Differential Diagnosis of Musculoskeletal Disorders
mnemonic: ABCDE'S
- Alignment
- Bone mineralization
- Cartilage loss
- Distribution
- Erosion
- Soft tissues
Prevalence of arthritis: 15% of population in USA
Conventional x-ray:
- narrowing of radiologic joint space:
- uniform = inflammatory arthritis
- nonuniform = degenerative arthritis
- evidence of disease on both sides of joint:
- osteopenia
- subchondral sclerosis
- erosion
- subchondral cyst formation
- malalignment
- joint effusion
- joint bodies
NUC:
- increase in regional blood flow (active disease)
- distribution of disease
MR:
- bone marrow edema = predictor of erosions
- Gd-DTPA enhancement of synovium (active disease)
- radiographically occult extraarticular inflammation = tenosynovitis + enthesitis
- irregularity + narrowing of articular cartilage
- SEPTIC ARTHRITIS
- Tuberculous
- Pyogenic
- Lyme arthritis
- Fungal arthritis: Candida, Coccidioides immitis, Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Sporothrix schenckii, Cryptococcus neoformans, Aspergillus fumigatus
N.B.: Tuberculous + fungal arthritis show Phemister triad- prominent osteoporosis,
- slower rate of destruction, and
- less joint narrowing than a pyogenic infection
- COLLAGEN / COLLAGEN-LIKE DISEASE
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Rheumatic fever
- Sarcoidosis
- BIOCHEMICAL ARTHRITIS
- Gout
- Chondrocalcinosis
- Ochronosis
- Hemophilic arthritis
- DEGENERATIVE JOINT DISEASE = Osteoarthritis
- TRAUMATIC
- Secondary osteoarthritis
- Neurotrophic arthritis
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis
- ENTEROPATHIC ARTHROPATHY
- INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
- Ulcerative colitis (in 10–20%)
- Crohn disease (in 5%): peripheral arthritis increases with colonic disease
- Whipple disease (in 60–90% transient intermittent polyarthritis: sacroiliitis, spondylitis)
- Resection of diseased bowel is associated with regression of arthritic symptomatology!
- INFECTIOUS BOWEL DISEASE
Infectious agents: Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia - after intestinal bypass surgery
- INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
Spondyloarthritis with Positive HLA-B 27 Histocompatibility Complex
- Ankylosing spondylitis 95%
- Reiter disease 80%
- Arthropathy of inflammatory bowel disease 75%
- Psoriatic spondylitis 70%
- Normal population 10%
Destructive Monoarthritis
- Any destructive monoarthritis should be regarded as infection until proved otherwise!
- Septic arthritis
- Monoarticular presentation of a systemic arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Amyloidosis
- Seronegative arthritis
- Joint tumor
- PVNS
- Synovial chondromatosis
- Articular hemangioma
Nonseptic Monoarthritis
- Gout
- Milwaukee shoulder
- Rapidly destructive articular disease
- Amyloid arthropathy
- Hemophilic arthropathy
- Primary synovial osteochondromatosis
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis
- Neuropathic arthropathy
- Foreign-body synovitis
Arthritis without Demineralization
- Gout
- Neuropathic arthropathy
- Psoriasis
- Reiter disease
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis
mnemonic: PONGS- Psoriatic arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Neuropathic joint
- Gout
- Sarcoidosis
Arthritis with Demineralization
mnemonic: HORSE
- Hemophilia
- Osteomyelitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter disease
- Scleroderma
- Erythematosus, systemic lupus
Deforming Nonerosive Arthropathy
- Collagen-vascular disease, especially SLE
- Rheumatoid arthritis (rare)
- Rheumatic fever (Jaccoud arthritis) (rare)
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reiter syndrome
- Infectious arthritis
mnemonic: COME CHAT
- Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate arthropathy
- Ochronosis
- Marfan syndrome
- Epiphyseal dysplasia
- Charcot joint = neuroarthropathy
