- PVCs originate within the ventricles, usually from an irritable ventricular focus.
- PVCs may be uniform (same form) or multiform (different forms).
- Usually a PVC is followed by a full compensatory pause because the sinus node timing is not interrupted. In contrast, a PVC may be followed by a noncompensatory pause if the PVC enters the sinusnode and resets its timing, enabling the following sinus P wave to appear earlier than expected.
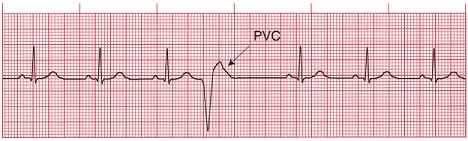
Rate: Depends on rate of underlying rhythm
Rhythm: Irregular whenever a PVC occurs
P Waves: None associated with the PVC
PR Interval: None associated with the PVC
QRS: Wide (greater than 0.10 sec), bizarre appearance
 Clinical Tip: Patients may sense PVCs as skipped beats. Because the ventricles are only partially filled, the PVC frequently does not generate a pulse.
Clinical Tip: Patients may sense PVCs as skipped beats. Because the ventricles are only partially filled, the PVC frequently does not generate a pulse.