Definition
Myxedema coma is a rare life-threatening complication of hypothyroidism characterized by profound lethargy or coma and usually accompanied by hypothermia.
| ||||||||||||||||
Physical Findings & Clinical Presentation
- Mental obtundation, profound lethargy or coma
- Hypothermia (rectal temperature <35° C [95° F]); often missed by using ordinary thermometers graduated only to 34.5° C (94.1° F) or because the mercury is not shaken below 36° C (96.8° F)
- Bradycardia, hypotension (attributable to circulatory collapse)
- Delayed relaxation phase of deep tendon reflexes, areflexia
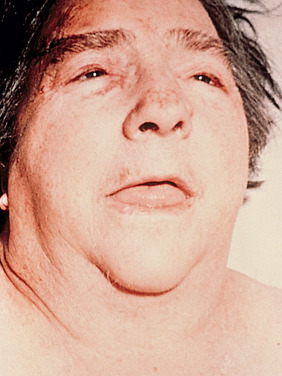
- Myxedema facies (Fig. E1)
- Alopecia, macroglossia, ptosis, periorbital edema, nonpitting edema, doughy skin
- Bladder dystonia and distention
- Pleural, pericardial, and peritoneal effusions