Unilateral, painless, abrupt change in vision, usually partial visual field loss; may have a history of transient visual loss (amaurosis fugax).
(See Figure 11.7.1.)
Critical
Superficial opacification or whitening along the distribution of a branch retinal artery. The affected retina becomes edematous.
Other
Narrowed branch retinal artery; boxcarring, segmentation of the blood column, or emboli are sometimes seen in the affected branch retinal artery. Cholesterol emboli appear as bright, reflective crystals, usually at a vessel bifurcation. CWSs may appear in the involved area.
11-7.1 Branch retinal artery occlusion with Hollenhorst plaque.
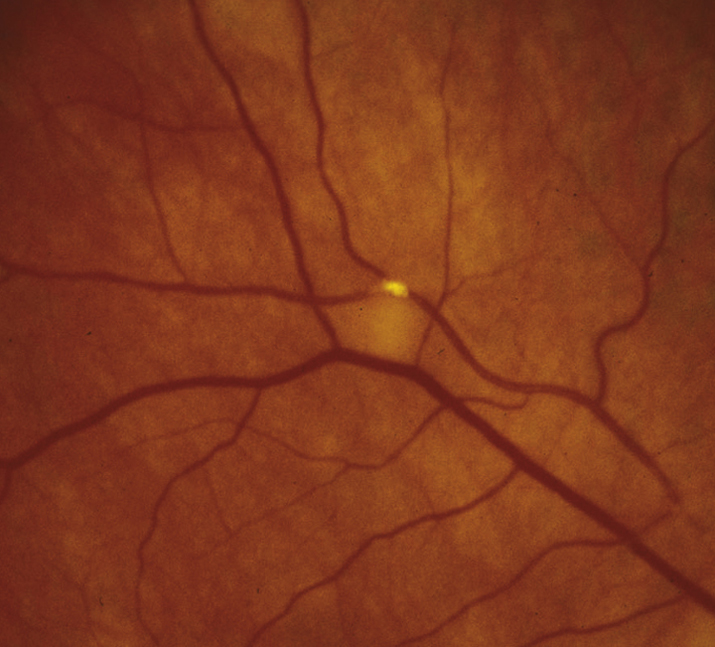
WorkupSee 11.6, CENTRAL RETINAL ARTERY OCCLUSION. Unlike in CRAO, an ERG is not helpful.
 NOTE: NOTE: |
When a BRAO is accompanied by optic nerve edema or retinitis, obtain appropriate serologic testing to rule out cat-scratch disease (Bartonella [Rochalimaea] henselae), syphilis, Lyme disease, and toxoplasmosis. |
