Types of Percussion
| Type | Purpose | Technique |
|---|---|---|
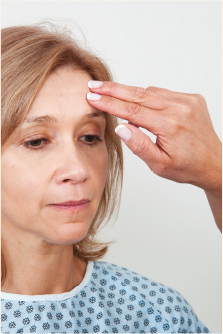
| Direct percussion Direct percussion of sinuses | To elicit tenderness or pain | Directly tap a body part with one or two fingertips such as over the sinuses. |
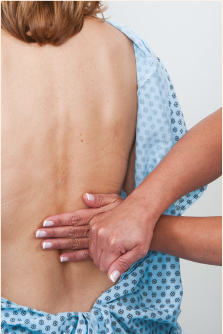
| Blunt percussion (most commonly used method of percussion) Blunt percussion of the kidneys | To detect tenderness over organs (e.g., kidneys) | Place one hand flat on the body surface and use the fist of the other hand to strike the back of the hand flat on the body surface. |
| Type | Purpose | Technique |
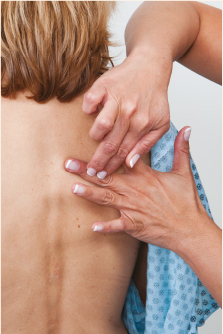
| Indirect percussion (least used method of percussion because of its low reliability) Indirect or mediate percussion of lungs | To elicit one of the following sounds over the chest or abdomen: tympany, resonance, hyperresonance, dullness, and flatness. As density increases, the sound of the tone becomes quieter. Solid tissue produces a soft tone, fluid produces a louder tone, and air produces an even louder tone (see Table 2-5). | Press middle finger of nondominant hand firmly on body part. Keep other fingers off body part to avoid dampening of the sound elicited. Strike the finger on the body part with the middle finger (with short fingernail) with two quick taps of the dominant hand. Flex dominant wrist (not forearm) quickly. Listen to sound. (Use quick wrist movement, not forearm.) |