

| Appearance (Skin Color) | Completely Pink Extremities Blue Blue, pale |
| Pulse (Heart Rate) | >100 <100 Absent |
| Grimace (Reflex Irritability) | Cough or Sneeze Grimace No response |
| Activity (Muscle Tone) | Active Motion Some Flexion of Extremities Limp |
| Respiration (Resp. Effort) | Good / Crying Irregular / Slow Absent |
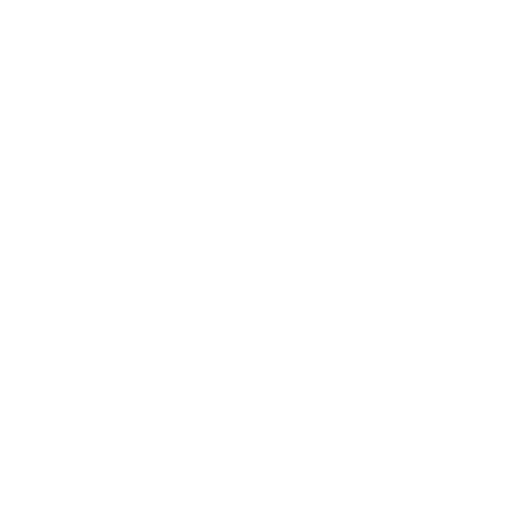
The Apgar score was devised in 1952 by Dr. Virginia Apgar as a simple and repeatable method to quickly and summarily assess the health of newborn children immediately after birth. This test was designed to evaluate a newborn's physical condition after delivery and to determine any immediate need for medical or emergency care. The scoring is performed at 1 minute and 5 minutes after birth. If the fetus is compromised, the score may be repeated at 10 and 20 minutes.
The acronym APGAR stands for:
These five factors are scored on a scale of 0-2, with 2 being the best score. The resulting Apgar score ranges from 0-10. The total score is calculated by adding the score for all the five components.
Interpretation of Apgar Score:
In most situations, a low Apgar score at one minute progresses to a normal score by 5 minutes. A score that remains low at 5 minutes is a major concern and usually requires intervention.
Reference:
Patel D, et al. Effect of a statewide neonatal resuscitation program on apgar scores among high risk neonates in illinois. Pediatrics. 2001;107(4):648-55.