Differential Diagnosis of Skull and Spine Disorders
Function:
- to restore anatomic alignment in fractures (fracture reduction)
- to stabilize degenerative disease
- to correct congenital deformities (scoliosis)
- to replace diseased / abnormal vertebrae (infection, tumor)
using paired / unpaired rods attached with
- Sublaminar wiring
= passing a wire around lamina + rod - Interspinous wiring
= passing a wire through a hole in the spinous process; a Drummond button prevents the wire from pulling through the bone - Subpars wiring
= passing a wire around the pars interarticularis - Laminar / sublaminar hooks
- used on rods for compression / distraction forces to be applied to pedicles / laminae
- upgoing hook curves under lamina
- downgoing hook curves over lamina
- Pedicle / transpedical screws
- connected by plates / rods spanning single / multiple segments
- crossbars (for additional strength)
- Rods
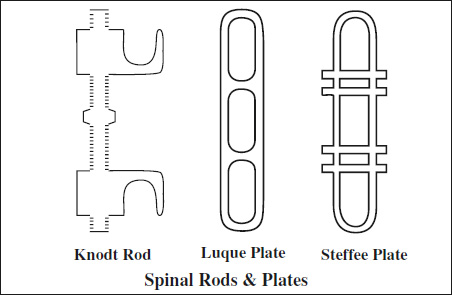
- Luque rod = straight / L-shaped smooth rod 6–8 mm in diameter
- O-ring fixator, rhomboid-shaped bar, Luque rectangle, segmental rectangle = preshaped loop to form a flat rectangle
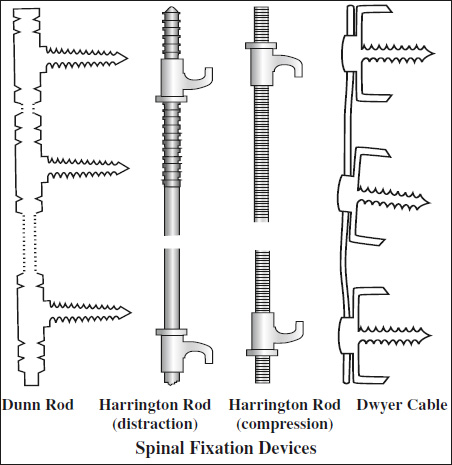
- Harrington distraction rod
- Harrington compression rod
- Knodt rod = threaded distraction rod with a central fixed nut (turnbuckle) and opposing thread pattern
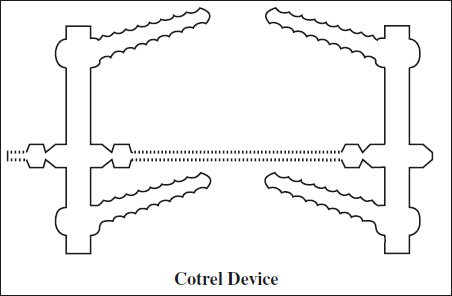
- Cotrel-Dubousset rods = a pair of rods with a serrated surface connected by a cross-link with ≥4 laminar hooks / pedicle screws
- Plates
- Roy-Camille plate
= simple straight plates with round holes - Luque plate
= long oval holes with clips encircling the plate - Steffee plate = straight plates with long slots
- Roy-Camille plate
- Translaminar / facet screw
= cancellous screws for single level fusion when posterior elements are left intact - Percutaneous pinning
= (hollow) interference screws placed across disk level
- Dwyer device
= screws threaded into vertebral body over staples embedded into vertebral body connected by braided titanium wire; placed on convex side of spine - Zielke device
= modified Dwyer system replacing cable with solid rod - Kaneda device
= 2 curved vertebral plates with staples attached to vertebral bodies with screws, plates connected by 2 threaded rods attached to screw heads - Dunn device
(similar to Kaneda device, discontinued)
Reconstruction after Diskectomy / Corpectomy
- Auto- / allograft bone block
- Allograft strut (eg, fibula, humerus)
- Interbody spacers: titanium / radiolucent material (eg, polyetheretherketone)
- ramp
- bone graft cage: open structure filled with bone graft material
- 2 radiopaque markers for assessment of spacer position: posterior marker should be ≥2 mm anterior to posterior vertebral body margin
- Vertebral body replacement device
- expandable hollow cylinder packed with bone graft / cement (Synex cage)
- mesh (Moss cage)
- stackable carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer cages held together by metallic rods
- Disk replacement device
Indication: pain from disk degeneration only
Contraindication: facet joint degeneration, <4 mm residual disk height, significant endplate degeneration
Complications of Spinal Instrumentation
- Pseudarthrosis
- corticated linear lucency across graft material
- focally increased signal on T2WI
- increased tracer activity on bone scintigraphy
- Malpositioned pedicle screws (2.4% complication rate)
- nerve root irritation (medial angulation of screw)
- disruption of cortical bone
- medial deviation
- lateral deviation
- penetration of anterior cortex (exception are sacral screws which may be anchored in anterior cortex of the sacrum for additional stability)
- lucent rim around screw threads ← loosening
- Malpositioned anterior cervical plate
- penetration into adjacent disk space / foramen transversarium / spinal cord / nerve roots
- Herniation of graft material
- anteriorly / posteriorly displaced graft
- Postoperative hematoma
- Surgery at wrong level
- Accelerated degenerative changes / ligamentous instability / fracture at adjacent levels
- Superficial / deep infection (diskitis, osteomyelitis)
- Arachnoiditis
Assessment of Bridging Spinal Fusion
Time from surgery: 6–9 months
- <3° of intersegmental positional change on lateral flexion + extension views
- visible bone formation in / about graft material
- minimal loss of disk height
- absence of lucency around implant
- absence of fracture of device / graft / vertebra