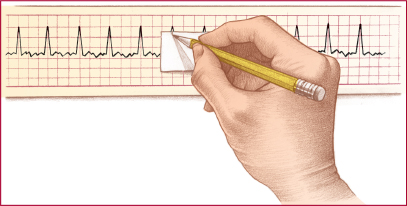
Place the ECG strip on a flat surface. Then position the straight edge of a piece of paper along the strip’s baseline. Move the paper up slightly so that the straight edge is near the peak of the R wave. With a pencil, mark the paper at the R waves of two consecutive QRS complexes, as shown above. This is the R-R interval.
Next, move the paper across the strip, aligning the two marks with succeeding R-R intervals. If the distance for each R-R interval is the same, the ventricular rhythm is regular. If the distance varies, the rhythm is irregular.
Use the same method to measure the distance between the P waves (the P-P interval) and determine whether the atrial rhythm is regular or irregular.
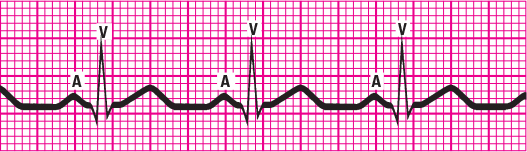
| With the ECG on a flat surface, place one point of the caliper on the peak of the first R wave of two consecutive QRS complexes. Then adjust the caliper legs so that the other point is on the peak of the next R wave, as shown above. This distance is the R-R interval.
Now pivot the first point of the caliper toward the third R wave and note whether it falls on the peak of that wave. Check succeeding R-R intervals in the same way. If the R-R intervals are the same length, the ventricular rhythm is regular. If the length varies, the ventricular rhythm is irregular.
Use the same method to measure the P-P intervals to determine whether the atrial rhythm is regular or irregular.
|