Anatomy and Metabolism of Bone
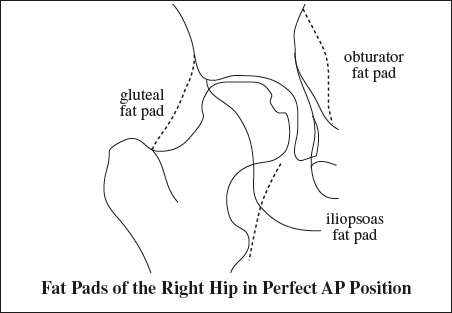
- Iliopsoas bursa
Location: surrounds iliopsoas tendon- largest bursa in body
- communication with hip in 15%
- Greater trochanteric bursae
- Trochanteric bursa
Location: covers posterior facet, beneath gluteus maximus muscle + iliotibial tract - Subgluteus medius bursa
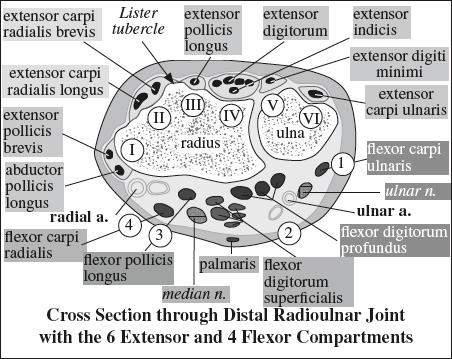
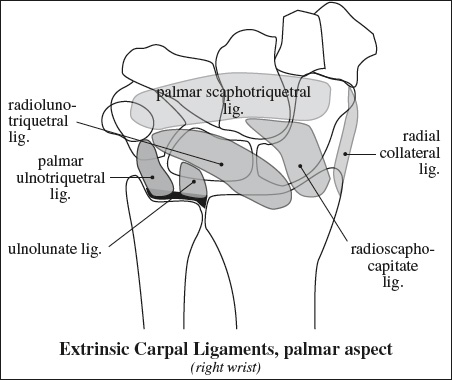

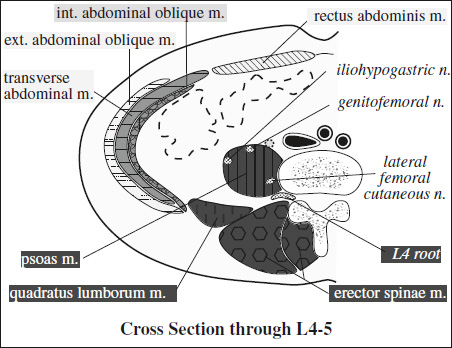
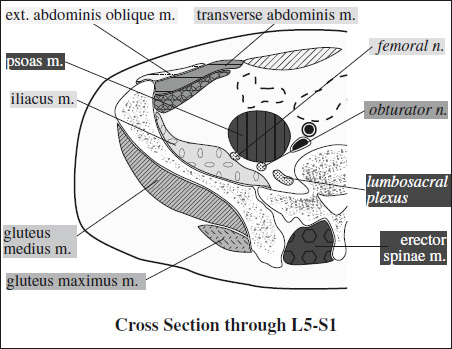


