Description
- Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted on the dura by the contents of the cranial vault; normal ICP is <15 mm Hg.
- Intracranial hypertension (ICH) is a neurological emergency that, if left untreated, can cause brain herniation, irreversible neuronal damage, compromised cerebral blood flow (CBF), and eventually death.
- Treatment includes medical management and possibly surgery (resection of the mass lesion or a decompressive craniectomy for cases refractory to medical management). These procedures are performed to improve brain tissue oxygenation and CBF.
- The cranium is comprised of
- Brain matter
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Blood; both arterial and venous
- A noncompliant intracranial vault with only a small reserve for additional volume (provided by the intervertebral spaces).
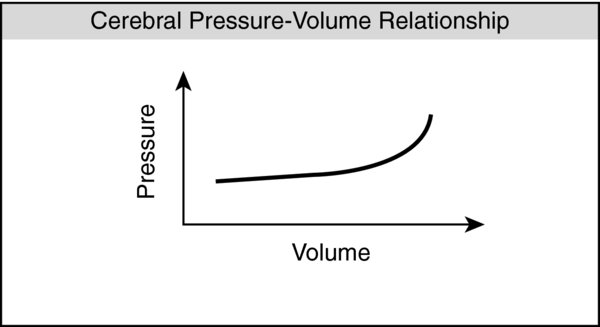
- Monroe–Kellie hypothesis: The intracranial volume is in dynamic equilibrium; the increase in one component volume will cause a decrease in volume of the other components in order to prevent increases in ICP.
- Cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) = MAP–ICP, where MAP is mean arterial pressure and ICP is intracranial pressure
- Normal cerebral autoregulation maintains CPP between 50 and 150 mm Hg (see Equation ).
- If the CPP is <50 mm Hg or >150 mm Hg, then CBF directly follows changes in perfusion pressure.
- PaO2: Severe hypoxia causes cerebral vasodilation. A PaO2 <50 mm Hg drastically increases CBF.
- PaCO2: CBF is directly proportional to changes in PaCO2. Between a PaCO2 of 20 and 80 mm Hg, blood flow changes ~1–2 mL/100 g/min per mm Hg of PaCO2.
- Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2): Cerebral metabolic activity is directly coupled to increases or decreases in CBF.
- Intracranial volume is comprised of
- Brain tissue: 80%
- CSF: 8–12%
- Intracerebral blood
- Radiological images of brain with high ICP will reveal a midline shift and effaced basal cisterns.
Physiology/Pathophysiology
- Once maximum capacitance is achieved, additional volume will quickly increase the ICP.
- Anatomical factors that increase ICP
- Brain tissue: Tumors, edema (ischemic stroke, cerebral contusion), trauma (epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, cerebral contusion), psuedomotor cerebri
- CSF: Hydrocephalus
- Blood: Hypoxia, hypercarbia, obstruction of venous return from head position, Valsalva maneuvers or increased intrathoracic pressures (coughing, gagging, excessive PEEP), seizures, severe hypertension, hypotension (vasodilation to maintain CBF can increase cerebral blood volume)
- Clinical signs of increased ICP
- Headache
- Nausea/vomiting
- Periodic or irregular breathing
- Decreased mental status (obtunded, comatose)
- Papilledema
- Cushing response: Severe hypertension, bradycardia, and irregular respirations
- This response indicates severe brain herniation. ICP leads to compression of intracerebral vessels and cerebral ischemia. Reflexively, the body activates hemostatic mechanisms to maintain cerebral perfusion by increasing the systemic BP (mainly systolic and hence widening the pulse pressure). Likely, the carotid baroreceptors sense the increased pressure and, in turn, activate the vagal response to slow the heart rate.
- Perioperative goals include maintaining the CPP by:
- Mean arterial pressure (MAP): Increase or maintain
- ICP: Decrease or prevent increases
- Monitors
- Standard ASA monitors, with special attention to capnography
- Arterial line for continuous BP monitoring and blood gas sampling (PaO2, PaCO2, glucose).
- Fluid intake and output with a Foley catheter and possibly a central venous catheter
- Continuous ICP monitoring
- Nerve stimulator to help determine depth of neuromuscular blockade
- EEG may be needed during barbiturate coma to determine depth of sedation, evaluate for seizures, and to help establish cerebral electrical silence.
- Induction and airway management
- Head of bed (HOB) at 30°. Facilitates cerebral venous drainage and decreases intracerebral blood volume. However, it may hinder brain tissue oxygenation.
- Intubation and controlled ventilation can facilitate (or avoid) hypoventilation.
- Rapid sequence intubation (RSI) should be used in emergent conditions. The benefits of quickly securing the airway and controlling respiratory parameters (avoiding hypoxia, hypercarbia) outweigh the small and transient increase in ICP from succinylcholine. However, if the patient is not adequately anesthetized or only partial muscle relaxation has occurred, ICP can increase during direct laryngoscopy and intubation.
- Maintenance is typically via a combined technique to minimize any further increases in ICP.
- Volatile anesthetics decrease CMRO2 in a dose-dependent manner, dilate cerebral blood vessels, and increase CBF (uncoupling).
- Nitrous oxide causes mild cerebral vasodilation. Its effects are generally mild especially when used with other IV agents.
