Description
- Respiratory alkalosis is a physiologic state of high pH (>7.45) and low partial pressure of carbon dioxide (paCO2) (<35 mm Hg).
- This clinical condition is caused by hyperventilation that results in excessive elimination of CO2.
- Respiratory alkalosis is commonly classified as either:
- Since pH homeostasis is essential for proper protein function, and consequently organ function, its derangement affects multiple organ systems including the cerebral, cardiovascular, renal, pulmonary, and GI systems.
Etiology/Risk Factors
- Central nervous system (CNS). The medullary respiratory center is affected by disease processes and input from peripheral and central receptors, as well as voluntary control from the cerebral cortex:
- Infection
- Tumor
- Brain injury
- Drug poisoning such as salicylates
- Caffeine
- Liver failure
- Fever
- Pain
- Anxiety
- Pulmonary
- Hypoxia governs breathing to a greater extent than CO2, thereby triggering the respiratory center to increase the respiratory rate and tidal volume (minute ventilation). It can result from pulmonary emboli, pneumonia, pneumothorax, pulmonary edema, aspiration, interstitial lung disease, asthma, emphysema or chronic bronchitis. Additionally, ascent to high altitudes can decrease the fraction of inspired oxygen.
- Iatrogenic: Mechanical hyperventilation
- Cardiovascular: Congestive heart failure, right-to-left shunt, and anemia result in low-oxygen states that stimulate peripheral receptors.
- Catecholamines increase ventilation via direct dilation of the smooth muscles of the bronchi.
- Nicotine and acetylcholine stimulate the carotid and aortic bodies.
- Hyperthyroidism increases the respiratory drive in response to hypoxemia and hypercapnia. The specific mechanism is not known.
- Systemic sepsis results in tissue hypoxia as well as metabolic acidosis. In addition, the lungs provide a large surface area for heat exchange thus helping to control body temperature via neural input from the hypothalamus.
- Pregnancy: Respiratory alkalosis is a normal physiologic response. A sustained elevation of progesterone causes a hypoxic ventilatory response as a result of its effect on carotid bodies, while estrogen acts on the CNS thereby augmenting carotid sinus nerve activity on ventilation.
Physiology/Pathophysiology
- Carbon dioxide is a product of cellular metabolism and is excreted via the lungs. It is transported in blood in three main ways:
- Bicarbonate ions in red blood cells (RBCs) and plasma (majority). After entering the RBC, CO2 combines with water via carbonic anhydrase to form carbonic acid; it is then broken down to H+ and HCO3-. The H+ binds to deoxyhemoglobin, while HCO3- is extruded from the cell in exchange for a Cl- ion to maintain electroneutrality. This reaction also occurs in the plasma, but at a slower rate due to the lack of carbonic anhydrase. This mechanism for transport also serves to buffer the extracellular fluid compartment against pH derangements.
- Bound to hemoglobin (Hgb) (carbaminohemoglobin) and protein
- Dissolved in blood; a small percentage exists in the gas form and exerts partial pressure that can be measured on an arterial blood gas reading.
- Chemoreceptors exist in the central and peripheral system and serve to detect changes in CO2 and pH; they send input to the medullary respiratory center.
- Central chemoreceptors are the primary regulators of respiratory rate and are located on the ventrolateral surface of the medulla oblongata in the brain; they detect changes in pH of CSF. Since CSF is separated from the blood, electrolytes do not diffuse freely into CSF. However, volatile gases such as carbon dioxide can move easily through the barrier. Once CO2 is in the CSF, it can react with water to eventually produce hydrogen ions and bicarbonate and thereby alter the CSF pH. With time, the chemoreceptor will eventually desensitize to the derangement.
- Peripheral chemoreceptors: aortic body and carotid body. Unlike the central chemoreceptors, they do not desensitize to stimulus. The aortic body receptors detect changes in the paO2 and paCO2 of the blood, whereas the carotid body receptors detect changes in the paO2, paCO2, and pH of the blood. The chemoreceptors serve to increase or decrease the respiratory rate and tidal volume, hence adjusting ventilation. Output from the peripheral receptors reaches the central respiratory centers, which in turn affect the ventilation.
- High altitude and hypoxia govern breathing to a greater extent than CO2. When the paO2 falls below 100 mm Hg, neural activity from peripheral receptors begins to increase. However, the paO2 needs to reach 60–65 mm Hg for a substantial increase in minute ventilation to occur and make the individual dependent on hypoxic ventilatory drive. This, consequently can result in respiratory alkalosis.
- pH derangements result when the buffering mechanisms are overwhelmed.
- Henderson Hasselback equation:
- HCO3- + H+

 H2CO3
H2CO3
 CO2 + H2O
CO2 + H2O - Acute: pH = 0.008 × (40–paCO2) and the
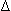 HCO3- = 0.2 ×
HCO3- = 0.2 × 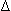 paCO2
paCO2 - Chronic: pH = 0.017 × (40–paCO2) and the
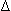 HCO3- = 0.5 ×
HCO3- = 0.5 × 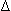 paCO2
paCO2
- Electrolyte derangements
- Hypokalemia. To offset the pH imbalance, hydrogen ions shift from intracellular to the extracellular space via the Na+-H+ ion exchanger (Na+ moves into the cell). The increase in intracellular Na+ stimulates the Na+-K+-ATPase, which results in a secondary intracellular shift of K+.
- Hypocalcemia. Alkalosis results in an increased negative charge on albumin that leads to increased Ca++ binding and decreased unbound Ca++ ions. Additionally, calcium binds to bone in exchange for hydrogen ions stored in bone material. Hypocalcemia can result in tetany and paresthesias.
- Decreased cerebral blood flow (CBF). CBF is directly proportional to paCO2 values between 20 and 80 mm Hg. Normal brain blood flow is 50 mL/100 g/min. A paCO2 value of 20 mm Hg will result in severely decreased CBF to 25 mL/100 g/min. Acute decreases below this value can produce EEG signs of cerebral ischemia.
- Cardiovascular system. Hypocalcemia can result in dysrhythmias and vasodilation.
- Pulmonary system. Hypocarbia can result in decreased pulmonary vascular resistance as well as increased bronchial smooth muscle tone from hypocalcemia.
- Medications. Respiratory alkalosis can potentiate the effects of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockade secondary to hypokalemia and alkalemia.
Prevantative Measures
- Perioperatively, the end-tidal CO2 should be monitored with adjustments made to the respiratory rate and tidal volume as appropriate. Arterial blood gas (ABG) measurements can confirm paCO2 and pH values, particularly when there is an increase in dead space ventilation.
- Increases in minute ventilation, particularly when spontaneously ventilating, may suggest pain or awareness under anesthesia and administration of opioids or deepening of the anesthetic should be considered.