Topic Editor: Robert Giles, MBBS, BPharm
Review Date: 9/14/2012
Definition 
- Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a common inherited condition characterized by the presence of multiple renal cysts. There are two major types of PKD: autosomal dominant PKD (ADPKD) and autosomal recessive PKD (ARPKD). PKD patients often have extrarenal cysts and systemic manifestations
Description 
- ADPKD is among the most common of human genetic conditions. ARPKD is somewhat rarer and is associated with renal cysts and hepatic fibrosis. It is commonly diagnosed in younger patients. This document focuses predominantly on ADPKD
- Epithelial lined cysts develop predominantly in the kidneys but also in other solid organs (e.g., liver, pancreas, spleen)
- Patients often present with flank pain, hypertension, hematuria, renal impairment or multiple cysts seen on ultrasonography
- Long term complications of ADPKD include:
- Cardiovascular disease (increased risk of disease)
- Chronic renal failure/End-stage renal disease (ESRD)
- Hypertension
- Intracranial aneurysms (including risk of rupture)
Epidemiology 
Incidence/ prevalence
- The estimated prevalence of ADPKD is between 1/400 and 1/1000. The estimated prevalence of ARPKD is 1/10,000 to 1/40,000
- In North America and Europe, ADPKD causes 6% to10% of ESRD cases
- Approximately 85% to 90% of patients with ADPKD have a mutation in the PKD1 gene on chromosome 16. Mutations in the PKD2 gene on chromosome 4 comprise the remainder of cases
Age
- Cysts begin to develop early in life, with symptoms and complications becoming more apparent with increasing age
- Patients who have symptoms at an earlier age are at increased risk of developing ESRD
Gender
- ADPKD may be slightly more severe in males than in females
Race
- ADPKD occurs worldwide and in all races
Risk factors
- A family history of PKD
- A family history of cerebral aneurysms
Etiology 
- Mutations in the PKD1 and PKD2 genes have been identified in 85% and 15% of ADPKD cases, respectively
- PKD1, codes for polycystin 1 protein
- PKD2, codes for polycystin 2 protein
- These polycystin proteins are involved in regulating the morphological configuration of epithelial cells
- Polycystins are felt to act in the primary cilium of renal tubules as mechanosensitive cation channels. Defective polycystins cause renal tubules to dilate and fill with glomerular filtrate leading to the formation of cysts
- Extrarenal cysts and other manifestation are caused via unclear mechanisms
[Outline]
History 
- Acute or chronic pain in the abdomen, flank, or back
- Hematuria
- Nephrolithiasis
- Positive family history for PKD
- Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTI)
- Renal impairment
Physical Findings on examination 
- Cardiac murmur – mitral valve prolapse (commonly associated with PKD)
- Flank mass (usually palpable and bilateral)
- Hernia – abdominal or inguinal (commonly associated with PKD)
- Hepatomegally (usually nodular)
- Hypertension
- Signs of renal failure: (uncommon on initial presentation)
- Anemia (pallor)
- Dry skin
- Edema
- Uremic fetor
[Outline]
PKD should be suspected in patients with a positive family, suggestive signs and symptoms or those with cysts detected on imaging studies. Ultrasound is the imaging study of choice with CT/MRI reserved for patients with equivocal results
Blood test findings 
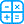
- Serum electrolytes, urea, creatinine: GFR - Cockcroft-Gault Method (Adult)
- Not particularly sensitive, as renal indices will be normal until the development of renal impairment
- Serial creatinine monitoring is useful to assess renal function over time
- Fasting lipid profile:
- Increased total and LDL cholesterol and elevated total cholesterol/HDL ratio is associated with progression of renal impairment
- C-reactive protein:
- Useful in the diagnosis of infected renal or hepatic cysts. A CRP>5 mg/dL is a non-specific marker of inflammation or infection
Other laboratory test findings 
- Urinalysis/gram stain and urine culture:
- Urinalysis is performed in the setting of possible UTI to evaluate for bacteriuria, leukocytes, nitrites, cell counts and culture
- Urinalysis can also be used to assess for hematuria, proteinuria, and microalbuminuria
- Genetic Testing for PKD1 or PKD2 mutation:
- Tests are advised when imaging studies are inconclusive
Radiograpic findings 
- Renal ultrasound
- A non-invasive and relatively inexpensive test with no radiation exposure. Unfortunately, it has poor sensitivity
- Extrarenal cysts can also be simultaneously imaged
- Ultrasonographic diagnostic criteria for PKD depend on the age of the patient, their underlying genetic predisposition and the number of cysts seen in each kidney
- CT and MRI
