Differential Diagnosis of Musculoskeletal Disorders
- Screws
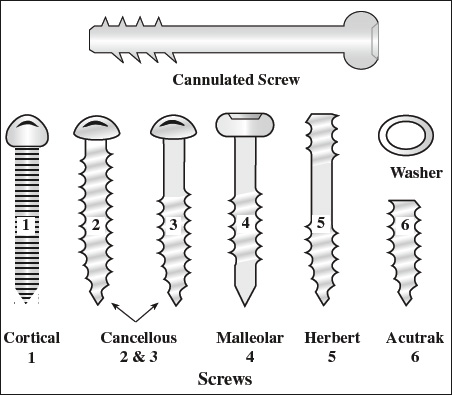
- Cannulated screw = hollow shaft screw inserted over guide pin (K-wire = Kirschner wire)
Use: fracture of femoral neck - Cortical screw = shallow finely threaded over entire length, blunt tip
Use: fixation of plates anchored in bone cortex - Cancellous screw = wide thread diameter with varying length of smooth shank between head + threads
Use: compression across fracture site anchored in soft medullary bone - Malleolar screw = partially threaded
- Herbert screw = cannulated screw threaded on both ends with wider pitch of proximal portion causing fragment compression, no screw head
Use: scaphoid + other carpal bone fractures - Interference screw = short, fully threaded, cancellous thread pattern, self-tapping tip, recessed head
Use: within tunnel holding bone graft of ACL and PCL reconstruction - Acutrak screw = cannulated screw fully threaded with variable thread pitch causing fragment compression, submerged without screw head
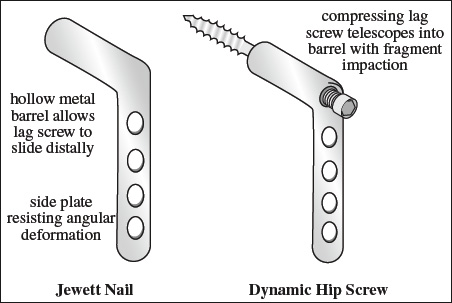
Use: scaphoid fracture - Dynamic hip screw = lag screw telescopes (= free to slide) within hollow metal barrel of angular side plate allowing impaction of fracture without perforation of subarticular cortex
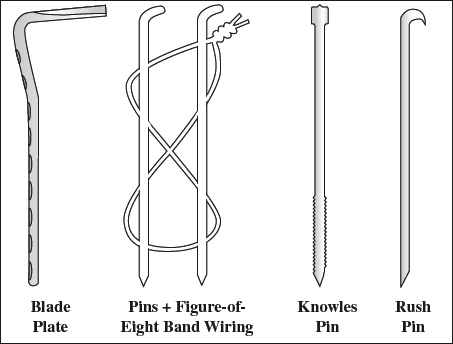
Use: intertrochanteric, subtrochanteric, subcapital fracture - Knowles pin
Use: proximal femoral neck fracture with tenuous blood supply - Radiolucent absorbable polycarbonate screw = “stealth hardware”
- Cannulated screw = hollow shaft screw inserted over guide pin (K-wire = Kirschner wire)
- Washer
- Flat washer = increase surface area over which force is distributed
- Serrated washer = spiked edges used for affixing avulsed ligaments / small avulsion fractures
- Plates
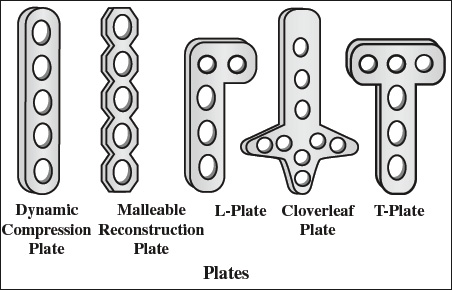
- compression plate
Use: compression of tension side of stable fractures - neutralization plate = protects fracture from bending, rotation + axial-loading forces
- buttress plate = support of unstable fractures in compression / axial loading
- Straight plate
- straight plate with round holes
- dynamic compression plate (DCP) = oval holes
- tubular plate = thin pliable plate with concave inner surface
- reconstruction plate = thin pliable / malleable plate to allow bending, twisting, contouring
- Special plates
T-shaped, L-shaped, Y-shaped, cloverleaf, spoon, cobra, condylar blade plate, dynamic compression screw system
- Straight plate
- compression plate
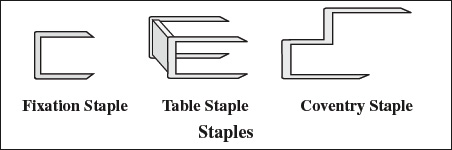
- Staples
Fixation = bone = epiphyseal = fracture staples with smooth / barbed surface- Coventry = stepped osteotomy staple
- stone = table staple
- Wires
- K wire (= Kirschner wire) = unthreaded segments of extruded wire of variable thickness
Use: temporary fixation - Cerclage wiring = wire placed around bone
Use: fixation of comminuted patellar fracture, holding bone grafts in position - Tension band wiring = figure-of-eight wire placed on tension side of bone
Use: olecranon / patellar fractures
- K wire (= Kirschner wire) = unthreaded segments of extruded wire of variable thickness
= smooth / threaded pins / wires attached to an external frame
- unilateral pin = enters bone only from one side
- Steinmann pin = large-caliber wire with pointed tip
- Rush pin = smooth intramedullary pin
- Schanz screw = pin threaded at one end to engage cortex, smooth at other end to connect to external fixation device
- Knowles pin (for femoral neck fracture)
- transfixing pin = passes through extremity supported by external fixation device on both ends
Intramedullary Fixation Devices
Use: diaphyseal long bone fractures
- nail / pin= driven into bone without reaming
- rod = solid / hollow device with blunted tip driven into reamed channel (reaming disrupts blood supply and may decrease the rate of fracture healing)
- interlocking nail = accessory pins / screws / deployable fins placed to prevent rotation
- Rush pin = beveled end + hooked end
Use: fibular shaft / tubular bone fractures - Ender nail = chisel-like end + oval in cross section; usually 3–4 at a time pushed through a cortical hole up or down the shaft across fracture under fluoroscopic control
Use: humeral shaft - Sampson rod = slightly curved rigid rod with fluted surface
- Küntscher nail = cloverleaf in cross section with rounded tip
Use: tibial / femoral shaft fracture - Zickel nail
Use: subtrochanteric fracture