This is a reference list only. It is not meant to be exhaustive in clinical content. Drug dosages follow Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) guidelines for adult patients and Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) guidelines for pediatric patients.
Before administering medications, especially IV medications, always consult an authoritative, current reference about dose, dilution, route, rate of administration, and interactions. Have a second licensed person independently check dose calculations, preparation, original orders, and infusion pump programming.
ACE Inhibitors
- Class: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
- Common Agents:Captopril, enalapril, lisinopril, ramipril.
- Indications: Acute MI, especially with ST elevation and with left ventricular dysfunction; HTN; heart failure without hypotension.
- Adult Dose: ACE inhibitor therapy should start with low-dose oral administration (with possible IV doses for some preparations) and increase steadily to achieve a full dose within 24 to 48 hours. An angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) should be administered to patients intolerant of ACE inhibitors.
- Captopril, acute MI dose: Begin with a single dose of 6.25 mg PO. Advance to 25 mg three times a day (TID) and then to 50 mg TID as tolerated.
- Enalapril (IV = Enalaprilat): PO: Begin with a single dose of 2.5 mg; titrate to 20 mg PO twice a day (BID). IV: 1.25 mg IV initial dose over 5 min, then 1.25–5 mg IV every 6 hours. IV form is contraindicated in STEMI (risk of hypotension).
- Lisinopril, acute MI dose: 5 mg within 24 hours after onset of symptoms, then 5 mg given after 24 hours, then 10 mg given after 48 hours, then 10 mg once daily.
- Ramipril: Begin with a single dose of 2.5 mg PO. Titrate PO BID as tolerated.
- Contraindications: Lactation, pregnancy, angioedema, hypersensitivity to ACE inhibitors, hypotension.
- Side Effects:Cough, dizziness, headache, fatigue, hypotension, hyperkalemia, renal insufficiency.
- Precautions: Reduce dose in renal failure. Caution in severe aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, unstented renal artery stenosis, severe CHF.
Adenosine (Adenocard)
- Class: Antiarrhythmic.
- Indications: Regular narrow-complex tachycardias, PSVT, and widecomplex tachycardia only if regular and monomorphic.
- Adult Dose: 6 mg IV in the antecubital or another large vein given rapidly over 1–3 sec followed by a 20-mL bolus of normal saline. If the rhythm does not convert, give 12 mg by rapid IVP in 1–2 min if needed. A third dose of 12 mg IVP may be given in another 1–2 min, maximum (max) total dose 30 mg.
- Pediatric Dose: 0.1 mg/kg (max dose 6 mg) IV/IO given rapidly over 1–3 sec followed by a 5- to 10-mL bolus of normal saline. If the rhythm does not convert, give 0.2 mg/kg (max dose 12 mg) IV/IO in 1–2 min if needed.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, sick sinus syndrome, second- or third-degree AV block (unless a functioning pacemaker is present), A-fib/A-flutter with underlying Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, drug-or poison-induced tachycardia, bronchospastic lung disease.
- Side Effects: Flushing; nausea; dizziness; headache; dyspnea; bronchospasm; chest pain or tightness; discomfort in neck, throat, or jaw; bradycardia; AV block; asystole; ventricular ectopic beats; VF.
- Precautions: Ineffective in treating A-fib, A-flutter, or VT. Less effective in patients taking theophylline or caffeine. Reduce dose in patients taking dipyridamole or carbamazepine or heart transplant patients.
Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP) Antagonists
- Class: Antiplatelet agents-thienopyridines (clopidogrel and prasugrel), cyclopentyltriazolopyrimidine (ticagrelor).
- Common Agents: Clopidogrel (Plavix), prasugrel (Effient), ticagrelor (Brilinta).
- Indications: Antiplatelet therapy for acute coronary syndromes (ACS) managed with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Clopidogrel: ACS, recent stroke, or peripheral arterial disease.
- Adult Dose: See individual order and drug for dosage.
- Contraindications: Acute pathological bleeding (e.g., peptic ulcer, intracranial bleeding). Prasugrel: Also history of TIA or stroke. Ticagrelor: Also history of intracranial hemorrhage, hepatic impairment.
- Side Effects: Bleeding, thrombocytopenia purpura. Ticagrelor: Dyspnea, increased serum creatinine. Stent thrombosis with premature discontinuation of therapy.
- Precautions: Increased risk of bleeding (chronic NSAID use, anticoagulation therapy, thrombocytopenia, trauma/surgery), thienopyridine hypersensitivity, severe hepatic impairment, severe renal impairment. Prasugrel: Caution in patients
 75 years old or patients <60 kg. Ticagrelor: Patients with hyperuricemia or gouty arthritis, patients at risk for bradycardia without pacemaker. Drugs must be withheld prior to CABG or elective surgery-Clopidogrel and ticagrelor: 5 days; prasugrel: 7 days. In patients at risk for stent thrombosis, consider bridging with IV glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor such as eptifibatide (Integrilin) while patient is off ADP antagonist; resume oral therapy as soon as possible after surgery when risk for postoperative bleeding is reduced.
75 years old or patients <60 kg. Ticagrelor: Patients with hyperuricemia or gouty arthritis, patients at risk for bradycardia without pacemaker. Drugs must be withheld prior to CABG or elective surgery-Clopidogrel and ticagrelor: 5 days; prasugrel: 7 days. In patients at risk for stent thrombosis, consider bridging with IV glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor such as eptifibatide (Integrilin) while patient is off ADP antagonist; resume oral therapy as soon as possible after surgery when risk for postoperative bleeding is reduced.
Albuterol (ProAir, Proventil, Ventolin)
- Class: Adrenergic beta2-agonist, bronchodilator.
- Indications:Asthma, COPD, anaphylaxis (bronchospasm), hyperkalemia.
- Adult Dose:For bronchospasm, metered-dose inhaler (MDI): 2 puffs every 4–6 hr prn; nebulizer: 2.5 mg 3–4 times daily prn or 1.25–5 mg every 4–8 hr prn. For severe bronchospasm and status asthmaticus: 5 mcg/min IV, titrate up every 15–30 min to 10–20 mcg/min. For severe acute asthma exacerbation, MDI: 4–8 puffs every 20 min up to 4 hr, then every 1–4 hr prn; nebulizer: 2.5–5 mg every 20 min for 3 doses, then 2.5–10 mg every 1–4 hr prn or 10–15 mg/hr by continuous nebulizer.
