Average Menstrual Cycle
- Every 28 days; 14 days after ovulation; duration 5 days
- Approximate blood loss 50 mL
- Controlled by the following feedback mechanisms:
- Hypothalamic-pituitary cycle
- Ovarian cycle
- Endometrial cycle
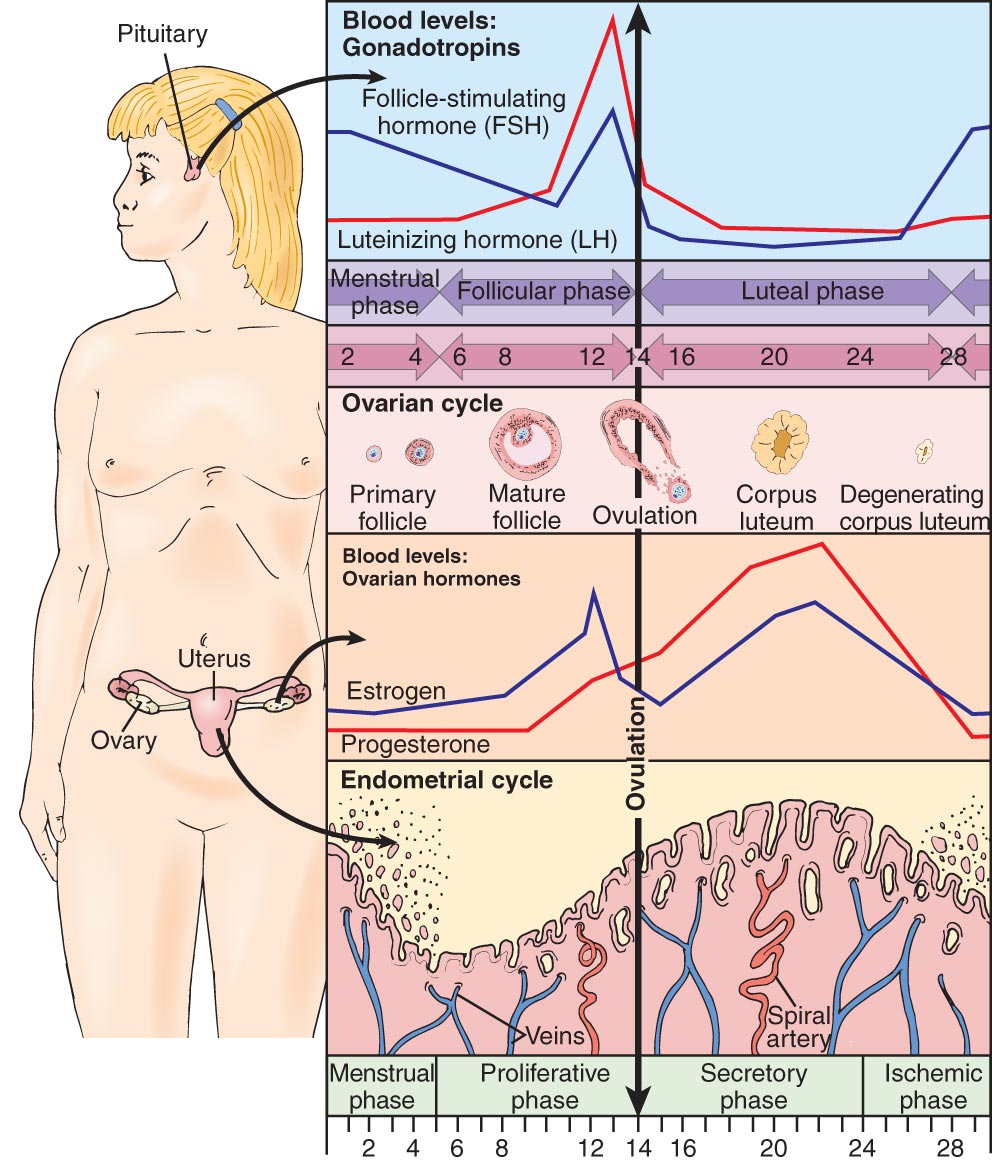
Hypothalamic-Pituitary Cycle
- ↓ Estrogen and progesterone stimulate the hypothalamus to secrete gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
- ↑ GnRH stimulates the anterior pituitary to secrete follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
- ↑ Levels of FSH stimulate development of the ovarian graafian follicles, which ↑ ovarian production of estrogen
- Midcycle, a slight ↓ estrogen triggers GnRH to stimulate the anterior pituitary to secrete luteinizing hormone (LH)
- A surge of LH and small ↑ in estrogen stimulate the graafian follicle to release an ovum (ovulation), changing the follicle into the corpus luteum. If fertilization does not occur, levels of estrogen and progesterone decrease and the corpus luteum regresses
Ovarian Cycle
- Follicular phase
- Before ovulation 1–30 follicles begin to develop under the influence of FSH and estrogen
- Under the influence of LH, one oocyte completes maturation and is released from the follicle (ovulation)
- Luteal phase
- Begins after ovulation and ends with menstruation
- Corpus luteum secretes estrogen/progesterone, peaks on day 8
- Corpus luteum regresses without conception
Endometrial Cycle
- Menstrual phase (day 1–5)
- Shedding of the functional
 of endometrium
of endometrium - Proliferative phase (day 5–ovulation)
- Rapid endometrial growth, influenced by estrogen
- Secretory phase (ovulation to 3 days before menses)
- Endometrium thickens with ↑ blood and glandular secretions influenced by progesterone
- Ischemic phase
- Spasm and necrosis of the functional layer of the endometrium