Differential Diagnosis of Nervous System Disorders
Classification of Primary CNS Tumors
Incidence: 9% of all primary neoplasms (5th most common primary neoplasm); 5–10÷100,000 population per year; account for 1.2% of autopsied deaths
- TUMORS OF BRAIN AND MENINGES
- Gliomas
ASTROCYTOMA (50%)- Astrocytoma (astrocytoma grades I–II)
- Glioblastoma (astrocytoma grades III–IV)
OLIGODENDROGLIOMA
PARAGLIOMA- Ependymoma
- Choroid plexus papilloma
GANGLIOGLIOMA
MEDULLOBLASTOMA - Pineal tumor
- Germinoma
- Teratoma
- Pineocytoma
- Pineoblastoma
- Pituitary tumor
- Pituitary adenoma
- Pituitary carcinoma
- Meningioma
- Nerve sheath tumor
- Schwannoma
- Neurofibroma
- Miscellaneous
- Sarcoma
- Lipoma
- Hemangioblastoma
- Gliomas
- TUMORS OF EMBRYONAL REMNANTS
- Craniopharyngioma
- Colloid cyst
- Teratoid tumor
- Epidermoid (0.2–1.8%)
- Dermoid
- Teratoma
CNS Tumors Presenting at Birth
- Hypothalamic astrocytoma
- Choroid plexus papilloma / carcinoma
- Teratoma
- Primitive neuroectodermal tumor
- Medulloblastoma
- Ependymoma
- Craniopharyngioma
CNS Tumors in Pediatric Age Group
Prevalence:
2.4÷100,000 (<15 years of age); 2nd most common pediatric tumor (after leukemia); 15% of all pediatric neoplasms; 15–20% of all primary brain tumors; M >F
- increased intracranial pressure
- increasing head size
- SUPRATENTORIAL (50%)
- Age: first 2–3 years of life
- Covering of brain: dural sarcoma, schwannoma, meningioma (3%)
- Cerebral hemisphere: astrocytoma (37%), oligodendroglioma
- Corpus callosum : astrocytoma
- 3rd ventricle: colloid cyst, ependymoma
- Lateral ventricle: ependymoma (5%), choroid plexus papilloma (12%)
- Optic chiasm: craniopharyngioma (12%), optic nerve glioma (13%), teratoma, pituitary adenoma
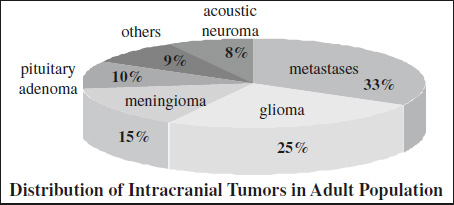
Incidence of Brain Tumors
All Age Groups Pediatric Age Group Glioma 34% Astrocytoma 50% Meningioma 17% Medulloblastoma 15% Metastasis 12% Ependymoma 10% Pituitary adenoma 6% Craniopharyngioma 6% Neurinoma 4% Choroid plexus papilloma 2% Sarcoma 3% Granuloma 3% Craniopharyngioma 2% Hemangioblastoma 2% Differences of Some Pediatric CNS Tumors
PNET Ependymoma Astrocytoma CT hyper iso hypo T2WI intermed. intermed. increased Enhancement moderate minimal nodule Calcification 10–15% 40–50% <10% Cyst formation rare common typical CSF seeding 15–40% rare rare Foraminal spread no yes no - Hypothalamus: glioma (8%), hamartoma
- Pineal region: germinoma, pinealoma, teratoma (8%)
- INFRATENTORIAL (50%)
- Age: 4–11 years
- Cerebellum: astrocytoma (31–33%), PNET / medulloblastoma (26–31%)
- Brainstem: glioma (16–21%)
- 4th ventricle: ependymoma (6–14%), choroid plexus papilloma
mnemonic: “BE MACHO”- Brainstem glioma
- Ependymoma
- Medulloblastoma
- AVM
- Cystic astrocytoma
- Hemangioblastoma
- Other
Supratentorial Tumor with Mural Nodule
- Extraventricular ependymoma
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
- Hemispheric pilocytic astrocytoma
- Ganglioglioma
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNET)
Supratentorial Midline Tumors
- Optic + hypothalamic glioma (39%)
- Craniopharyngioma (20%)
- Astrocytoma (9%)
- Pineoblastoma (9%)
- Germinoma (6%)
- Lipoma (6%)
- Teratoma (3.5%)
- Pituitary adenoma (3.5%)
