Cause:
- Idiopathic;
- Circulating immune complexes
- Poststreptococcal (Ann IM 1979;91:76), types 4, 12, 57, and Red Lake (Nejm 1970;283:832) from skin lesions or throat; these types never cause acute rheumatic fever (Nejm 1970;283:561)
- Postviral including coxsackie B, echo, influenza A and B, and adenovirus pharyngitis infections cause 4% (Ann IM 1979;91:697)
Pathophys:Circulating ag/ab complexes deposited in “lumpy” way in basement membrane
In adults, <50% are poststreptococcal; more commonly due to skin infections when does occur; in children >95% are poststrep, often in epidemics. Males > females among children
Sx:History of strep infection 10-14 d before; abrupt onset; malaise; headache; facial edema; flank pain; cloudy urine
Si:Hypertension, periorbital facial edema, hematuria, oliguria
Correlates with anuria and biopsy; best when strep cause; better with younger age; once healed no later deterioration (Nejm 1982;307:725); microhematuria can persist for up to year afterward
Fig 17.2 Course of AGN
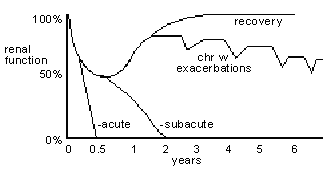
acute = 2% children; subacute = 4% children; chronic with exacerbations = 4% children, 40% adults; recovery = 90% children, 50% adults (New Eng J Med 1978;298:767; Ann IM 1974;80:342)
Hypertensive crisis; can recur in renal transplants (Nejm 2002;347:103)
r/o SBE, hypersensitivity angiitis, polyarteritis nodosa, Goodpasture’s, SLE, anaphylactoid purpura
Lab:
Chem:Elevated creatinine and BUN; proteins normal
Hem:ESR elevated
Path:Renal biopsy shows grossly swollen “flea-bitten” kidneys; microscopically, focal or diffuse (SLE) glomerular involvement, diagnostic infiltration by polys, and lumpy deposition of immune complexes; rapidly progressive GN in anti-BM antibody (Goodpasture’s) or small vessel vasculitis (Vasculitis Etiologies) etiologies have diagnostic crescent formation, and linear immunofluorescent antibody deposition in antibasement membrane type
Serol:ASO titer >400 Todd U is diagnostic of strep, >125 U is suggestive; C3 <100 mg % via alternate pathway and in contrast to normal CH50 and C4 (Nejm 1992;327:1366)
Urine:Hematuria with rbc casts; r/o collagen vascular disease, SBE, vasculitis, severe hypertension, ATN, vascular occlusion, trauma, hereditary nephritis; GOODPASTURE’S SYNDROME w antibasement membrane type IV collagen antibodies (Nejm 2003;348:2543) and hemoptysis, rx’d w plasma exchange, Cytoxan and steroids (Ann IM 2001;134:1033)
- Proteinuria >30 mg but <6 gm/24 h; resolution doesn’t guarantee no permanent damage
- Creatinine clearance low
Rx: Penicillin × 2 wk acutely, no value as prophylaxis; supportive of renal failure