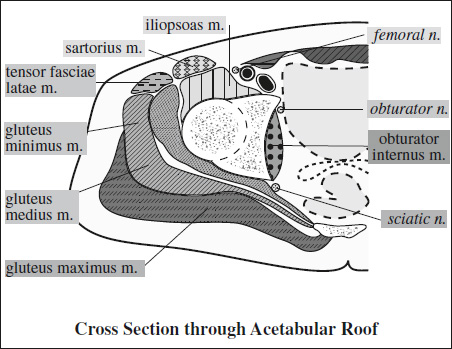


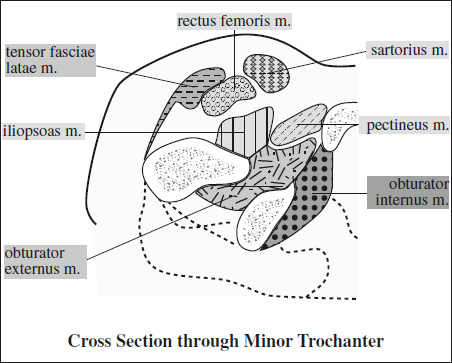
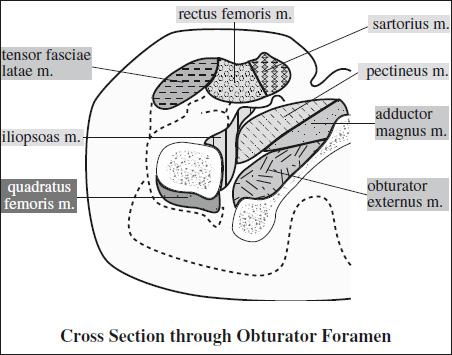
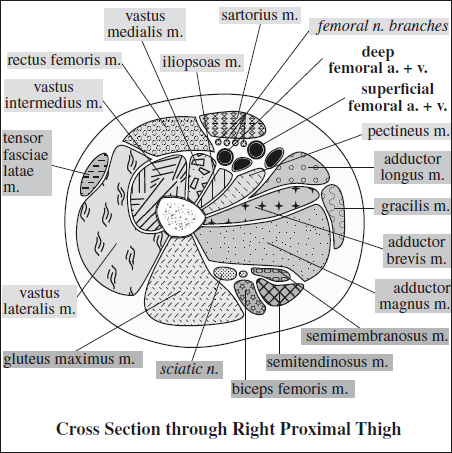
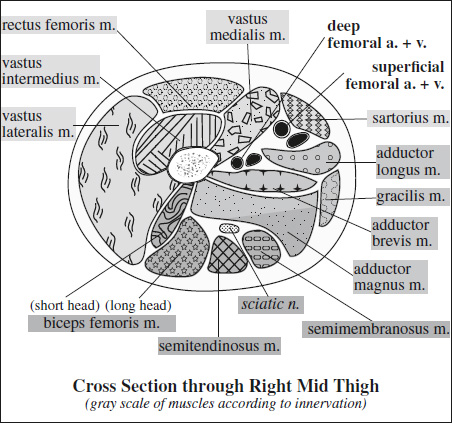

