= PANTOTHENATE KINASE-ASSOCIATED NEURODEGENERATION
= rare familial neurodegenerative metabolic disorder with abnormal iron retention in basal ganglia
Cause: mutation of PANK2 gene encoding pantothenate kinase → neurodegeneration with iron accumulation
Age: 2nd decade of life
Histo: hyperpigmentation and symmetrical destruction of globus pallidus + substantia nigra
Types:
- classic early-onset rapidly progressive disease
- atypical late-onset slowly progressive disease
- progressive gait impairment + rigidity of limbs
- slowing of voluntary movements, dysarthria
- choreoathetotic movement disorder, progressive dementia
CT:
- low- (= tissue destruction) / high-density (= dystrophic calcification) foci in globus pallidus
MR:
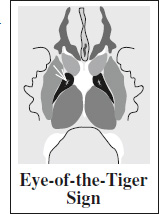
- “eye-of-the-tiger” sign = high-signal-intensity center surrounded by the more typical hypointensity in globus pallidus:
- initially bilateral hypointense globus pallidus on T2WI (= iron accumulation)
- later central hyperintense foci on T2WI (= tissue destruction + gliosis)