ICDs can deliver a range of therapies depending on the arrhythmia detected and how the device is programmed. Therapies include antitachycardia pacing, cardioversion, defibrillation, biventricular pacing, and bradycardia pacing. | Therapy | Description |
|---|
| Antitachycardia pacing | This is usually the first line of therapy, when an ICD with lead wires detects a ventricular arrhythmia. A short series of rapid, electrical pacing pulses are used to interrupt monomorphic VT and return the heart to its normal rhythm. This pain-free therapy usually effectively terminates VT. | 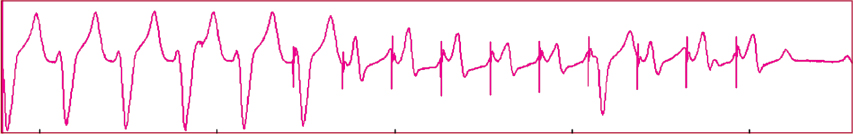
| | Cardioversion | A low- or high-energy shock (up to 41 J) is timed to the R wave to terminate VT and return the heart to its normal rhythm. | | Defibrillation | A high-energy shock (up to 41 J) to the heart is used to terminate ventricular fibrillation and return the heart to its normal rhythm. | | Bradycardia pacing | Electrical pacing pulses are used when the heart’s natural electrical signals are too slow. ICD systems can pace in any way that a pacemaker can pace, including biventricular pacing. |
|
|
