Cause:Atypical Mycobacterium spp.(MOTT = mycobacterium other than tuberculosis)
M. scrofulaceumand kansasii(MSK) (Ann IM 1998;129:698): Endemic in soil (kansasii); little person-to-person spread. In midwest especially
M. aviumand intracellulare(MAI): Major problem in AIDS where is 3rd most common opportunistic infection after pneumocystis and Kaposi's (Nejm 1996;335:428); COPD patients, emerging among immunocompetent patients
M. fortuitumand other fast growers (FG): Normal throat inhabitant?
Sx:
MSK: Pulmonary, scrofula, skin ulcers. Seen in AIDS pts (Ann IM 1991;114:861)
MAI: Pulmonary, esp in COPD, AIDS, and previously damaged lung but not always
FG: Pulmonary; subcutaneous abscess; corneal infection
Si:Pulmonary
MAI: Quite virulent in HIV pts
FG: Spontaneous resolution w/o rx or w debridement
MSK: Full gamut like regular tbc; drug resistance common
FG: r/o M. marinum, which causes SWIMMING POOL GRANULOMA(Nejm 1997;336:1065)
Lab:
Bact:All are nicotinic acid nonproducers in contrast to M. bovisand tuberculosis. All are acid fast; grow at 25°C; are avirulent to guinea pigs; chromogen characteristics: MSK shows photochromogen
MAI, no chromogen; FG no chromogen and fast growth (2-7 d); r/o scotochromogen types, which are rarely clinically significant
Skin tests:MSK and MAI are specific and cause 2nd strength PPD to be positive
Rx:
for MSK: Rifampin, etc
for MAI (big problem in AIDS pts)
prophylaxis (Nejm 1996;335:428), routinely in all AIDS pts w CD4 counts <100-200/cc (Nejm 1993;329:828) or perhaps only if <100, if no disseminated M. aviumcomplex disease yet; can d/c prophylaxis when CD4 >100 again after HIV rx (Nejm 2000;342:1085)
- Rifabutin retards dissemination in AIDS pts (Med Let 1993;35:36); 300 mg po qd prophylaxis; prevents 55% of expected cases; no resistance develops but can induce rifampin resistance (Nejm 1996;334:1573)
- Clarithromycin 500 mg po bid (Nejm 1996;335:384) prevents 69%; resistance develops in 45%
- Azithromycin 1200 mg po q wk (Nejm 1996;335:392) prevents 59% of expected cases; or used w rifabutin prevents 85%; resistance develops in 11%
of disease: surgery, if possible, + 3-4 drugs (Nejm 1996;335:377; 1993;329:898; Ann IM 1994;121:905) like clarithromycin or azithromycin + ethambutol + clofazimine or rifabutin or rifampin or ciprofloxacin or amikacin; interferon-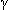 may also help (Nejm 1994;330:1348)
may also help (Nejm 1994;330:1348)
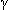 may also help (Nejm 1994;330:1348)
may also help (Nejm 1994;330:1348)