Description
- Transcranial Doppler (TCD) studies provide a noninvasive, real-time method of assessing cerebral hemodynamics.
- TCD measurements and utility are based on the concept that velocity is inversely related to the area of the artery's lumen; vasospasm narrows the lumen and hence results in increased velocity.
- It may be used as an indirect measure of blood flow and to evaluate the state of cerebral autoregulation.
- TCD ultrasonography utilizes the principle that sound waves transmitted at a certain frequency will be reflected back at a different frequency as a result of relative motion between the source and the receiver.
- TCD signal frequency remains constant in soft tissues but changes according to the motion of red blood cells (RBCs) in their path. The difference in frequency between the transmitted and reflected waves is the Doppler shift.
- The Doppler shift is affected mainly by the velocity of blood flow and the angle of insonation (the angle between the ultrasound beam and the blood flow direction).
- "Gating" is changing the depth of interrogation. This allows for measurements at different loci along the longitudinal axis of the vessel.
- At low frequency (2 MHz), the attenuation of signals by the skull and soft tissues is less than with conventional Doppler instruments (5–10 MHz)
- Pulsed ultrasound waves are directed at intracerebral arteries through acoustic windows (see Anatomy).
- Cerebral blood flow velocity (CBFV) is calculated and displayed against time. Three velocities are calculated:
- Peak systolic velocity (PSV) derived from the waveform
- End-diastolic velocity (EDV) derived from the waveform
- Mean velocity (FVm) = (PSV + [EDV × 2])/3 is considered the best indicator.
- The pulsatility index (PI) and resistance index (RI) are also calculated. The PI is directly related to the difference in the systolic and diastolic velocity and inversely related to the mean velocity. PI = (PSV - EDV)/FVm. Normal values range from 0.85–1.10 and are influenced by the blood pressure, partial pressure of carbon dioxide, and vessel compliance (it is not influenced by the angle of insonation). RI, as its name implies, is also a reflection of vascular resistance.
Acoustic windows are found at natural foramina or thin areas of the skull where the sound wave can penetrate more easily. There are three natural acoustic windows:
- Transtemporal: Above the zygomatic arch. Insonates the arteries in the Circle of Willis (middle, anterior, and posterior cerebral arteries—MCA, ACA, and PCA). After identification of the MCA, the artery is followed to the bifurcation of the internal carotid artery into the MCA and ACA. Blood flow in the MCA is toward the probe and the Doppler signal is depicted above the zero line, while the ACA signal is below the zero line.
- Transorbital: Over the eyelid. Insonates the ipsilateral carotid siphon and its collateral ophthalmic artery. Possibility of scanning for contralateral MCA and ACA.
- Transforaminal (or suboccipital): Between the atlas and the base of the skull. Scanning of vertebral arteries and basilar artery potentially up to its bifurcation into the PCA.
Physiology/Pathophysiology
- A mean FV (FVm) >120 cm/s can be caused by
- Vasospasm
- Hyperemia
- Increased PaCO2
- Arterial stenosis
- Increased age
- Volatile anesthetics
- Causes of decreased FV can be caused by
- Increased PI and RI can be seen by
- Increased ICP
- Hydrocephalus
- Traumatic brain injury
- Intracerebral hemorrhage
- Stroke
- Brain death
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)
- Vasospasm typically occurs in the large arteries at the base of the brain within 7 days following a SAH. It is thought to be secondary to the presence of extravasated blood.
- Depending on the diagnostic tool and frequency of testing, the incidence of vasospasm is almost 100% but is symptomatic in only 20–30% of cases (described as delayed ischemic deficit [DID]).
- TCD was shown to detect vasospasm 2.5 days before the appearance of DID and can potentially improve patient outcomes if early intervention is implemented.
- To detect vasospasm, TCD utilizes the principle that the velocity of blood flow in an artery is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area of that artery.
- A mean MCA flow velocity (FVm) >120 cm/s is abnormal and >200 cm/s corresponds to severe vasospasm.
