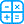
- Measures difference in alveolar (A) and arterial (a) oxygen concentration
- Depends on alveolar interface with pulmonary capillaries
- Calculation A-a Gradient ~ [FiO2 x (760-47)-(1.25 x pCO2)] - pO2
B. Shunt and Other V/Q Mismatch
- Pulmonary Embolism
- COPD, Asthma (mucus plugging, bronchoconstriction)
- Pulmonary Hypertension (effective capillary destruction; reduced DLCO)
- Cardiac Shunts
- Atrial or Ventricular Septal Defects
- Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO)
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
C. Impaired Gas Exchange (at alveolar level)
- Inflammation: pneumonia
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Sarcoidosis and other infiltrative lung diseases
- Alveolar Cell Carcinoma
- Cardiogenic (CHF)
- ARDS (non-cardiogenic)
- Ischemia is usual precipitant in patients with pre-existing disease
- Acute Mitral Regurgitation: ischemia, infarction
- Arrhythmia
- Heart Failure systolic and diastolic dysfunction with volume overload
- Papillary muscle rupture
- Acute Lung Process: ARDS, Diffuse Pneumonia
F. Orthodexia [1]
- Decrease in arterial oxygen saturation from recumbent to erect position
- Recurrent pulmonary emboli
- Chronic lung disease
- Liver disease (hepatopulmonary syndrome)
- Previous pneumonectomy
- Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
- Patent foramen ovale (PFO)