AUTHOR: Glenn G. Fort, MD, MPH
Definition
A hordeolum is an acute inflammatory process affecting the eyelid and arising from the meibomian (posterior) or Zeis (anterior) glands. It is most often infectious and usually caused by Staphylococcus aureus. When infection involves the meibomian glands, it is called meibomianitis.
Synonyms
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Physical Findings & Clinical Presentation
- Abrupt onset with pain and erythema of the eyelid
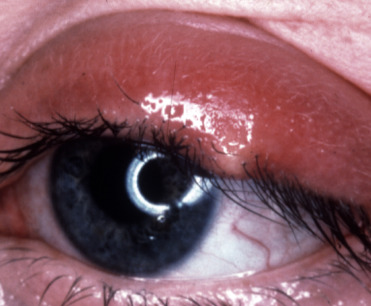
- Localized, tender mass in the eyelid (Fig. E1)
- May be associated with blepharitis
- External hordeolum: Points toward the skin surface of the lid and may spontaneously drain
- Internal hordeolum: Can point toward the conjunctival side of the lid and may cause conjunctival inflammation
Etiology
- 75% to 95% of cases are caused by S. aureus, which includes methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains.
- Occasional cases are caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, other streptococci, gram-negative enteric organisms, or mixed bacterial flora.