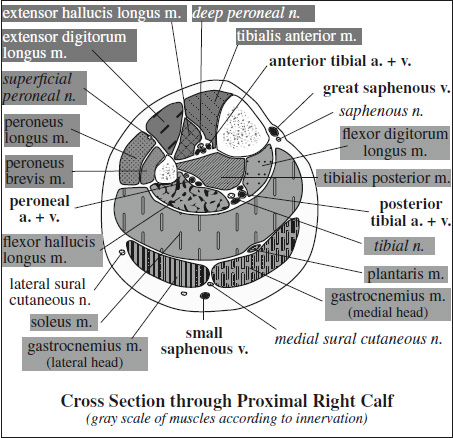


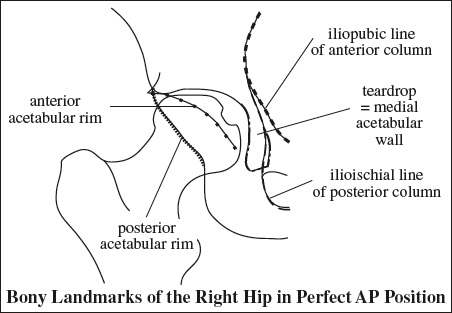
Innervation of Pelvis & Thigh Muscles
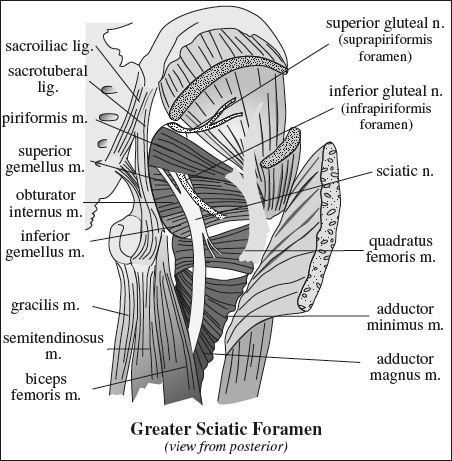
Supplying Nerve Muscles Innervated Sacral plexus piriformis, inferior gemellus, superior gemellus, obturator internus, quadratus femoris Femoral nerve iliopsoas, pectineus, quadriceps (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius), sartorius Obturator nerve adductor brevis, adductor longus, anterior head of adductor magnus (also supplied by sciatic nerve), obturator externus, gracilis Sciatic nerve › tibial division long head of biceps femoris, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, adductor magnus › peroneal division short head of biceps femoris Superior gluteal n. gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fasciae latae Inferior gluteal n. gluteus maximus 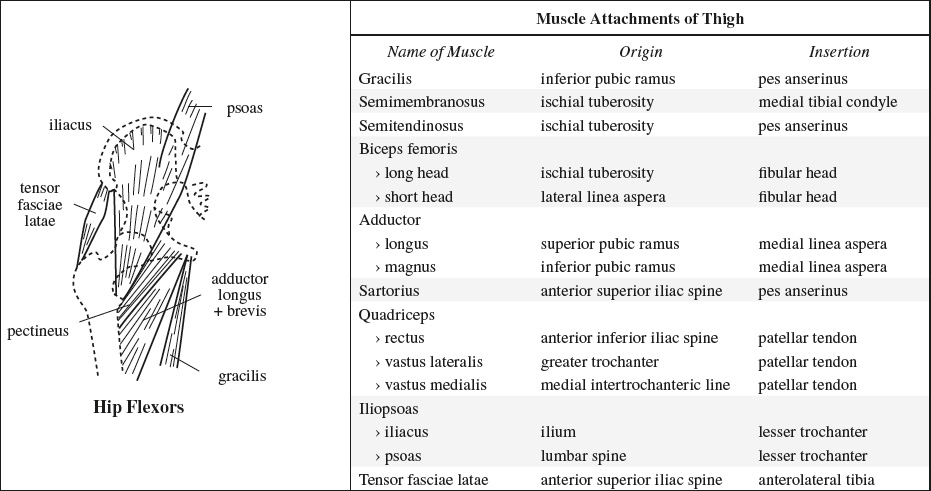
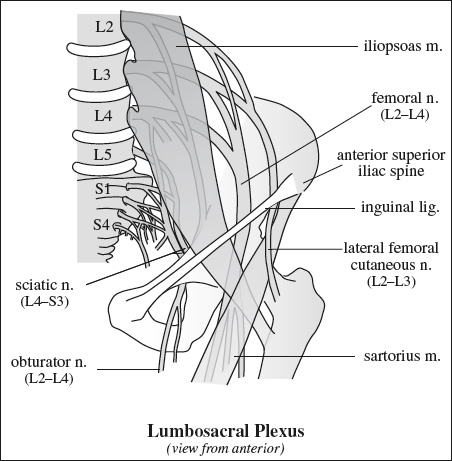
Location: covers superior portion of lateral facet, beneath lateral portion of gluteus medius m. - Subgluteus minimus bursa
Location: covers superomedial portion of anterior facet, beneath + medial to gluteus minimus m.
- Trochanteric bursa
- Ischiotrochanteric bursa
- Obturator externus bursa
Location: posteroinferior communication of hip joint capsule - Ischial bursa (= weaver's bottom)
- Paralabral cyst
Function: primary stabilizing structure of anterolateral knee together with lateral capsular ligaments
Consists of:
- Distal extension of superficial + deep layers of fascia lata
- Tensor fasciae latae
- Gluteus maximus m.
- Gluteus medius m.
Insertion:
- supracondylar tubercle of lateral femoral condyle
- intermuscular septum of distal femur (deep component)
- Gerdy tubercle (main site of superficial component) = anterolateral tubercle of tibia
[Pierre Nicolas Gerdy (1797–1856), surgeon in Paris] - patella + patellar ligament
- Most frequently injured muscle!
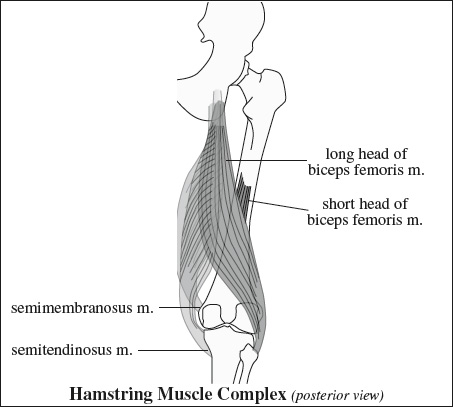
- medial hamstring
Function: flexion + medial rotation of knee joint as thigh is swung forward and hip extended- Semimembranosus m.
Origin: superolateral aspect of ischial tuberosity (beneath semitendinosus m.)
Course: medial + anterior to other hamstring muscles with connections to tendons of adductor magnus m. + long head of biceps m.
Insertion: via 5 tendinous arms on- medial tibial condyle (anterior1 + direct2 + inferior3 arm) deep to tibial collateral ligament
- posterior oblique lig. (capsular4 arm)
- arcuate lig. (oblique popliteal lig.5)
Innervation: single branch off tibial division of sciatic n. - Semitendinosus m.
Origin: inferomedial impression of upper portion of ischial tuberosity conjoined with long head of biceps femoris m.
Insertion: Gerdy tubercle conjoined with gracilis m.
Innervation: tibial n. (2 separate branches)
- Semimembranosus m.
- lateral hamstring
Function: flexion + lateral rotation of knee joint- Biceps femoris m.
Insertion: head of fibula, lateral condyle of tibia, fascia of leg- long head
Origin: medial facet of ischial tuberosity
Innervation: tibial portion of sciatic n. - short head (does not cross 2 joints, may be absent)
Origin: lateral linea aspera + lateral supracondylar line + intermuscular septum
Used as: landmark to distinguish between proximal and distal hamstring injuries
Innervation: peroneal division of sciatic n.
- long head
- Biceps femoris m.
