Red, tiger, or green top tube
Venous blood
Reject specimen if there is:
- Hemolysis
- Turbidity
When monitoring serial levels of AST collect specimen at the same time each day as some variation may occur based upon time of day.
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST), formerly known as serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), is an intracellular enzyme involved in amino acid metabolism.
- Present in cells of the liver, heart, skeletal muscles, kidneys, pancreas and red blood cells
- Released into serum when there is cellular damage
- Used primarily to evaluate acute liver disease or injury
Testing of AST is useful to:
- Help in the detection and differential diagnosis of acute liver diseases and injuries, as part of the panel of liver function tests.
- In the past used in diagnosis of myocardial infarction in correlation with creatine kinase and LDH levels (now troponin, myoglobin and creatine kinase used)
- Monitor course of the disease and effectiveness of therapy in hepatic disorders
- Monitor treatment with drugs which are potentially hepatotoxic or nephrotoxic
- In alcoholic hepatitis, the AST is usually more elevated than the ALT (the reverse is typical in viral hepatitis)
Additional information:
- AST levels are high at birth and decrease with age
- Generally, AST is more sensitive but less specific than alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in detecting liver disease
- In patients with hepatitis C, an AST/ALT ratio > 1 suggests cirrhosis
Consult your laboratory for their normal ranges as these may vary somewhat from the ones listed below.
| Conv. Units (U/L) | SI Units (µKat/L) | |
|---|---|---|
| Adult (M) | 0-45 | 0-0.77 |
| Adult (F) | 0-35 | 0-0.60 |
| < 2 years | 10-80 | 0.17-1.36 |
| Newborn | 15-60 | 0.26-1.02 |
An increased AST level is seen in the following conditions:
Acute elevation of AST:
- Liver Diseases
- Hepatitis (autoimmune, infectious, traumatic)
- Cholestasis
- Intrahepatic
- Extrahepatic
- Alcoholism
- Hepatic necrosis
- Hepatotoxicity
- Ingestion of poisonous mushrooms
- Carbon tetrachloride poisoning
- High doses of vitamin A
- Drugs (see section below)
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Liver abscess
- Metastatic carcinoma
- Primary liver carcinoma
- Shock liver (injury to the liver)
- Heart Disorders
- Acute myocardial infarction
- Acute myocarditis
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Congestive heart failure
- Pericarditis
- Recent cardiac catheterization or angioplasty
- Skeletal Muscle related conditions
- Exercise (Strenuous)
- Intramuscular injections (rarely)
- Surgery (Extensive)
- Skeletal muscle diseases such as Duchenne's muscular dystrophy
- Trauma
- Red Blood cells related conditions
- Anemia; Hemolytic
- Anemia; Megaloblastic
- Other
- Acute pancreatitis
- Acute pulmonary infarction
- Acute renal failure
- Burns (2nd/3rd degree)
- Cerebrovascular accident
- Delirium tremens
- Dermatomyositis
- Eclampsia
- Heat exhaustion/Heat stroke
- Heparin therapy
- Hypothyroidism
- Seizures
- Shock
- Tissue necrosis
Chronically elevated AST:
- Hepatic
- Alcohol abuse
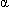 -1 antitrypsin deficiency
-1 antitrypsin deficiency- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Drugs (see section below)
- Fatty liver
- Hemochromatosis
- Hepatitis; Autoimmune
- Hepatitis; B or C (Chronic)
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- Steatosis
- Wilson's disease (
 40 years)
40 years) - Nonhepatic (AST increases more than ALT)
- Acquired muscle diseases
- Celiac sprue
- Inherited disorders of muscle metabolism
- Strenuous exercise
Drugs known to increase result:
- Those causing cholestasis:
- Amitriptyline
- Anabolic-androgenic steroids
- Benzodiazepines
- Chlorothiazide
- Chlorpropamide
- Dapsone
- Erythromycin
- Estrogens
- Ethionamide
- Gold salts
- Imipramine
- Mercaptopurine
- Nitrofurans
- Oral contraceptives
- Penicillins
- Phenobarbital
- Phenothiazines
- Progesterone
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Those causing hepatocellular damage:
- Acetaminophen
- Acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin)
- Allopurinol
- Amiodarone
- Anabolic steroids
- Anticonvulsants
- Asparginase
- Azithromycin
- Bromocriptine
- Captopril
- Carbamazepine
- Cephalosporins
- Chloramphenicol
- Clindamycin
- Clofibrate
- Danazol
- Diclofenac
- Enflurane
- Ethambutol
- Ethionamide
- Fenofibrate
- Fluconazole
- Fluoroquinolones
- Foscarnet
- Gentamicin
- Hydralazine
- Ibuprofen
- Indomethacin
- Interferon
- Interleukin-2
- Isoniazid (INH)
- Levamisole
- Levodopa
- Lincomycin
- Low-molecular weight heparin
- Methyldopa
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors
- Naproxen
- Niacin
- Nifedipine
- Nitrofurans
- Opiates
- Oral contraceptives
- Probenecid
- Phenybutazone
- Phenytoin
- Procainamide
- Quinine
- Ranitidine
- Retinol
- Ritodrine
- Salicylates (in children)
- Statins (Mevacor, Pravachol, Lipitor, Crestor, etc)
- Sulfonylureas
- Sulfamethoxazole
- Tetracycline
- Tobramycin
- Trimethoprim
- Valproic acid
- Verapamil
A low result is usually of no clinical significance.
Decreased levels of AST are seen in the following conditions:
- Long-term kidney dialysis
- Pregnancy
- Uremia
- Vitamin B6 deficiency
Drugs known to decrease result:
- metronidazole
- trifluperazine
- some herbs/naturals such as Chinese fructus schizandrae sinensis
- Canadian Association of Gastroenterology Practice Guidelines. Evaluation of abnormal liver enzyme tests. The Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology 1998;12(6): 417-421.
- Lab tests online. AST [Homepage on internet] ©2001-2006 [updated 2006 Mar 17;cited 2006 Jul 7] Available from http://labtestsonline.org/understanding/analytes/ast/test.html
- http://hepatitis-central.com/hcv/labs/liverenzymes.htm
- Laboratory Corporation of America. Aspartate Aminotransferase [Homepage on internet] c2003 [updated 2003 May 14;cited 2006 Jul 7] Available from http://www.labcorp.com/datasets/labcorp/html/chapter/mono/pr007900.htm
- MedlinePlus: Medical Encyclopedia. AST [Homepage on internet] c2005 [updated 2005 Feb 14;cited 2006 Jul 7] Available from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003472.htm
- Nissl J. BC HealthGuide. Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) [Homepage on internet] c1995-2006 [updated 2004 Apr 12;cited 2006 Jul 7] Available from http://www.bchealthguide.org/kbase/topic/medtest/hw20331/descrip.htm
- Stransky J, Ryzlova M, Stritesky J, et al. [Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) more than alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels predict the progression of liver fibrosis in chronic HCV infection.][Article in Czech] Vnitr Lek 2002 Oct;48(10):924-8.