Function: mixed nerve responsible for motor innervation of muscles of facial expression + taste of anterior ⅔ of tongue + parasympathetic innervation of lacrimal and submandibular glands
- Lacrimation (via greater superficial petrosal nerve)
- Stapedius reflex: sound damping
- Taste of anterior ⅔ of tongue (via chorda tympani nerve to lingual nerve)
- Facial expression (platysma + orbicularis oculi)
- Secretion of lacrimal + submandibular + sublingual glands (via nervus intermedius)
Nuclei: one motor nucleus + two sensory nuclei located within ventrolateral pons
- Motor nucleus: ventrolateral deep in reticular formation of the caudal part of the pons
Innervation to: stapedius m., stylohyoid m., posterior belly of digastric m., occipitalis m., buccinator, muscles of facial expression, platysma - Nucleus solitarius (sensory nucleus)
- nervus intermedius: sensation from anterior ⅔ of tongue, skin on + adjacent to ear
- Superior salivatory nucleus (parasympathetic secretomotor innervation)
- greater petrosal n.: secretion of lacrimal glands, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses
- chorda tympani: submandibular + sublingual glands
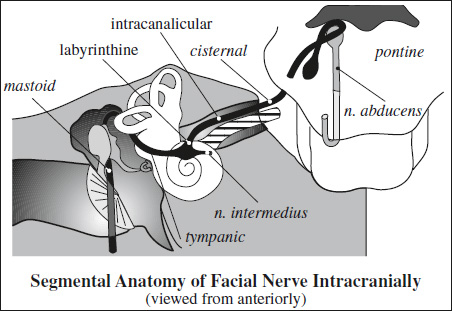
Exit from brainstem: 2 separate nerve roots traversing cerebellopontine angle cistern
- motor root anteriorly
- sensory root posteriorly
Segments: circuitous course
- intracranial segment from brainstem to porus acusticus internus:
- pontine segment:
- motor root fibers of facial n. run dorsomedially towards 4th ventricle
- curve anterolaterally to hook around upper pole of abducens nucleus (= geniculum)
- form facial colliculus (= elevation in floor of 4th ventricle)
- nerve descends anterolaterally through reticular formation + continues lateral from corticospinal tract
- cisternal segment:
- facial n. exits from lateral aspect of brainstem at pontomedullary junction
- courses anterolaterally in cerebellopontine angle cistern to internal auditory canal (IAC) above crista falciformis
- pontine segment:
- intracanalicular (IAC) segment
- labyrinthine segment emerges from anterosuperior aspect of IAC
- 3–4 mm short segment of facial n. traveling anterolaterally within its own bony canal (= fallopian canal) and curving anteromedially over top of cochlea
- terminates in anteromedial genu (geniculate ganglion) where greater superficial petrosal n. branches pass anteromedially to carry parasympathetic fibers to lacrimal gland
- tympanic segment
= 12 mm long segment from geniculate ganglion to posterior genu underneath lateral semicircular canal- horizontal segment: facial n. at first (anterior) genu makes a 130° turn posteriorly + horizontally along medial wall of mesotympanum lateral to vestibule between lateral semicircular canal (above) and oval window (below) to reach sinus tympani
- “snake eyes” on COR CT at level of cochlea corresponding to proximal portion of tympanic + distal portion of labyrinthine segments
- inferior to lateral semicircular canal + superolateral to oval window on COR CT at level of oval window
- anterior genu superomedial to cochlear promontory
- “snake eyes” on COR CT at level of cochlea corresponding to proximal portion of tympanic + distal portion of labyrinthine segments
- pyramidal segment: at sinus tympani facial n. turns gently posteroinferiorly to form second / posterior genu in pyramidal eminence; gives off the nerve for the stapedius muscle
- horizontal segment: facial n. at first (anterior) genu makes a 130° turn posteriorly + horizontally along medial wall of mesotympanum lateral to vestibule between lateral semicircular canal (above) and oval window (below) to reach sinus tympani
- mastoid segment (longest segment with 15–20 mm)
facial n. assumes a more vertical position + descends just behind the posterior wall of the tympanic cavity from posterior genu through anterior mastoid (= medial wall of aditus ad antrum) + gives off chorda tympani just prior to exit from skull base through stylomastoid foramen - parotid / extracranial segment
facial n. travels forward between superficial + deep lobes of parotid gland lateral to styloid process + external carotid a. + retromandibular v.
Branches:
- Greater superficial petrosal nerve (parasympathetic + motor fibers) arises from geniculate ganglion, runs anteromedially, and exits at the facial hiatus on the anterior surface of the temporal bone + passes under Meckel cave near foramen lacerum
- forms vidian nerve after receiving sympathetic fibers from deep petrosal nerve, which surrounds the internal carotid artery
- Stapedial nerve (motor fibers) arises from proximal descending facial n.
- Chorda tympani (sensory + parasympathetic fibers) leaves facial n. about 5–6 mm above stylomastoid foramen from the lateral aspect of the mastoid segment of the facial nerve
- ascends in subtle curvature superoanteriorly in a bony canal (= canaliculus chorda tympani)
- perforates posterior wall of tympanic cavity
- proceeds anteriorly within tympanic cavity and crosses medial to handle of malleolus underneath mucosa of tympanic cavity
- exits temporal bone through a minute canal (= anterior canaliculus) near petrotympanic fissure
- joins lingual nerve (= branch of V2) containing sensory taste fibers from anterior ⅔ of tongue + secretomotor fibers for submandibular + sublingual glands