AUTHOR: Glenn G. Fort, MD, MPH
Septic arthritis is a highly destructive form of joint disease most often caused by hematogenous spread of organisms from a distant site of infection. Direct penetration of the joint as a result of trauma or surgery and spread from adjacent osteomyelitis may also cause bacterial arthritis. Any joint in the body may be affected.
- Hallmark: Acute onset of monoarticular joint pain, erythema, heat, and immobility
- Limited range of motion of the joint
- Effusion, with varying degrees of erythema and increased warmth around the joint
- Single joint affected in 80% to 90% of cases of nongonococcal arthritis
- Gonococcal dermatitis-arthritis syndrome:
- Febrile patient at presentation
- Most commonly affected joints in adult: Knee and hip, but any joint may be involved; in children-hip
- Bacteria spread from another locus of infection.
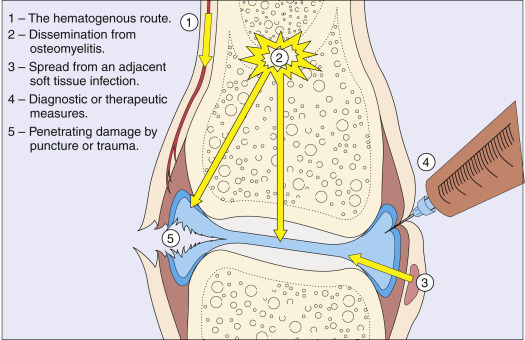
- Predisposing factors: Rheumatoid arthritis, prosthetic joints, advanced age, immunodeficiency (HIV, diabetes mellitus [DM], immunosuppressive drugs), gout, sexual activity (gonococcal arthritis), skin infections, cutaneous ulcers (contiguous spread), recent joint surgery, recent intraarticular infection. Risk factors for development of septic arthritis are summarized in Table 1. Fig. E1 illustrates routes by which bacteria can reach the joint.
- The most common nongonococcal organisms are staphylococci (40%), streptococci (28%), and gram-negative bacilli (19%). Less common are mycobacteria (8%), gram-negative cocci (3%), anaerobes (1%), and gram-positive bacilli (1%).
- Staphylococci (S. aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococcal species) account for >50% of prosthetic-hip and prosthetic-knee infections. S. aureus is very common in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
TABLE 1 Risk Factors for Development of Septic Arthritis
| Age >80 yr | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | |||
| Presence of a prosthetic joint in the knee or the hip | |||
| Recent joint surgery | |||
| Skin infection | |||
| Previous septic arthritis | |||
| Recent intra-articular injection | |||
| HIV or AIDS | |||
| Intravenous drug abuse | |||
| End-stage renal disease on hemodialysis | |||
| Advanced hepatic disease | |||
| Hemophilia with or without AIDS | |||
| Sickle cell disease | |||
| Underlying malignancy | |||
| Hypogammaglobulinemia (susceptible to Mycoplasma infections) | |||
| Late complement-component deficiency (susceptible to Neisseria infections) | |||
| Low socioeconomic status with high rate of comorbidities |
AIDS, Acquired immunodeficiency virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
From Firestein GS et al: Firestein & Kelley’s textbook of rheumatology, ed 11, Philadelphia, 2021, Elsevier.