- Pediatric Dose:For bronchospasm, MDI 2 puffs every 4–6 hr prn; nebulizer children 2–12 yr: 0.63–1.25 mg 3–4 times daily prn; nebulizer children
 12 yr: 2.5 mg 3–4 times. For mild to moderate asthma or anaphylaxis, hyperkalemia, MDI: 4–8 puffs every 20 min prn; nebulizer, <20 kg: 2.5 mg every 20 min, >20 kg: 5 mg every 20 min. For severe asthma exacerbation, MDI children <12 yr: 4–8 puffs every 20 min for 3 doses, then every 1–4 hr prn; MDI children
12 yr: 2.5 mg 3–4 times. For mild to moderate asthma or anaphylaxis, hyperkalemia, MDI: 4–8 puffs every 20 min prn; nebulizer, <20 kg: 2.5 mg every 20 min, >20 kg: 5 mg every 20 min. For severe asthma exacerbation, MDI children <12 yr: 4–8 puffs every 20 min for 3 doses, then every 1–4 hr prn; MDI children  12 yr: 4–8 puffs every 20 min for up to 4 hr, then every 1–4 hr prn; nebulizer children <12 yr: 0.15 mg/kg every 20 min for 3 doses, then 0.15–0.3 mg/kg every 1–4 hr, or 0.5 mg/kg/hr by continuous nebulizer; nebulizer children
12 yr: 4–8 puffs every 20 min for up to 4 hr, then every 1–4 hr prn; nebulizer children <12 yr: 0.15 mg/kg every 20 min for 3 doses, then 0.15–0.3 mg/kg every 1–4 hr, or 0.5 mg/kg/hr by continuous nebulizer; nebulizer children  12 yr: 2.5–5 mg every 20 min for 3 doses, then 2.5–10 mg every 1–4 hr prn, or 10–15 mg/hr by continuous nebulizer.
12 yr: 2.5–5 mg every 20 min for 3 doses, then 2.5–10 mg every 1–4 hr prn, or 10–15 mg/hr by continuous nebulizer. - Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, tachyarrhythmias, risk of abortion during first or second trimester.
- Side Effects:Angina, arrhythmias, palpitations, tachycardia, flushing, dizziness, headache, insomnia, irritability, angioedema, rash, urticaria, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, asthma exacerbation, cough.
- Precautions: Use of spacer with MDI is recommended. Caution in cardiovascular disease (arrhythmias, HTN, heart failure), diabetes (may increase serum glucose), glaucoma (increased intraocular pressure), hyperthyroidism (may stimulate thyroid activity), hypokalemia (decreased serum potassium), seizure disorders (CNS stimulation/excitation).
Amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone)
- Class: Antiarrhythmic, class III.
- Indications: Management of life-threatening shock-refractory VF or pulseless VT, recurrent hemodynamically unstable VT. Conversion of A-fib, SVT. Control of rapid ventricular rate in pre-excited atrial arrhythmias. Control of hemodynamically stable VT, polymorphic VT with normal QT interval, or wide-complex tachycardia of uncertain origin.
- Adult Dose:Cardiac arrest: 300 mg IV/IO; consider additional 150 mg IV/IO in 3–5 min if needed. Wide- and narrow-complex tachycardia (stable): 150 mg IV over first 10 min (15 mg/min)-may repeat infusion of 150 mg IV every 10 min as needed; slow infusion of 360 mg IV over next 6 hr (1 mg/min); maintenance infusion of 540 mg over next 18 hr (0.5 mg/min). Max cumulative dose 2.2 g IV in 24 hr.
- Pediatric Dose:Cardiac arrest: 5 mg/kg IV/IO bolus (max 300 mg), may repeat to max of 15 mg/kg (or 2.2 g in adolescents) in 24 hr; Wide- and narrow-complex tachycardia (stable): 5 mg/kg IV/IO load over 20–60 min (max 300 mg), may repeat to max of 15 mg/kg/day (2.2 g/day in adolescents).
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, cardiogenic shock, symptomatic bradycardia or second- or third-degree AV block without functioning pacemaker, severe sinus node dysfunction.
- Side Effects: Vasodilation, hypotension, bradycardia, proarrhythmic effects, visual impairment, hepatotoxicity, pulmonary toxicity, CHF. May prolong QT interval, producing torsade de pointes.
- Precautions: Avoid concurrent use with procainamide. Correct hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia, if possible, before use. Draw up amiodarone through a large-gauge needle to reduce foaming. For slow or maintenance IV infusion, mix the medication only in a glass bottle containing D5W or NS and administer through an in-line filter using a volumetric pump. Use with caution in thyroid disease, pulmonary disease, or hepatic impairment, and in patients on warfarin.
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid, ASA)
- Class: Antiplatelet.
- Indications: Acute coronary syndrome, symptoms suggestive of cardiac ischemia, post-percutaneous coronary interventions, A-fib, stroke, peripheral arterial disease.
- Adult Dose:Acute coronary syndrome: 162–325 mg PO. Chewing the tablet is preferable; use non–enteric-coated tablets for more rapid antiplatelet effect. Give within minutes of onset of ischemic symptoms. Other indications: 81–325 mg PO daily.
- Contraindications: Known allergy to aspirin, third trimester of pregnancy, bleeding.
- Side Effects:Anorexia, nausea, epigastric pain, bleeding, anaphylaxis.
- Precautions: GERD, active ulcers, asthma, bleeding disorders, or thrombocytopenia.
- Class: Anticholinergic, parasympatholytic, vagolytic.
- Indications: Symptomatic sinus bradycardia, junctional escape rhythm, or second-degree type I block. Not likely to be effective in second-degree type II or third-degree AV block with wide QRS complex.
- Adult Dose: 1 mg IV given every 3–5 min as needed, max total dose 3 mg (0.04 mg/kg).
- Pediatric Dose: 0.02 mg/kg IV/IO; maximum single dose 0.5 mg; may repeat dose once in 3–5 min; maximum total dose for child: 1 mg, for adolescent: 3 mg. May give 0.04–0.06 mg/kg, flush with 5 mL normal saline if administering by ET. Use ET route only if IV/IO access is not available.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, acute angle-closure glaucoma, asthma, prostatic hypertrophy, myasthenia gravis.
- Side Effects: Tachycardia, headache, dry mouth, nausea, constipation, dilated pupils, flushing, hypotension.
