AUTHOR: Glenn G. Fort, MD, MPH
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins that is often refractory to treatment with infectious and noninfectious etiologies.
Eyelid infection or inflammation
| ||||||||||||||||
- Common in children, particularly those with atopic dermatitis and eczema
- Adults with seborrhea involving the eyelids
- Common symptoms: Red eyes, burning sensation, excessive tearing, blurred vision, pruritic eyelids.
- Chronically infected lids are usually diffusely erythematous with collarettes (fibrin exudate) at the base of the lashes.
- Lid margins thicken over time, with associated loss of eyelashes (madarosis), misdirected growth of lashes (trichiasis), and overflow or inspissation of the meibomian glands (Fig. E1).
- Associated conjunctivitis with erythema and edema but no discharge.
- Chalazion: Chronic sterile inflammation of an oil gland of the eyelid.
- Superficial punctate erosions of the inferior corneal epithelium are common.
- More severe findings, such as corneal pannus, ulcerative keratitis, or lid ectropion, are less common.
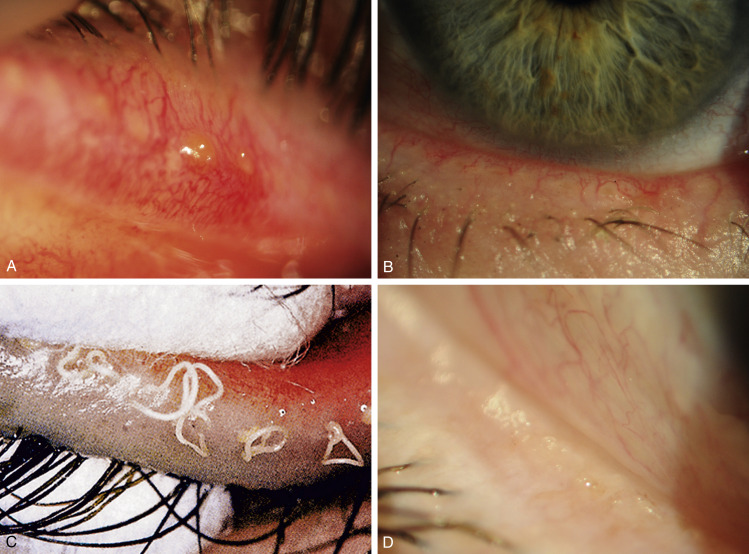
Figure E1 Chronic posterior blepharitis.
A, Capping of meibomian gland orifices by oil globules; B, hyperemic, telangiectatic lid margin; C, expressed toothpaste-like material; D, froth on the eyelid margin.
From Bowling B: Kanski’s clinical ophthalmology, a systematic approach, ed 8, Philadelphia, 2016, Elsevier. Fig C, Courtesy of J Silbert, from Silbert J: Anterior segment complications of contact lens wear, Boston, 1999, Butterworth-Heinemann.
Multiple: Bacterial and nonbacterial causes:
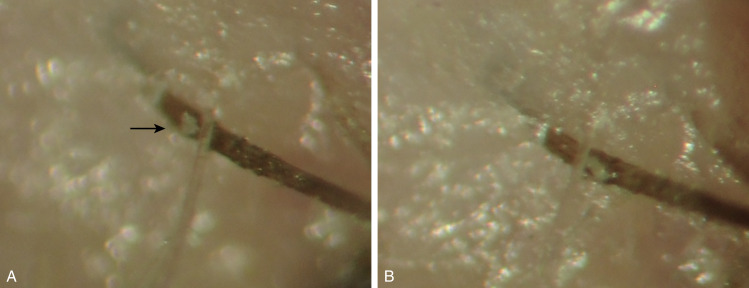
- Staphylococcal infection most common but streptococcal, Moraxella, and other bacterial infections; viral infections (e.g., herpes simplex, herpes zoster, Molluscum contagiosum); and a number of ectoparasites (Fig. E2), including pediculosis, may cause blepharitis
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Rosacea
- Dry eye (keratoconjunctivitis sicca): Decrease in tear volume
- Meibomian gland dysfunction
- Contact lens intolerance
- Two categories of blepharitis (Table E1):
A, Mite visible at eyelash base as a whitish lesion (arrow) after lash manipulation following clearance of collarette; B, photograph taken 2 seconds later showing rapid migration.
From Bowling B: Kanski’s clinical ophthalmology, a systemic approach, ed 8, Philadelphia, 2016, Elsevier.
TABLE E1 Summary of Characteristics of Chronic Blepharitis
| Feature | Anterior Blepharitis | Staphylococcal | Seborrheic | Posterior Blepharitis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lashes | Deposit | Hard | Soft | |
| Loss | ++ | + | ||
| Distorted or trichiasis | ++ | + | ||
| Lid margin | Ulceration | + | ||
| Notching | + | ++ | ||
| Cyst | Hordeolum | ++ | ||
| Meibomian | ++ | |||
| Conjunctiva | Phlyctenule | + | ||
| Tear film | Foaming | ++ | ||
| Dry eye | + | + | ++ | |
| Cornea | Punctate erosions | + | + | ++ |
| Vascularization | + | + | ++ | |
| Infiltrates | + | + | ++ | |
| Commonly associated skin disease | Atopic dermatitis | Seborrheic dermatitis | Acne rosacea |
Note: Blepharitis patients have normal skin microflora in greater amounts (mostly S. epidermidis and Propionibacterium acnes). (S. aureus and S. epidermidis can be cultured in 10%-35% and 90%-95% of healthy persons, respectively.)
From Bowling B: Kanski’s clinical ophthalmology, a systemic approach, ed 8, Philadelphia, 2016, Elsevier.