- To differentiate between increased systemic flow velocities in the ipsilateral ICA and vasospasm, the Lindegaard Ratio (LR) is used (FVMCA/FVICA). If the FV is elevated, then the LR value indicates the following
- <3 hyperemia
- 3–6 mild vasospasm
- >6 severe vasospasm
- TCD measurements can be repeated at the bedside daily or more frequently as part of a comprehensive protocol for vasospasm detection and management.
- Although it can aid in the diagnosis of vasospasm, the effect of TCD on improving patient outcome has not yet been established.
- Stroke prevention in sickle cell disease (SCD)
- There is Class I evidence that supports the use of TCD for assessing the risk of stroke in children with SCD.
- Children with SCD are at risk of progressive occlusion of large intracranial arteries (ICA and MCA).
- Mean FV >200 cm/s is considered abnormal and requires transfusion to lower hemoglobin S concentration (below 30%).
- Stroke risk assessment
- The benefit of carotid artery revascularization to prevent stroke in asymptomatic patients with carotid artery disease has not been clearly defined. To that extent, the presence of embolic signals in the MCA is being studied as a predictor of risk of stroke.
- Asymptomatic patients with microembolic signals (MES), have a 15.6% risk of stroke compared to 1% risk of those who do not.
- Thus, TCD may be useful in the selection of high-risk asymptomatic patients to undergo carotid revascularization.
- Stroke treatment
- The rate of recanalization is increased when TCD monitoring is utilized during thrombolysis; this is possibly due to improved exposure of the clot to thrombolytics.
- Microbubbles injected with thrombolytics increased the rate of recanalization.
- Traumatic brain injury
- TCD may have a role in the assessment of ICP, cerebral autoregulation, and vasospasm.
- ICP: Intracranial hypertension is associated with increased PI. TCD may have a role in ICP estimation in patients with stroke, liver failure, preeclampsia, and other conditions where the use of invasive ICP measurement has not been established.
- Autoregulation: Cerebral autoregulation maintains a constant CBF at MAP between 60 and 160 mm Hg. Loss of autoregulation is common after TBI. Whether a change in FV reflects changes in BP and CO2 levels is being studied as an indicator of an intact autoregulation.
- Vasospasm: FV decreases during the first 48 hours and then increases for the following 72 hours. The increase may represent vasospasm or hyperemia. Using LR, the cause can be distinguished, potentially improving patient management.
- Brain death: Can serve as a tool to demonstrate cerebral circulatory arrest. Patients must have demonstrated flow before death, as 8% of the population lack acoustic windows. Three waveforms are associated with arrest: Oscillating flow, small systolic spikes, and no signal.
- Carotid endarterectomy (CEA)
- TCD is useful in monitoring for cerebral ischemia during CEA, as well as for detecting perioperative emboli, postoperative thrombosis, and postoperative hyperperfusion.
- It still remains unclear at what FV shunt placement is indicated.
- Emboli occurring during dissection and wound closure are particulate and are more important in predicting adverse events than predominantly gaseous emboli that occur during shunt placement and cross-clamp release.
- Occurrence of particulate emboli may be amenable to changes in surgical technique such as back bleeding, flushing, and the use of Dextran-40.
- Postoperative hyperperfusion is seen in ~1% of patients and may present with headache, facial and eye pain, neurologic deficit, and seizures. FV may be up to 230% above baseline and could potentially be used to guide hemodynamic management.
- TCD has not yet been shown to improve outcome in CEA patients.
- Cardiac surgery
- Loss of cerebral autoregulation and occurrence of emboli may be seen during cardiopulmonary bypass.
- TCD may be useful in guiding perfusion pressure management, but data has not demonstrated an improvement in outcome.
- There is some evidence to support the use of TCD during surgical repair of type A aortic dissection with retrograde cerebral perfusion.
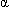 )/V; where Vf is the velocity of blood flow, Fsrc is the transmitted frequency source, V is the speed of sound in soft tissue (constant value 1540 m/s), and a is the angle of insonation.
)/V; where Vf is the velocity of blood flow, Fsrc is the transmitted frequency source, V is the speed of sound in soft tissue (constant value 1540 m/s), and a is the angle of insonation.