- Precautions: Use caution in myocardial ischemia and hypoxia. Avoid in hypothermic bradycardia and in second-degree (Mobitz type II) and third-degree AV block with wide QRS complex, asystole, bradycardic PEA. Caution in colon disease, hepatic or renal impairment, hiatal hernia, obstructive uropathy, hyperthyroidism.
Beta Blockers
- Class: Beta blockers, antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic, antianginal.
- Common Agents:Atenolol, esmolol, labetalol, metoprolol tartrate, carvedilol, propranolol.
- Indications: MI, unstable angina, PSVT, A-fib, A-flutter, HTN, CHF.
- Adult Dose:Atenolol, acute MI: 5 mg IV over 5 min. Wait 10 min, then give second dose of 5 mg IV over 5 min. In 10 min, if tolerated well, begin oral regimen with 50 mg PO; titrate to effect.
- Esmolol: 0.5 mg/kg (500 mcg/kg) over 1 min, followed by 0.05 mg/kg (50 mcg/kg) per min infusion; max: 0.3 mg/kg (300 mcg/kg) per min. If inadequate response after 5 min, may repeat 0.5 mg/kg (500 mcg/kg) bolus and then titrate infusion up to 0.2 mg/kg (200 mcg/kg) per min; higher doses unlikely to be beneficial. Has a short half-life (2–9 min).
- Labetalol: 10 mg IV push over 1–2 min. May repeat or double every 10 min to a max dose of 150 mg, or give initial dose as a bolus, then begin infusion at 2–8 mg/min.
- Metoprolol Tartrate, acute MI: 25–50 mg every 6–12 hours PO; then transition over next 2–3 days to twice-daily dosing of metoprolol tartrate or to daily metoprolol succinate; titrate to daily dose of 200 mg as tolerated. IV: 5 mg IV every 5 min as tolerated up to 3 doses; titrate to heart rate and blood pressure.
- Carvedilol: 6.25 mg twice daily; titrate to 25 mg twice daily as tolerated.
- Propranolol, for SVT: 0.5–1 mg over 1 min, repeated as needed up to a total dose of 0.1 mg/kg.
- Contraindications: Heart rate <50 bpm, systolic BP <100 mm Hg, second- or third-degree AV block or sick sinus syndrome without functioning pacemaker, severe decompensated left ventricular failure, cardiogenic shock. Nonselective beta blockers are contraindicated in bronchospastic disease.
- Side Effects: Hypotension, dizziness, bradycardia, headache, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, depression.
- Precautions: Concurrent use with calcium channel blockers, such as verapamil or diltiazem, can cause hypotension. Use beta-1 selective agents with caution in patients with a history of bronchospasm. Use caution in thyroid disease, peripheral arterial disease, and diabetes (monitor blood glucose levels frequently).
- Class: Minerals, electrolytes, calcium salt.
- Indications: Hyperkalemia, hypocalcemia, hypermagnesemia; antidote for calcium channel blocker or beta blocker overdose.
- Adult Dose: 500–1000 mg (5–10 mL of a 10% solution) over 2–5 min IV; may be repeated as needed. Note: comparable dose of 10% calcium gluconate is 15–30 mL.
- Pediatric Dose: 20 mg/kg (0.2 mL/kg) IV/IO slow push during arrest or if severe hypotension, repeat as needed.
- Contraindications:Hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia, VF, digoxin toxicity.
- Side effects: Bradycardia, hypotension, hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia, VF, syncope, nephrolithiasis, flushing, dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
- Precautions: Incompatible with sodium bicarbonate (precipitates). Caution in patients with renal impairment, respiratory acidosis, hypokalemia, hyperparathyroidism.
Digoxin (Lanoxin)
- Class: Antiarrhythmic, cardiac glycoside.
- Indications: To slow ventricular response in A-fib or A-flutter; rarely, as a positive inotrope in CHF.
- Adult Dose: IV loading doses: 0.004–0.006 mg/kg (4–6 mcg/kg initially over 5 min; second and third boluses of 0.002–0.003 mg/kg (2–3 mcg/kg) to follow at 4–8 hour intervals (total loading dose 8–12 mcg/kg divided over 8–16 hours). Check digoxin levels no sooner than 4 hours after IV dose; no sooner than 6 hours after oral dose. Monitor heart rate and ECG. Maintenance dose is affected by body mass and renal function. Caution: Amiodarone interaction; reduce digoxin dose by 50% when used with amiodarone.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, uncontrolled ventricular arrhythmias, AV block without functioning pacemaker, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis (IHSS), constrictive pericarditis, A-fib with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome.
- Side Effects: Accelerated junctional rhythm, atrial tachycardia with block, AV block, asystole, VT, VF, ventricular bigeminy and trigeminy, dizziness, weakness, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, blurred or yellow vision, headache, hypersensitivity, hypokalemia.
- Precautions: Avoid electrical cardioversion of stable patients. If the patient’s condition is unstable, use lower current settings such as 10–20 J. Use cautiously in elderly patients and patients with heart failure, acute MI, renal impairment, and hypothyroidism. Correct electrolyte abnormalities, monitor digoxin levels, monitor for clinical signs of toxicity. Hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and hypercalcemia may precipitate digitalis toxicity. Reduce digoxin dose by 50% in patients on amiodarone.
Digoxin Immune FAB (Fragment Antigen Binding) (DigiFab)
- Class: Antidote to digoxin and digitoxin.
- Indications: Symptomatic digoxin toxicity or acute ingestion of unknown amount of digoxin.
- Adult Dose: Depends on serum digoxin levels. One 40-mg vial binds to approximately 0.5 mg of digoxin. Dose is typically administered over 30 min.
- Contraindications: Allergy only, otherwise none known. Allergy to sheep proteins or other sheep products.
- Side Effects: Worsening of CHF, rapid ventricular response in patients with A-fib, hypokalemia, postural hypotension, increased serum digoxin levels due to bound complexes (clinically misleading because bound complex cannot interact with receptors).
- Precautions: Heart failure, renal impairment.
Diltiazem (Cardizem)
- Class: Calcium channel blocker, antiarrhythmic, class IV.
- Indications: To control ventricular rate in A-fib and A-flutter; to terminate PSVT (reentry SVT) refractory to adenosine with narrow QRS complex and adequate BP.
- Adult Dose: 15–20 mg (0.25 mg/kg) IV given over 2 min. May repeat in 15 min at 20–25 mg (0.35 mg/kg) IV given over 2 min. Start maintenance drip at 5–15 mg/hr and titrate to HR.