- Hemophilic arthropathy
- Acromegaly
- Trauma
Synovial Disease with Decreased Signal Intensity
= blooming” artifact of low SI on gradient-echo pulse sequences ← magnetic susceptibility artifact of hemosiderin
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Hemophiliac arthropathy
- Synovial hemangioma
mnemonic: WHIP A DOG
- Wilson disease
- Hemochromatosis, Hemophilia, Hypothyroidism, 1° Hyperparathyroidism (15%), Hypophosphatasia, Familial Hypomagnesemia
- Idiopathic (aging)
- Pseudogout (CPPD)
- Arthritis (rheumatoid, postinfectious, traumatic, degenerative), Amyloidosis, Acromegaly
- Diabetes mellitus
- Ochronosis
- Gout
mnemonic: 3 C's
|
= SYNOVIAL CYST = SUBARTICULAR PSEUDOCYST
= NECROTIC PSEUDOCYST = GEODES
Etiology: bone necrosis allows pressure-induced intrusion of synovial fluid into subchondral bone; in conditions with synovial inflammation
Cause by mnemonic: COORS
- CPPD
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteonecrosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Synovial tumor
- size of cyst usually 2–35 mm
- may be large + expansile (especially in CPPD)
DDx:
- Giant cell tumor
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis
- Metastasis
- Intraosseous ganglion
- Brown tumor of hemophilia
- Calcinosis of chronic renal failure = uremic tumoral acalcinosis = secondary tumoral calcinosis = tumoral calcification
- Tumoral calcinosis
= cyst located in the vicinity of a synovial joint
- Ganglion
= mucin-containing cyst arising from tendon sheath / joint capsule / bursa / subchondral bone lined by flat spindle-shaped cells - Synovial cyst
= cyst continuous with joint capsule lined by synovial cells (term is used by some synonymously with ganglion) - Meniscal cyst
= associated with meniscal tear, in >90% of a tear with horizontal component - Bursa
= synovial lining, forms in area of friction, may communicate with joint
- Osteochondrosis dissecans
- Synovial osteochondromatosis
- Chip fracture from trauma
- Severe degenerative joint disease
- Neuropathic arthropathy
Rice Bodies
= subset of loose bodies as a nonspecific response to chronic synovial inflammation resembling polished rice
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Tuberculous arthritis
Pathogenesis:
- microinfarction of synovium / detachment of hypertrophied synovium → sloughed synovium falls into joint space → coated with fibrinogen
- precipitate of fibrin + fibronectin / core of mononuclear cells, blood cells and amorphous material
MRI:
- well-defined nodules of intermediate SI on T1WI + relatively low intensity on T2WI
DDx:
- Synovial osteochondromatosis (monoarticular, large joint, hyperintense cartilage components on T2WI)
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis (monoarticular, large joint, hemosiderin deposition)
- PROLIFERATIVE SYNOVIAL PROCESS
- Lipoma arborescens
- Synovial osteochondromatosis
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- INFECTIOUS GRANULOMATOUS DISEASE
- Tuberculous arthritis
- Coccidioidomycosis arthritis
- DEPOSITION DISEASE
- Gout
- Amyloid arthropathy
- VASCULAR MALFORMATION
- Synovial hemangioma
- Arteriovenous malformation
- MALIGNANCY
- Synovial chondrosarcoma
- Synovial sarcoma
- Synovial metastasis: primary lung cancer
- Peculiar joint anatomy
- Cyclops lesion
Intraarticular Process with Cortical Erosion
- Pigmented villonodular synovitis
- Synovial osteochondromatosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Synovial hemangioma
- Lipoma arborescens
Erosions of DIP Joints
- Inflammatory osteoarthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Gout
- Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Frostbite
- Septic arthritis
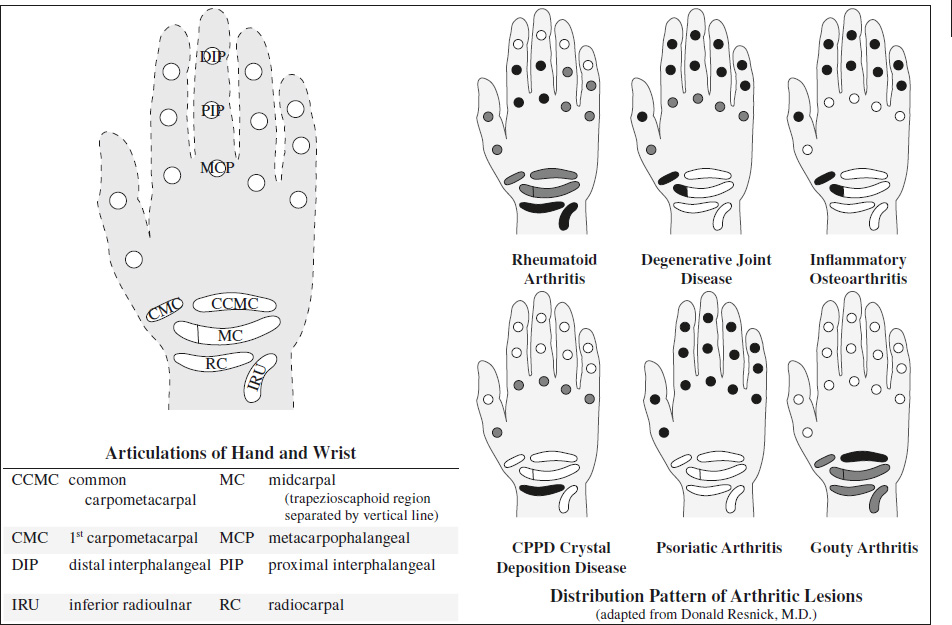
Articular Disorders of Hand and Wrist
- Osteoarthritis = degenerative joint disease = abnormal stress with minor + major traumatic episodes