- CT is more sensitive than ultrasonography and can detect cysts as small as 0.5 cm. CT may be useful if PKD is suspected in children or in complicated cases (e.g., kidney stones, suspected tumors)
- MRI is more sensitive than either ultrasonography or CT scanning. Due to expense, availability and patient factors; its use is not routine. MRI can clearly differentiate other pathologies from simple cysts (e.g., renal cell carcinomas). In patients without a family history MRI is significant if it shows >10 cysts in each kidney
- Screening for cerebral aneurysm remains an area of controversy. Methods of screening include CT or MRI angiography. Some recommend screening in patients with PKD and a family history of hemorrhagic stroke or cerebral aneurysm
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
- PET/CT is useful for detecting cyst infection in ADPKD patients. Increased uptake suggests infection
- Barium enema
- It is used for the diagnosis of colonic diverticula which may found more frequently in patients with PKD
- Doppler studies and 2-dimensional echocardiography
- May be used to exclude mitral prolapse, which is often associated with ADPKD
[Outline]
General treatment items 
- Treatment for PKD is largely supportive as no specific interventions have been shown to slow progression of cyst development. Numerous agents are currently under investigation
- Current therapy is geared toward preventing progression to ESRD and limiting cardiovascular mortality (e.g., blood pressure / lipid control, lifestyle modifications)
- Prompt treatment of infections
- Minimization of hematuria
- Adequate analgesia
- Recognition and treatment of complications of ESRD, including hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, or renal transplantation in such patients
- A low-salt diet is recommended in patients with hypertension or renal failure. Increased fluid intake and dietary protein restriction may be helpful
- Blood pressure should be maintained 130/80. Patients with significant proteinuria or evidence of left ventricular hypertrophy may benefit from even lower blood pressure goals. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) have been shown to slow progression to ESRD and are first line therapy. Agents other and ACEs or ARBs are often needed in patients who progress to renal failure
- Contact sports should be avoided as they expose enlarged cystic kidneys and liver to risk of trauma
- Hematuria secondary to cyst rupture or nephrolithiasis is a common and generally a self-limited complaint. Maintenance of adequate hydration, and adequate analgesia is recommended
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be avoided in patients with renal impairment
- Urinary tract infection (UTI) is common and need to be treated promptly to prevent complications. Antibiotic choice should be based on previous urine culture and sensitivities, patient allergies and local resistance patterns. Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin or fosfomycin are appropriate first line agents. Consider ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, or a 2nd – 4th generation cephalosporin if resistant strains of E. coli are common
- Urinary tract infections can be complicated by cyst infections. Cyst infections are difficult to treat and require lipophilic antibiotics to penetrate the cyst walls. Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole, ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin should be first line therapy. Clindamycin, vancomycin and metronidazole also penetrate cyst walls, but have gram positive and/or anaerobic spectrum, which are less common in UTI
- Infected cysts may require surgical/radiological drainage when there is a failure to respond to appropriate antibiotics
- Surgical resection of cysts may be considered for cyst complications in patients with chronic pain, hematuria or recurrent infections
Medications with specific doses 
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors)
- Benazepril
- Captopril
- Enalapril [Oral]
- Enalapril [IV]
- Fosinopril
- Lisinopril
- Moexipril
- Perindopril
- Quinapril
- Ramipril
- Trandolapril
Angiotensin II Receptor antagonists (ARB's)
- Azilsartan
- Candesartan
- Eprosartan
- Irbesartan
- Losartan
- Olmesartan
- Telmisaratan
- Valsartan
Antibiotics
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate
- Cefaclor
- Cefepime
- Cefixime
- Cefotaxime
- Cefotetan
- Cefoxitin
- Cefpodoxime
- Ceftazidime
- Ceftriaxone
- Cefuroxime [Oral]
- Cefuroxime [IV]
- Ciprofloxacin [Oral]
- Ciprofloxacin [IV]
- Clindamycin [Oral]
- Clindamycin [IVl]
- Fosfomycin
- Levofloxacin [Oral]
- Levofloxacin [IV]
- Metronidazole [Oral]
- Metronidazole [IV]
- Nitrofurantoin
- Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole [Oral]
- Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole [IV]
- Vancomycin
- Adult dosing:
- Pediatric dosing:
[Outline]