- Contraindications: Drug- or poison-induced tachycardia, wide-complex tachycardia of uncertain origin, rapid A-fib and A-flutter with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, sick sinus syndrome, second- or third-degree AV block (unless a functioning pacemaker is present), hypotension with systolic BP less than 90 mm Hg, acute MI with pulmonary congestion.
- Side Effects: Hypotension, bradycardia (including AV block), chest pain, ventricular arrhythmias, peripheral edema, flushing, heart failure, syncope.
- Precautions: Severe hypotension in patients receiving beta blockers. Caution in patients with hepatic or renal disease, heart failure, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Class: Adrenergic direct-acting beta1-agonist, inotrope.
- Indications: To increase myocardial contractility in patients with decompensated heart failure with systolic BP 70–100 mm Hg and no signs of shock.
- Adult Dose: Continuous infusion (titrate to patient response): 2–20 mcg/kg/min, max 40 mcg/kg/min.
- Pediatric Dose: Same as adult dose, titrate to patient response.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis (IHSS), suspected or known poison- or drug-induced shock. Do not mix with sodium bicarbonate.
- Side Effects: Tachycardia, HTN, hypotension, increased ventricular ectopy, chest pain, palpitations, restlessness, headache, nausea, vomiting.
- Precautions: Avoid in patients with systolic BP <100 mm Hg and signs of shock; correct hypovolemia before use, if needed. MI: may increase myocardial oxygen demand.
Dopamine (Intropin)
- Class: Alpha- and beta1-adrenergic agonist, inotrope, vasopressor.
- Indications: Symptomatic bradycardia and hypotension, cardiogenic shock.
- Adult Dose: Continuous infusion (titrate to patient response): low dose 1–5 mcg/kg/min (renal dose); moderate dose 5–10 mcg/kg/min (cardiac dose); high dose 10–20 mcg/kg/min (vasopressor dose). Mix 400 mg/250 mL in normal saline, lactated Ringer’s solution, or D5W (1600 mcg/mL).
- Pediatric Dose:Cardiogenic shock, distributive shock: 2–20 mcg/kg/min IV/IO infusion, titrate to desired effect.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to sulfites, pheochromocytoma, VF
- Side Effects: Tachyarrhythmias, angina, hypotension, palpitations, vasoconstriction, dyspnea, headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Precautions: Hypovolemia, MI. Adjust dosage in elderly patients and in those with occlusive vascular disease. Ensure adequate IV volume repletion with normal saline before infusion. Taper slowly. Do not mix with sodium bicarbonate. Use care with peripheral administration; infiltration with extravasation can cause tissue necrosis. A central line is preferred. Use a volumetric infusion pump. Caution in patients with occlusive vascular disease and patients taking MAO inhibitors.
Epinephrine (Adrenalin)
- Class: Alpha-beta adrenergic agonist (sympathomimetic: inotrope, vasopressor, bronchodilator).
- Indications: Cardiac arrest: PEA, asystole, pulseless VT, VF; hypotension with severe bradycardia. Anaphylaxis, severe asthma exacerbation.
- Adult Dose: Cardiac arrest: 1 mg IV/IO (10 mL of 1:10,000 solution) every 3–5 min prn; follow each dose with 20 mL IV flush. Give 2.0–2.5 mg diluted in 10 mL normal saline or sterile water if administering by ET tube. Profound bradycardia or hypotension: 2–10 mcg/min IV infusion; add 1 mg (1 mL of a 1:1000 solution) to 500 mL normal saline or D5W. Anaphylaxis: 0.2–0.5 mg (1:1000 solution) IM (1:1000 solution) every 5–15 min prn or 0.1–0.25 mg (1:10,000 solution) IV every 5–15 min, then 1–4 mcg/min IV prn. Severe asthma exacerbation: 0.3–0.5 mg (1:1000 solution) SQ/IM every 20 min × 3 doses prn. Max 1 mg/dose.
- Pediatric Dose: Cardiac arrest or symptomatic bradycardia: 0.01 mg/kg (0.1 mL/kg) 1:10,000 IV/IO every 3–5 min as needed (max 1 mg; 10 mL). Give 0.1 mg/kg (0.1 mL/kg) 1:1000, flush with 5 mL normal saline if administering by ET tube. Use ET route only if IV/IO access is not available. Repeat every 3–5 min as needed. Anaphylaxis: 0.01 mg/kg (1:1000 solution) SQ/IM every 5–20 min × 3 doses prn or 0.01 mg/kg (1:10,000 solution) IV × 1, then 0.1 mcg/kg/min IV prn. Severe asthma exacerbation: 0.01 mg/kg (1:1000 solution) SQ/IM every 20 min × 3 doses prn. Max 0.5 mg/dose.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to adrenergic amines, hypovolemic shock, coronary insufficiency. No contraindication in cardiac arrest.
- Side Effects: Angina, HTN, tachycardia, VT, VF, nervousness, restlessness, palpitations, tremors, weakness, diaphoresis, anxiety, headache, nausea.
- Precautions: Use caution in HTN and increasing heart rate (may cause increased myocardial oxygen demand). Higher doses can contribute to post-arrest cardiac impairment but may be needed to treat poison- or drug-induced shock. Avoid mixing with alkaline solutions.
Fibrinolytic Agents
- Class: Thrombolytic, fibrinolytic.
- Common Agents:Alteplase (Activase, t-PA), reteplase (Retavase), streptokinase (Streptase), tenecteplase (TNKase).
- Indications: Acute ST elevation MI within the past 12 hr. Alteplase is the only fibrinolytic agent approved for acute ischemic stroke and must be started less than 3 hr from the onset of symptoms.
- Adult Dose: See individual order and drug for route and dosage.
- Contraindications: Active internal bleeding within 21 days (except menses), neurovascular event within 3 months, major surgery or trauma within 2 weeks, aortic dissection, severe (uncontrolled) HTN, bleedingdisorders, prolonged CPR, lumbar puncture within 1 week. History of any intracranial bleeding, oral anticoagulation therapy, severe stroke.
- Side Effects: Hypotension, reperfusion arrhythmias, heart failure, headache, increased bleeding time, deep or superficial hemorrhage, flushing, urticaria, anaphylaxis.