- Meningioma (2%)
- Choroid plexus papilloma (2%)
Classification by Histology
- Astrocytic tumors (33.5%)
- “Primitive” neuroectodermal tumor = PNET (21%)
- Medulloblastoma (16%)
- Ependymoblastoma (2.5%)
- PNET of cerebral hemisphere (2.5%)
- Mixed gliomas (16%)
- Malformative tumors (11.5%)
- Craniopharyngioma (5.5%)
- Lipoma (4.5%)
- Dermoid cyst (1%)
- Epidermal cyst (0.5%)
- Choroid plexus tumors (4%)
- Ependymal tumors (4%)
- Tumors of meningeal tissues (3.5%)
- Meningioma (3%)
- Meningeal sarcoma (0.5%)
- Germ cell tumors (2.5%)
- Germinoma (1.5%)
- Teratomatous tumor (1%)
- Neuronal tumors
- Gangliocytoma (1.5%)
- Tumors of neuroendocrine origin
- Pituitary adenoma (1%)
- Oligodendroglial tumors (0.5%)
- Tumors of blood vessel
- Hemangioma (1%)
= peripherally located cortical neoplasms serving as a seizure focus
- Ganglioglioma
- Desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma
- Gangliocytoma
- Dysplastic cerebellar gangliocytoma
- Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor
- METASTASES FROM PRIMARY CNS TUMOR
- via commissural pathways: corpus callosum, internal capsule, massa intermedia
- via CSF: ventricles / subarachnoid cisterns
- satellite metastases
- MULTICENTRIC CNS TUMOR
- true multicentric gliomas (4%)
- concurrent tumors of different histology (coincidental)
- MULTICENTRIC MENINGIOMAS (3%) without neurofibromatosis
- MULTICENTRIC PRIMARY CNS LYMPHOMA
- PHAKOMATOSES
- Generalized neurofibromatosis:
meningiomatosis, bilateral acoustic neuromas, bilateral optic nerve gliomas, cerebral gliomas, choroid plexus papillomas, multiple spine tumors, AVMs - Tuberous sclerosis:
subependymal tubers, intraventricular gliomas (giant cell astrocytoma), ependymomas - Von Hippel-Lindau disease:
retinal angiomatosis, hemangioblastomas, congenital cysts of pancreas + liver, benign renal tumors, cardiac rhabdomyomas
- Generalized neurofibromatosis:
Multifocal Deep Hemispheric Masses
- Primary CNS Lymphoma
- Gliomatosis cerebri
- nonenhancing tumor extension (common)
CNS Tumors Metastasizing Outside CNS
mnemonic: MEGO
- Medulloblastoma
- Ependymoma
- Glioblastoma multiforme
- Oligodendroglioma
Large Heterogeneous Intracerebral Mass
- High-grade glioma
- increased relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) in zone of edema on perfusion-weighted images
- Metastasis
- reduced relative cerebral blood volume (rCBV) in zone of edema on perfusion-weighted images
Mass with Large Tumor Vessels and Edema
- Glioblastoma multiforme
- Meningioma
mnemonic: TEACH
- Tumor: astrocytoma, metastasis, oligodendroglioma
- Edema
- Abscess
- Cyst, Contusion
- Hematoma, Herpes
- Oligodendroglioma (frequent, although rare tumor)
- Low-grade astrocytoma (in 10–20%)
mnemonic: Ca2+ COME
- Craniopharyngioma
- Astrocytoma, Aneurysm
- Choroid plexus papilloma
- Oligodendroglioma
- Meningioma
- Ependymoma
- Classification of Primary CNS Tumors
- CNS Tumors Presenting at Birth
- CNS Tumors in Pediatric Age Group
- Superficial Gliomas
- Multifocal CNS Tumors
- CNS Tumors Metastasizing Outside CNS
- Large Heterogeneous Intracerebral Mass
- Mass with Large Tumor Vessels and Edema
- Avascular Mass of Brain
- Calcified Intracranial Mass