Cause:Genetic, autosomal dominant, on chromosome 4; even elderly onset patients often turn out to have 35+ CAG repeats on chromosome 4
Pathophys:CAG triplet repeats (36-121) on chromosome 4 (Nejm 1994;330:1401) somehow cause degeneration of caudate and lenticular nuclei, as well as frontal lobe; 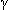 -aminobutyric acid (GABA) deficient in these areas (Nejm 1973;288:337)
-aminobutyric acid (GABA) deficient in these areas (Nejm 1973;288:337)
Origin in England; brought here by colonists; may have been the etiologies of several Salem witches; "Woody Guthrie disease"
Equal racial incidence
Sx:
Onset usually around age 35 yr
Chorea of arms, legs, face; pediatric onset often has no chorea and looks like Parkinson's
Si:Chorea and dementia with preservation of memory longer than problem-solving skills
Live about 15 yr after diagnosis of the disease
Suicide common (approx ~7%)
r/o inherited cerebellar ataxia, myoclonus in Alzheimer's, Creutzfelt-Jakob disease, Wilson's disease a-beta lipoproteinemia/acanthocytosis, tardive dyskinesia, and infarction of basal ganglia
Lab:
L-dopa evocation trial: gradually increase from 250 mg to 1 gm qd, usually increases chorea (reversibly) at least in patient with barely perceptible, questionable si's (Nejm 1972;286:1332; Lancet 1970;2:1185)
DNA restriction fragment length methods can detect in asx patients in at least 1/2 of cases (Nejm 1988;318:535); and this information provided with counseling decreases anxiety in the high- as well as the low-risk groups (Nejm 1992;327:1401)
Xray:
CT and MRI characteristically show caudate atrophy
PET scans in asx show decrease in glucose metabolism in caudate nucleus (Nejm 1987;316:357)
Rx:Prevent by genetic counseling
of disease: phenothiazines like haloperidol (Haldol) or other ancillary drugs like reserpine to decrease chorea
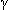 -aminobutyric acid (GABA) deficient in these areas (Nejm 1973;288:337)
-aminobutyric acid (GABA) deficient in these areas (Nejm 1973;288:337)