- Precautions: Use cautiously in patients with severe renal or hepatic disease. Initiate bleeding precautions. Monitor patient for bleeding complications.
Fondaparinux (Arixtra)
- Class: Factor Xa inhibitor, anticoagulant.
- Indications: To inhibit thrombin generation by inhibiting factor Xa in patients with ACS; anticoagulation in patients with history of heparininduced thrombocytopenia (HIT); deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis in patients undergoing orthopedic surgery or abdominal surgery; pulmonary embolism (PE); acute DVT without PE.
- Adult Dose:STEMI: 2.5 mg IV bolus followed by 2.5 mg SQ daily for up to 8 days. Acute DVT/PE, acute thrombosis: 5–10 mg SQ daily (based on body weight) up to 5–9 days, start coumadin therapy on first or second day, discontinue fondaparinux when INR
 2 for at least 24 hr. Other uses: 2.5 mg SQ daily for up to 8 days (up to 10 days for abdominal surgery, up to 11 days for hip replacement or total knee replacement surgery, up to 14 days for total hip or total knee arthroplasty or hip fracture surgery).
2 for at least 24 hr. Other uses: 2.5 mg SQ daily for up to 8 days (up to 10 days for abdominal surgery, up to 11 days for hip replacement or total knee replacement surgery, up to 14 days for total hip or total knee arthroplasty or hip fracture surgery). - Contraindications: Creatinine clearance <30 mL/min, hypersensitivity, body weight <50 kg when used for prophylaxis, active major bleeding, bacterial endocarditis, thrombocytopenia associated with positive in vitrotest for antiplatelet antibody in presence of fondaparinux.
- Side Effects: Bleeding, edema, hypotension, insomnia, dizziness, headache, rash, constipation, vomiting, diarrhea, urinary retention, moderate thrombocytopenia.
- Precautions: Increased risk of bleeding, creatinine clearance 30–50 mL/min, patients >75 years old, patients <50 kg being treated for DVT/PE. Discontinue 24 hr before CABG and administer unfractionated heparin.
Furosemide (Lasix)
- Class: Loop diuretic.
- Indications: CHF with acute pulmonary edema, hypertensive crisis, post-arrest cerebral edema, edema associated with hepatic or renal disease.
- Adult Dose: 0.5–1 mg/kg IV given over 1–2 min; may repeat at 2 mg/kg IV given over 1–2 min. Alternative: 20–40 mg IV, increase by 20 mg IV every 2 hr until desired response is obtained, max 160–200 mg/dose.
- Pediatric Dose: 0.5–1 mg/kg IV/IO, may increase by 1 mg/kg IV every 2 hr until desired response is obtained, max 6 mg/kg/dose.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity (cross-sensitivity with thiazides and sulfonamides may occur), uncontrolled electrolyte imbalance, hepatic coma, anuria, hypovolemia.
- Side Effects: Severe dehydration, hypovolemia, hypotension, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremia, hyperglycemia, dizziness, ototoxicity.
- Precautions: Use cautiously in severe liver disease accompanied by cirrhosis or ascites, electrolyte depletion, diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, lactation, severe renal disease, gout. Risk for ototoxicity with increased dose or rapid injection. Monitor electrolytes closely.
Glycoprotein IIB/IIIA Inhibitors
- Class: Antiplatelet agents, GP IIb/IIIa inhibitors.
- Common Agents:Abciximab (ReoPro), eptifibatide (Integrilin), tirofiban (Aggrastat).
- Indications: Acute coronary syndromes managed medically (eptifibatide and tirofiban) and those undergoing PCI (all three agents).
- Adult Dose: See individual order and drug for dosage.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, active internal bleeding or bleeding disorder within past 30 days, history of bleeding diathesis, history of stroke within 30 days, history of hemorrhagic stroke, uncontrolledHTN (systolic BP >200 mm Hg, diastolic pressure >110 mm Hg), major surgery or trauma within 1 month, concomitant use of another GP IIb/IIIa inhibitor, dependency on hemodialysis.
- Side Effects: Bleeding, hypotension, thrombocytopenia.
- Precautions: Patients at increased risk for bleeding, patients <70 kg, platelet count <150,000/mm3, renal impairment. Discontinue
 2–4 hr prior to CABG. Abciximab (ReoPro) must be administered with aspirin and heparin.
2–4 hr prior to CABG. Abciximab (ReoPro) must be administered with aspirin and heparin.
Heparin (Unfractionated Heparin [UFH])
- Class: Anticoagulant.
- Indications: Acute coronary syndromes (ACS): STEMI, NSTEMI, unstable angina (UA), during PCI; prophylaxis and treatment of thromboembolic disorders such as DVT, pulmonary embolus; anticoagulant for extracorporeal and dialysis procedures.
- Adult Dose:ACS: 60 units/kg IV bolus, max 4000 units, followed by continuous IV infusion of 12 units/kg/hr, max 1000 units/hr, check APTT every 4–6 hr, adjust infusion to maintain APTT 50–70 sec for 48 hr or until angiography. Thromboprophylaxis: 5000 units SQ every 8–12 hr. Treatment of DVT/PE: 80 units/kg or 5000 unit IV bolus, followed by continuous IV infusion of 18 units/kg/hr; adjust infusion to maintain therapeutic APTT.
- Pediatric Dose:Systemic heparinization for infants <1 year: 75 units/kg IV over 10 min, followed by initial maintenance infusion of 28 units/kg/hr; check APTT every 4 hr and adjust heparin dose to maintain APTT 60-85 sec. For children >1 year: 75 units/kg over 10 min, followed by initial maintenance infusion of 20 units/kg/hr, adjust heparin to maintain APTT 60–85 sec.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), severe thrombocytopenia, uncontrolled active bleeding unless due to DIC; recent intracranial, intraspinal, or eye surgery; uncontrolled HTN.
- Side Effects: Bleeding, HIT, thrombocytopenia, hyperkalemia, osteoporosis with use >6 mo.
- Precautions: Patients at increased risk for bleeding; patients with heparin resistance (antithrombin deficiency, increased heparin clearance elevations in heparin-binding proteins, elevations in factor VIII and/or fibrinogen). Female patients >60 yr old may require lower doses. Check platelet count daily.
Ibutilide (Corvert)
- Class: Antiarrhythmic, class III.
- Indications: SVT, including A-fib and A-flutter; most effective for conversion of A-fib or A-flutter of short duration (
 48 hr).
