Cause:Aberrant conduction pathways with different conduction rates within the AV node (AV NODAL REENTRANT TACHYCARDIA[AVNRT]), or outside the AV node (AV RENTRANT TACHYCARDIA [AVRT],WOLFF-PARKINSON-WHITE SYNDROME[WPW]) (Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome) allowing setup of circus movement continous stimulation when the aberrant or usual pathway conducts retrograde; or ectopic irritable atrial focus (PAROXYSMAL ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA [PAT]), often associated with digoxin toxicity especially if manifest w associated block, eg, 2:1 or 3:1
Pathophys:Re-entrant tachycardias occur with things that increase excitability, decrease refractory period, and increase conduction velocity
Figure 2.2 Circus Tachycardias
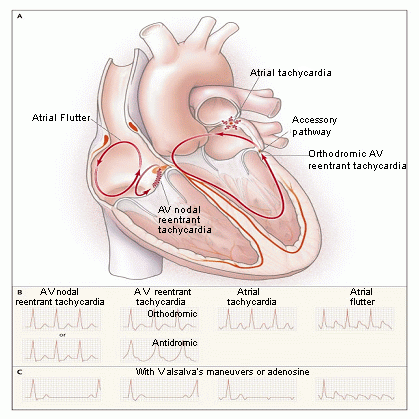
Reproduced with permission from E.Delacretaz. Suprventricular Tachycardia. New Eng J Med 2006;354:1039. Copyright 2006 Mass. Medical Society, all rights reserved.
AVNRT and AVRT each represent 60% and 30% respectively of all PSVTs; PAT constitutes 9%, and rare other syndromes likePERMANENT JUNCTIONAL REENTRANT TACHYCARDIA(PJRT), the last 1%.
Sx:Paroxysmal episodes of palpitations often associated with dizziness, nausea; preciptated by caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, hyperthyroid states, ephedrine in diet supplements, etc.; relieved by valsalva maneuver by patient often. Neck pounding in AVNRT types but not accessory pathway (WPW or AVRT) SVT because nearly coincident atrial and ventricular contraction in former cause cannon waves in neck, which can be felt (Nejm 1992;327:772)
Si:Rapid tachycardia 150-210/min
Recurrent from teenage years on
Rare permanent junctional reentrant tachycardia variant associated with myocardopathy if stays in arrhythmia a long time, reversible if rx'd.
Post PAT T-wave inversions may last days-weeks (Nejm 1995;332:161)
Lab:EKG shows SVT w narrow complexes; AVNRT usually has no apparent P waves, AVRT has Ps closer to the last QRS than the next, and PAT and PJRT have Ps closer to the next QRS and beyond the T wave. PSVT is very regular, even when aberrant and wide, unlike Vtach; QRS aberrancy always <0.14 sec whereas Vtach often (>50%) >0.14 sec, axis is –30° to +120° unlike the LAD with Vtach 60% of time (J. Love 9/85) (see Brugada criteria Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardias (PSVTs))
Rx:Carotid sinus pressure
Adenosine 6-12 mg iv, gone in 10 sec, potentiated by dipyridamole and carbamazepine, inhibited by theophyllines (Med Let 1990;32:63); or verapamil 5-10 mg iv; perhaps propranolol iv 1-5 mg
Electrical cardioversion with sync if meds fail or if unstable, ok to do even if dig on board as long as levels therapeutic and not toxic, and K+ ok (Ann IM 1981;95:676); in resistant cases, implanted atrial burst pacers (Ann IM 1987;107:144); or catheter ablation of atrial slow pathway works 95% of the time (Med Let 1996;38:40, Nejm 1994;330:1481), but can rarely cause fatal esophageal-atrial fistula (Ann IM 2006;144:372).
For chronic prevention: avoid stimulants;  -blockers; may be verapamil or digoxin though both can worsen some
-blockers; may be verapamil or digoxin though both can worsen some

 -blockers; may be verapamil or digoxin though both can worsen some
-blockers; may be verapamil or digoxin though both can worsen some