Target areas: DIP, PIP, 1st CMC, trapezioscaphoid; bilateral symmetric / asymmetric- joint space narrowing
- subchondral eburnation
- marginal osteophytes + small ossicles
- radial subluxation of 1st metacarpal base
- Radiocarpal joint normal unless history of trauma
- Erosive osteoarthritis = inflammatory osteoarthritis
Age: predominantly middle-aged / postmenopausal women- acute inflammatory episodes
Target areas: DIP, PIP, 1st CMC, trapezioscaphoid; bilateral symmetric / asymmetric- central erosions combined with osteophytes = subchondral “gull wing” erosions
- joint space narrowing + sclerosis
- rare ankylosis
- Psoriatic arthritis
= rheumatoid variant / seronegative spondyloarthropathy; peripheral manifestation in monoarthritis / asymmetric oligoarthritis / symmetric polyarthritis
Target areas: all hand + wrist joints (commonly distal); bi- / unilateral asymmetric polyarticular changes- “mouse ears” marginal erosions
- intraarticular osseous excrescences
- new bone formation ± fusion
- osteoporosis may be absent
- Rheumatoid arthritis
= synovial proliferative granulation tissue = pannus- Target areas: PIP (early in 3rd), MCP (earliest changes in 2nd + 3rd), all wrist joints (early in RC, IRU), ulnar styloid; both hands in relative symmetric fashion
- fusiform soft-tissue swelling
- regional periarticular osteoporosis
- diffuse loss of joint space
- marginal + central poorly defined erosions
- joint deformities
- Gouty arthritis
- monosodium urate crystals in synovial fluid
- asymptomatic periods from months to years
Target areas: commonly CCMC + all hand joints- development of chronic tophaceous gout = lobulated soft-tissue masses
- well-defined eccentric erosions with overhanging edge (often periarticular) + sclerotic margins
- preservation of joint spaces
- absence of osteoporosis
- most extensive changes in common carpometacarpal compartment:
- scalloped erosions of bases of ulnar metacarpals
- Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease = CPPD
- Target areas: MCP (2nd, 3rd), radiocarpal; bilateral symmetric / asymmetric changes
- chondrocalcinosis + periarticular calcifications:
- calcification of triangular fibrocartilage
- “degenerative changes” in unusual locations:
- narrowing ± obliteration of space between distal radius and scaphoid ± fragmentation of surfaces
- scapholunate separation
- destruction of trapezioscaphoid space
- no erosions
- + large osteophytes = hemochromatosis
- SLE
- = myositis, symmetric polyarthritis, deforming nonerosive arthropathy, osteonecrosis
- Target areas: PIP, MCP
- reversible deformities
- Scleroderma = progressive systemic sclerosis (PSS)
- Target areas: DIP, PIP, 1st CMC
- tuft resorption
- soft-tissue calcifications
Arthritis Involving Distal Interphalangeal Joints
mnemonic: “POEM”
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Erosive osteoarthritis
- Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis
Ankylosis of Interphalangeal Joints
mnemonic: “S - Lesions”
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Erosive osteoarthritis
- Still disease
Arthritis of Interphalangeal Joint of Great Toe
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reiter disease
- Gout
- Degenerative joint disease
- Approach to Arthritis
- Signs of Arthritis
- Classification of Arthritides
- Monoarthritis
- Arthritis without Demineralization
- Arthritis with Demineralization
- Deforming Nonerosive Arthropathy
- Arthritis with Periostitis
- Premature Osteoarthritis
- Synovial Disease with Decreased Signal Intensity
- Chondrocalcinosis
- Subchondral Cyst
- Periarticular Calcified Mass
- Periarticular Cyst
- Loose Intraarticular Bodies
- Intraarticular Mass
- Intraarticular Process with Cortical Erosion
- Articular Disorders of Hand and Wrist
- Arthritis Involving Distal Interphalangeal Joints
- Ankylosis of Interphalangeal Joints
- Arthritis of Interphalangeal Joint of Great Toe