48 hr). - Adult Dose:Patients weighing 60 kg or more: 1 mg IV given over 10 min; may repeat the same dose in 10 min if arrhythmia does not terminate. Patients weighing <60 kg: 0.01 mg/kg IV given over 10 min; may repeat the same dose in 10 min if arrhythmia does not terminate.
- Contraindications: Known hypersensitivity, history of polymorphic VT, QTc greater than 440 msec.
- Side Effects: Nonsustained or sustained monomorphic or polymorphic VT, torsade de pointes, AV block, CHF, HTN, headache, tachycardia, hypotension, nausea and vomiting.
- Precautions: Continuous ECG monitoring for 4–6 hr after administration or until QTc returns to baseline. Monitor for AV block. Skilled personnel and resuscitative equipment must be readily available. Correct electrolyte abnormalities prior to use. If A-fib has lasted longer than 48 hr, anticoagulation is required before cardioversion with ibutilide. Monitor QTc. Not recommended for chronic atrial fibrillation. Caution in patients with heart failure or hepatic impairment.
Isoproterenol (Isuprel)
- Class: Beta-adrenergic agonist.
- Indications: Medically refractory symptomatic bradycardia when transcutaneous or transvenous pacing is not available, refractory torsade de pointes unresponsive to magnesium, bradycardia in heart transplant patients, beta blocker poisoning.
- Adult Dose: IV infusion: mix 1 mg/250 mL in normal saline, lactated Ringer’s solution, or D5W, run at 2–10 mcg/min, and titrate to patient response. In torsade de pointes, titrate to increase heart rate until VT is suppressed.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to drug or sulfites, digitalis intoxication, angina, tachyarrhythmias, concurrent use with epinephrine (can cause VF or VT).
- Side Effects: Arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, hypotension, angina, anxiety, tachycardia, palpitations, skin flushing, dizziness, tremors, headache, nausea, vomiting, restlessness.
- Precautions: May increase myocardial ischemia. Use caution in patients with renal impairment, cardiovascular disease, distributive shock, hyperthyroidism, diabetes. High doses are harmful except in beta blocker overdose.
Lidocaine (Xylocaine)
- Class: Antiarrhythmic, class Ib, local anesthetic.
- Indications: Alternative to amiodarone in VF or pulseless VT. Use in stable VT, wide-complex tachycardia of uncertain origin.
- Adult Dose:Cardiac arrest from VF or VT: 1.0–1.5 mg/kg IV/IO (or 2–4 mg/kg via ET tube); for refractory VF or pulseless VT may repeat 0.5–0.75 mg/kg IV/IO every 5–10 min, max dose 3 mg/kg. Stable VT, wide-complex tachycardia of uncertain origin: 0.50–0.75 mg/kg up to 1.0–1.5 mg/kg; may repeat 0.50–0.75 mg/kg every 5–10 min, max total dose 3 mg/kg. If conversion is successful, start an IV infusion of 1–4 mg/min (30–50 mcg/kg/min) in normal saline or D5W.
- Pediatric Dose: 1 mg/kg IV/IO bolus for loading dose. Give 2–3 mg/kg, flush with 5 mL normal saline if administering by ET tube. Use ET route only if IV/IO access is not available. Maintenance: 20–50 mcg/kg/min IV/IO infusion (repeat bolus [0.5–1 mg/kg IV/IO] when infusion is initiated if bolus has not been given within previous 15 min).
- Contraindications: Prophylactic use in acute MI, advanced AV block without functioning pacemaker, hypotension, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, hypersensitivity to amide local anesthetics.
- Side Effects:Confusion, agitation, anxiety, tinnitus, blurred vision, dizziness, tremors, hallucinations, seizures, hypotension, bradycardia, cardiovascular collapse, respiratory arrest, slurred speech.
- Precautions: CHF, respiratory depression, shock. Reduce maintenance dose (not loading dose) in presence of impaired liver function or left ventricular dysfunction or in the elderly. Stop infusion if signs of CNS toxicity develop.
- Class: Electrolyte, antiarrhythmic.
- Indications: Torsade de pointes, hypomagnesemia, life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias due to digitalis toxicity, status asthmaticus, seizures.
- Adult Dose:Cardiac arrest (due to hypomagnesemia or torsade de pointes): 1–2 g IV (2–4 mL of a 50% solution) diluted in 10 mL of D5W over 1–2 min. Torsade de pointes (non–cardiac arrest with pulse) or acute MI with hypomagnesemia: load with 1–2 g mixed in 50–100 mL of D5W infused over 5–60 min IV, then infuse 0.5–1.0 g/hr IV (titrate to control torsade). Seizures: 2 g IV diluted in 10 mL of D5W over 10 min.
- Pediatric Dose:Torsade de pointes (cardiac arrest-pulseless VT): 25–50 mg/kg IV/IO bolus (max dose 2 g).Torsade de pointes(non–cardiac arrest with pulses) or hypomagnesemia: 25–50 mg/kg IV/IO over 10–20 min. Status asthmaticus: 25–50 mg/kg/IV/IO (max dose 2 g) over 15–30 min.
- Contraindications: Hypermagnesemia, hypocalcemia, AV block.
- Side Effects: HTN, bradycardia, cardiac arrest, respiratory depression, altered LOC, flushed skin, diaphoresis, hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia, hypophosphatemia.
- Precautions: Renal insufficiency, occasional fall in BP with rapid administration. Monitor serum magnesium levels. Caution in patients with myasthenia gravis. Correct concurrent hypokalemia and hypocalcemia.
- Class: Opiate narcotic analgesic.
- Indications: Chest pain unrelieved by nitroglycerin; CHF and dyspnea associated with pulmonary edema.
- Adult Dose: 2–4 mg IV (given over 1–5 min), administer every 5–30 min as needed if hemodynamically stable; may repeat dose of 2–8 mg at 5- to 15-min intervals if needed.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, heart failure due to chronic lung disease, respiratory depression, hypercarbia, hypotension, bowel obstruction, severe asthma, acute or severe hypercarbia. Avoid in patients with RV infarction.
- Side Effects: Respiratory depression, hypotension, nausea and vomiting, bradycardia, altered LOC, seizures, somnolence, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, pruritus, dry mouth, urinary retention.
- Precautions: Administer slowly and titrate to effect. Reverse with naloxone (0.4–2.0 mg IV) if necessary. Use caution in cerebral edema and pulmonary edema with compromised respiration. Use caution with hypovolemic patients; be prepared to administer volume. Use caution in renal and hepatic impairment, seizure disorder, CNS depression, head injury, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, prostatic hypertrophy, shock.
