Description
- Hyperglycemia (>180–200 mg/dL) is common in diabetics as well as critically ill patients without diabetes. It can result from
- Stress-induced hyperglycemia compared to diabetic hyperglycemia has been reported to increase the length of hospital stay and in-hospital mortality.
Epidemiology
Prevalence
- Approximately 23 million patients have diabetes.
- Type 2 diabetes is seen in ~12.9% of people older than 20 years of age.
Physiology/Pathophysiology
- In healthy individuals, the blood glucose level is closely regulated by insulin production, hepatic glucose uptake, and production.
- Insulin actions include
- Counterregulatory hormones (cortisol, catecholamine, growth hormone) decrease peripheral glucose uptake, inhibit hepatic glucose uptake, and increase hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis.
- Hyperglycemia
- Insulin deficiency (or insulin resistant states) can result in fat catabolism and increased formation of acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA will then form ketone bodies.
- Immune function. Impairs phagocytic function (adherence and chemotaxis) of neutrophils and monocytes. Believed to be secondary to elevated cytosolic calcium in polymorphonuclear (PMN) leukocytes that result in reduced ATP synthesis as well as reduced superoxide formation in leukocytes.
- Fluid balance. Glycosuria promotes dehydration and various electrolyte imbalances. It can cause serum hypertonicity and acidosis.
- Cardiovascular system. Hyperglycemia can increase systolic and diastolic BP, prolong the QTc, and elevate catecholamine levels. Hyperglycemia can increase platelet activation and adhesion, leading to thrombosis; as well as inflammatory markers such as TNF
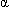 , IL-6, and IL-18. Studies have also demonstrated that it affects ischemic preconditioning of the heart and reduced coronary collateral blood flow.
, IL-6, and IL-18. Studies have also demonstrated that it affects ischemic preconditioning of the heart and reduced coronary collateral blood flow. - Central nervous system (CNS). The penumbra area that surrounds the ischemic zone in the brain is at increased risk for further infarction in hyperglycemic states because of the ensuing acidosis and high lactate levels. High levels of lactate can damage astrocytes, endothelial cells, and neurons.
- Glycemic control. Studies have yielded varying results.
- In critically ill surgical patients, tight glycemic control using intensive insulin therapy (between 80 and 110 mg/dL) has shown improved outcomes.
- However, subsequent studies in the medical intensive care unit (ICU) have failed to show similar benefits in all patients and more hypoglycemic episodes observed in patients with more than 3 days of hospital stay.
- Furthermore, glucose variability has been shown to be more important than maintaining the glucose level in a certain range. Fluctuation of blood glucose can cause increased apoptosis, cytokine expression, and oxidative stress markers.
Prevantative Measures
Surgical and anesthetic techniques that can minimize hyperglycemia responses:
- Minimally invasive surgery. The stress of surgery can reduce insulin sensitivity and the release of counterregulatory hormones that can cause hyperglycemia.
- Avoid hypovolemia which can trigger a hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic (HHNK) state (severe hyperglycemia often >600 mg/dL, hyperosmolarity often >320 mOsm/kg, glycosuria with worsening hypovolemia, and central nervous system depression). Dehydration combined with baseline impaired insulin production can further decrease insulin levels and worsen hyperglycemia (compared to diabetic ketoacidosis, HHNK has sufficient levels of insulin to prevent lipolysis and ketone production).
- Prevent nausea and vomiting (can lead to hypovolemia and electrolyte imbalances). Identify patients at risk and avoid drugs with emetic properties (if possible) and administer prophylactic treatment.
- Appropriate pain relief management to reduce the stress of surgery
- Neuraxial blockade. General anesthesia can result in a greater release of stress hormones compared to local or epidural anesthesia. Volatile anesthetic agents can inhibit insulin release and increase hepatic glucose output.