect, 1/3 more become positive (>10 mm) in elderly but of questionable significance in the young and elderly (Ann IM 1994;120:190; Jags 2007;55:1592). Ignore old BCG immunization in interpreting, esp if >5-10 yr ago. False negs with overwhelming infection, sarcoid, or other anergy.
5 mm in HIV pts (Ann IM 1997;126:123) or pts w pulmonary scars or recent contacts, >10 mm in others or perhaps even >15 mm in very low risk; repeat in 2-3 wk to get booster effect, 1/3 more become positive (>10 mm) in elderly but of questionable significance in the young and elderly (Ann IM 1994;120:190; Jags 2007;55:1592). Ignore old BCG immunization in interpreting, esp if >5-10 yr ago. False negs with overwhelming infection, sarcoid, or other anergy.