Naloxone (Narcan)
- Class: Opioid antagonist.
- Indications: Reversal of opioid overdose/toxicity unresponsive to oxygen and ventilator support, such as respiratory and neurological depression.
- Adult dose:Opioid associated life-threatening emergencies: IM or IV 0.04–0.4 mg, repeated every 2–3 min, if necessary. Intranasal: 2 mg, repeated every 3–5 min, if necessary. Reversal of respiratory depression with therapeutic opioid doses: 0.04–0.4 mg IV, IM; may repeat until ventilation is adequate, up to 0.8 mg. Postoperative reversal: 0.1–0.2 mg IV every 2–3 min until adequate ventilation.
- Pediatric Dose: For total reversal, birth to 5 yr: 0.1 mg/kg IV every 2–3 min as needed, max dose 2 mg, >5 yr: 2 mg IV every 2–3 min prn up to 10 mg. For partial reversal: 0.001–0.005 mg/kg IV (1–5 mcg/kg), repeat as needed every 2–3 min. For postoperative reversal: 0.01 mg/kg IV every 2–3 min prn. Continuous IV/IO infusion: 0.002–0.16 mg/kg (2–160 mcg/kg) per hour IV/IO infusion.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, meperidine-induced seizures.
- Side Effects: Secondary to reversal (withdrawal) of narcotic analgesia and sedation. Recurrent respiratory depression, pain, hypertension, hypotension, irritability, agitation, diaphoresis, seizures.
- Precautions: May precipitate symptoms of acute withdrawal in opioiddependent patients. Use caution in patients with a history of seizures and patients with cardiovascular disease. Abrupt postoperative reversal may cause nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, tachycardia, hypertension, seizures, pulmonary edema, arrhythmias.
Nitroglycerin (Nitrostat, Nitrolingual [Pump spray])
- Class: Antianginal, nitrate, vasodilator.
- Indications: Acute coronary syndrome, angina, CHF associated with acute MI, hypertensive urgency with ACS.
- Adult Dose: Sublingual route, 0.3–0.4 mg (1 tablet); repeat every 3–5 min if chest pain is not relieved, max 3 doses/15 min. Aerosol, spray for 0.5–1.0 sec at 3- to 5-min intervals (provides 0.4 mg/dose), max 3 sprays/15 min. IV bolus administration at 12.5–25.0 mcg (if no sublingual or spray used). IV infusion: mix 25 mg/250 mL (100 mcg/mL) in D5W, start at 5 mcg/min and titrate by 5 mcg/min every 3–5 min to 20 mcg/min. If patient remains symptomatic, titrate by 10–20 mcg/min every 3–5 min, max 200 mcg/min.
- Pediatric Dose: 0.25–0.50 mcg/kg/min IV/IO infusion, titrate by 1 mcg/kg/min every 15–20 min as needed to typical dose range of 1–5 mcg/kg/min (max 10 mcg/kg/min). In adolescents, begin with 5–10 mcg per minute (this dose is not per kg per min), and increase to max or 200 mcg per min.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, systolic BP less than 90 mm Hg, pericardial tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, severe bradycardia or severe tachycardia associated with hypotension; sildenafil (Viagra) or vardenafil (Levitra) within 24 hr, tadalafil (Cialis) within 48 hr; right ventricular infarction, increased intracranial pressure, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction, restrictive cardiomyopathy, increased intracranial pressure.
- Side Effects: Hypotension with reflex tachycardia, syncope, headache, flushed skin, dizziness, paradoxical bradycardia.
- Precautions: Do not mix with other medications; titrate IV to maintain systolic BP above 90 mm Hg. Mix only in glass IV bottles and infuse only through non-PVC tubing; standard polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tubing can bind up to 80% of the medication, making it necessary to infuse higher doses. Do not shake aerosol spray (affects metered dose).
Norepinephrine (Levophed)
- Class: Alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonist, vasopressor.
- Indications: Treatment of persistent shock after adequate volume replacement, cardiogenic shock, low systemic vascular resistance shock, septic shock, hemodynamically significant hypotension.
- Adult Dose: Start at 0.1–0.5 mcg/kg/min, titrate to response up to 8–12 mcg/min, maintenance infusion usually 2–4 mcg/min. Use volumetric infusion pump.
- Pediatric Dose: Start at 0.05–0.1 mcg/kg/min, titrate to response, up to 2 mcg/kg/min. Use volumetric infusion pump.
- Contraindications: Hypovolemic shock prior to adequate volume replacement, mesenteric or peripheral vascular thrombosis except as emergency measure to maintain coronary and cerebral perfusion. Do not administer in same line as alkaline solutions.
- Side Effects: Arrhythmias, hypertension, headache, anxiety, dyspnea, skin necrosis with extravasation.
- Precautions: Use caution in patients on MAO inhibitors as drug may cause prolonged hypertension; infuse into large vein and avoid extravasation; use caution in patients with ischemic heart disease: increases myocardial oxygen consumption, may induce arrhythmias, tachycardia, hypertension.
Oxygen
- Class: Gas.
- Indications: Cardiopulmonary emergencies with shortness of breath and chest pain, cardiac or respiratory arrest, hypoxemia. Used to optimize oxygen saturation less than 94%.
- Adult and Pediatric Dose: Nasal cannula 1–6 L/min (21%–44% oxygen), Venturi mask 4–12 L/min (24%–50% oxygen), simple mask 5–8 L/min (40%–60% oxygen), partial rebreathing mask 6–10 L/min (35%–60% oxygen), non-rebreathing mask 6–15 L/min (60%–100% oxygen), bagvalve mask 15 L/min (95%–100% oxygen).
- Contraindications: None reported.
- Side Effects: Drying of respiratory mucosa, possible bronchospasm if oxygen is extremely cold and dry. Oxygen supports combustion and can fuel a fire. Hypoventilation in patients with severe COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, oxygen toxicity.
- Precautions: Respiratory arrest in patients with hypoxic respiratory drive. The patient needs an airway and adequate ventilation before oxygen is effective.
Procainamide (Pronestyl)
- Class: Antiarrhythmic, class Ia.
