Bone and Soft-Tissue Disorders
= SLIPPED CAPITAL FEMORAL EPIPHYSIS
= atraumatic fracture through hypertrophic zone of physeal plate
Frequency: 2÷100,000 people
Etiology: growth spurt, renal osteodystrophy, rickets, childhood irradiation, growth hormone therapy, trauma (Salter-Harris type I epiphyseal injury)
Pathogenesis: widening of physeal plate during growth spurt + change in orientation of physis from horizontal to oblique increases shear forces
Mean age: 13 years for often overweight boys (range, 8–17 years), 11 years for girls; M÷F = 3÷1; Black >White
Associated with:
- malnutrition, endocrine abnormality, developmental dysplasia of hip (during adolescence)
- delayed skeletal maturation (after adolescence)
- hip pain (50%) / knee pain (25%) for 2–3 weeks
Location: usually unilateral; bilateral in 20–37% (at initial presentation in 9–18%)
- widening of epiphyseal growth plate (preslip phase):
- irregularity + blurring of physeal physis
- demineralization of neck metaphysis
- posteromedial displacement of head (acute slip):
- decrease in neck-shaft angle with alignment change of growth plate to a more vertical orientation
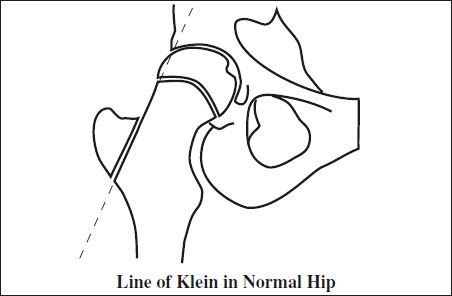
- line of Klein (= line drawn along superior edge of femoral neck) fails to intersect the femoral head
- epiphysis appears smaller ← posterior slippage: early slips are best seen on cross-table LAT view
CAVE: positioning into a frog leg view may cause further displacement
- sclerosis + irregularity of widened physis (chronic slip):
- metaphyseal “blanch” sign = area of increased opacity in proximal part of metaphysis (healing response)
Grading (based on femoral head position):
- mild = displaced by <⅓ of metaphyseal diameter
- moderate = displaced by ⅓/⅔ of diameter
- severe = displaced by >⅔ of metaphyseal diameter
Cx:
- Chondrolysis = acute cartilage necrosis (7–10%)
= rapid loss of >50% of thickness of cartilage- joint space <3 mm
- Avascular necrosis of femoral head (10–15%): risk increases with advanced degree of slip, delayed surgery for acute slip, anterior pin placement, large number of fixation pins, subcapital osteotomy
- Pistol-grip deformity = broadening + shortening of femoral neck in varus deformity
- Degenerative osteoarthritis (90%)
- Limb-length discrepancy ← premature physeal closure
Rx:
- limitation of activity
- prophylactic pinning
- osteotomy
- Attempted reductions increase risk of AVN!