- Propofol decreases CBF and CMRO2 and has some anticonvulsant properties.
- Opioids have little direct effect on CBF, CMRO2, and ICP. Respiratory depression may cause changes in PaCO2.
- Muscle relaxation has no direct effect on the brain.
- Succinylcholine can potentially increase ICP but that effect can be attenuated with a defasciculating dose of a nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocker and adequate induction agent.
- Head flexion and rotation can impede venous outflow from the brain and should be avoided.
- Hyperventilation: Adjusting the PaCO2 to 30–35 mm Hg is one of the fastest techniques to decrease ICP. Decreases in the PaCO2 alkalinize the CSF and cause cerebral vasoconstriction. This phenomenon, however, fades with time as the CSF readjusts to a normal pH (vasoconstrictive effects typically last 11–20 hours). Avoid excessive hyperventilation (PaCO2 <25 mm Hg), as it can contribute to cerebral ischemia.
- Maintain a CPP >60 mm Hg. With increased ICP, cerebral perfusion is maintained by systemic hypertension and sympathetic hyperactivity. To that extent, caution is advised in treating hypertension as it may result in cerebral ischemia (hypotension is an independent risk factor for poor outcomes). At the same time, the risk of persistent systemic hypertension includes cerebral edema and intracranial hemorrhage. Furthermore, cerebral autoregulation can be compromised in areas of brain injury and complicates the management of systemic hypertension. If treatment is undertaken, short-acting titratable drugs (beta-blockers, propofol) can be used to lower the BP and avoid increases in ICP. Avoid drugs such as nifedipine, nitroglycerine, or nitroprusside as they can induce cerebral vasodilation and worsen ICP.
- Mannitol is a hyperosmolar agent that is commonly used to lower ICP (effect is dose-dependent). IV bolus doses of 0.25–1 g/kg can begin to decrease the ICP in 1–5 minutes (peak effect of 20–60 minutes, duration up to 6 hours). Redosing may be required for continued clinical effect. Advantages include its free radical scavenging properties and reduction in CSF production. Adverse effects include hypotension (initial vasodilatory response), exacerbation of congestive heart failure (initial intravascular osmotic effect), electrolyte abnormalities (later diuresis), and cerebral edema (areas of compromised blood-brain barrier, or rebound from prolonged administration). Mannitol is, thus, contraindicated in hypovolemic and hypotensive patients.
- Hypertonic saline creates an osmotic gradient for interstitial intracerebral fluid to shift intravascularly. This reduces overall brain volume and decreases ICP. This has a more pronounced effect compared to mannitol and can be used in a hypovolemic and/or hypotensive patient needing intravascular volume expansion. Potential adverse effects include hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, platelet dysfunction, prolonged coagulation parameters, and central pontine myelinolysis.
- Furosemide: A loop diuretic that may decrease the production of CSF; less effective than hypertonic saline and mannitol.
- Sedation and analgesia: Pain and agitation can increase ICP and should be addressed. Benzodiazepines can decrease CMRO2 and CBF without effects on the ICP; beware of hypotension or hypercarbia.
- Avoid seizures: Consider antiepileptics to avoid significant increases in CMRO2, CBF, and ICP.
- Avoid hyperglycemia: Associated with poor neurological outcomes. The optimal target glucose range is uncertain but generally maintained below 220 mg/dL.
- Corticosteroids decrease vasogenic edema from primary and metastatic tumors; a common regimen is dexamethasone 4 mg IV every 6 hours. Steroids can increase serum glucose levels and if left uncontrolled can lead to hyperglycemia.
- Barbiturate coma has not been shown to improve outcomes but can be considered in refractory, elevated ICP. Proposed mechanisms: a coupled reduction in CBF with decreased CMRO2 and arterial vasoconstriction (decreases CBF). Disadvantages include the loss of neurological exam and hypotension.
- CSF drainage: Removal of CSF is a quick and reliable method to lower the ICP. The most common method is through a ventriculostomy that has the advantage of being both a therapeutic and diagnostic maneuver. Disadvantages include a risk of infection, hemorrhage, and difficulty in placement with diffuse cerebral edema or slit-like ventricles. Fiberoptic monitoring devices can be placed in the subarachnoid space, epidural space, or brain parenchyma. They are easier to place but cannot remove volume and cannot be recalibrated. An external ventricular device can be placed for temporary measures, while ventricular shunts are placed for chronic ICP management (i.e., hydrocephalus).
- Avoid hyperthermia: Increases in temperature can elevate the CMRO2 and hence CBF. Outcome studies have demonstrated worsened neurologic injury in traumatic brain injury. Treatment includes antipyretics, cooling blankets, and treatment of infectious causes.
- Hypothermia: Controversial with no studies showing improved neurological outcomes. It may be considered in cases of severe refractory ICH maximized on medical management.
- Extubation and emergence
- Extubation criteria are the same as with any surgical procedure (confirm that neurological issues are stable or resolved); if extubation is not possible, consider appropriate sedation. Avoid bucking/straining/coughing that can worsen ICP or cause cerebral hemorrhage. Consider IV lidocaine to attenuate the gag reflex to suctioning/extubation. Rapid awakening is also important to conduct a neurological assessment postoperatively.