- Indications: Recurrent VT or VF, PSVT refractory to adenosine and vagal stimulation, rapid A-fib with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, stable wide-complex tachycardia of uncertain origin, maintenance after conversion. Stable monomorphic VT with normal QTc and preserved LV function.
- Adult Dose: 20 mg/min IV infusion or up to 50 mg/min under urgent conditions, until arrhythmia is suppressed, max 17 mg/kg loading dose. Maintenance IV infusion: mix 1 g/250 mL (4 mg/mL) in normal saline or D5W, run at 1–4 mg/min.
- Pediatric Dose:Atrial flutter, SVT, VT (with pulses): 15 mg/kg IV/IO load over 30–60 min.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, second- and third-degree AV block (unless a functioning pacemaker is in place), prolonged QT interval, torsade de pointes, hypersensitivity, systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Side Effects: Hypotension, widening QRS, headache, nausea and vomiting, flushed skin, seizures, ventricular arrhythmias, AV block, cardiovascular collapse, arrest.
- Precautions: Monitor BP every 2–3 min while administering procainamide. If QRS width increases by 50% or more, or if systolic BP decreases to less than 90 mm Hg, stop the drug. Monitor for prolonged PR interval and AV block. Monitor for QT prolongation. May precipitate or exacerbate CHF. Reduce the total dose to 12 mg/kg and maintenance infusion to 1–2 mg/min if cardiac or renal dysfunction is present. Use cautiously in heart failure, myasthenia gravis, and hepatic or renal disease. Avoid concurrent use with drugs that prolong the QT interval (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol).
Sodium Bicarbonate
- Class: Alkalinizing agent, buffer.
- Indications: Known preexisting hyperkalemia, bicarbonate-responsive acidosis such as diabetic ketoacidosis or tricyclic antidepressant overdose, metabolic acidosis associated with prolonged resuscitation with effective ventilation.
- Adult Dose: 1 mEq/kg IV; may repeat 0.5 mEq/kg every 10 min. Dosing is best guided by calculated base deficits or bicarbonate concentration with arterial blood gas analysis if available.
- Pediatric Dose: 1 mEq/kg IV/IO slow bolus; 4.2% concentration recommended for use in infants less than 1 month of age. Dosing is best guided by calculated base deficits or bicarbonate concentration with arterial blood gas analysis, if available.
- Contraindications: Metabolic and respiratory alkalosis, hypochloremia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypercarbic acidosis, hypernatremia, severe pulmonary edema.
- Side Effects: Hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypernatremia, metabolic alkalosis, edema, seizures, tetany, exacerbation of CHF, tissue hypoxia, intracellular acidosis.
- Precautions: CHF, renal disease, cirrhosis, hypernatremia, hypervolemia, toxemia, concurrent corticosteroid therapy. Not recommended for routine use in cardiac arrest because adequate ventilation and CPR are the major “buffer agents” in this case. Incompatible with many drugs; flush the line before and after administration.
Vasopressin (Pitressin)
- Class: Vasopressor, hormone.
- Indication: Cardiac arrest: an alternative to epinephrine in shockrefractory VF and pulseless VT, PEA, and asystole. Vasodilatory shock/septic shock.
- Adult Dose:Cardiac arrest: 40 units IV/IO single dose to replace first or second dose of epinephrine as an alternative. Vasodilatory shock: 0.01–0.04 units/min continuous IV infusion.
- Pediatric Dose:Cardiac arrest: 0.4–1 unit/kg IV/IO, max 40 units. Vasodilatory shock: 0.0002–0.002 unit/kg/min continuous IV infusion.
- Contraindications: Hypersensitivity.
- Side Effects: Bradycardia, HTN, angina, MI, arrhythmias, dizziness, headache, nausea and vomiting, abdominal cramps, diaphoresis, bronchoconstriction, anaphylaxis.
- Precautions:Coronary artery disease (may precipitate angina or MI), CHF, hepatic or renal impairment; seizure disorders, asthma, vascular disease.
Verapamil (Calan, Isoptin)
- Class: Calcium channel blocker, antiarrhythmic, class IV, antihypertensive.
- Indications: PSVT (with narrow QRS and adequate BP) refractory to adenosine; rapid ventricular rates in A-fib, A-flutter, and MAT.
- Adult Dose: 2.5–5.0 mg IV over 2 min; may give second dose, if needed, of 5–10 mg IV in 15–30 min, max dose 20 mg. An alternative second dose is 5 mg IV every 15 min, max dose 30 mg.
- Contraindications: A-fib with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, widecomplex tachycardia of uncertain origin, second- or third-degree AV block (unless a functioning pacemaker is in place), sick sinus syndrome, hypotension, severe CHF, cardiogenic shock, concurrent IV beta blocker, VT.
- Side Effects: Hypotension, exacerbation of CHF with left ventricular dysfunction, bradycardia, AV block, constipation, peripheral edema, headache, dizziness, fatigue, paralytic ileus, hepatotoxicity.
- Precautions: Concurrent oral beta blockers, CHF, impaired hepatic or renal function, myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction; may decrease myocardial contractility. In geriatric patients administer slowly over 3 min.
Common Medication Formulas
IV Fluid Drip Rate Table (gtt/min)
Rate: (mL/hr) 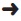 | TKO | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 250 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 gtt/mL set | 5 | 8 | 13 | 17 | 21 | 25 | 29 | 33 | 42 |
| 12 gtt/mL set | 6 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 50 |
| 15 gtt/mL set | 8 | 13 | 19 | 25 | 31 | 37 | 44 | 50 | 62 |
| 20 gtt/mL set | 10 | 17 | 25 | 33 | 42 | 50 | 58 | 67 | 83 |
| 60 gtt/mL set | 30 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 250 |
Universal Formula-Figure Out Drip Rates and Drug Amounts
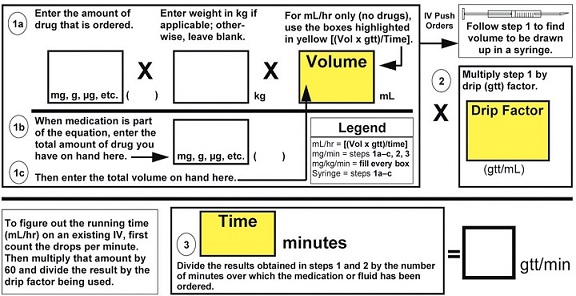
Note: The abbreviation mcg (microgram) means the same as μg (used in the above formula); mcg is used most commonly to prevent medication errors.
