= HPE = spectrum of congenital structural forebrain + midface anomalies characterized by failure of prosencephalon to divide (= cleavage disorder) → varying degrees of frontal lobe “fusion” (= noncleavage of cerebral hemispheres)
Etiology: multifactorial with environmental factors (maternal diabetes, ethyl alcohol, cigarette smoking, retinoic acid); chromosomal and genetic abnormalities; teratogen exposure; syndromic associations
Classic holoprosencephaly is a primary defect of ventral induction and patterning → total / partial failure of separation of prosencephalon into 2 separate hemispheres.
Pathogenesis:
arrested lateral ventricular growth in 6-week embryo → lack of cleavage / diverticulation of forebrain (= prosencephalon), laterally (cerebral hemispheres), transversely (telencephalon, diencephalon), horizontally (optic + olfactory structures) → cortical brain tissue develops to cover monoventricle and fuses in midline → posterior part of the monoventricle becomes enlarged and saclike
Associated with: agenesis of corpus callosum, septo-optic dysplasia, absence of cavum septi pellucidi
- Septum pellucidum always absent!
Sequence of disorders in prosencephalic ventral induction:
aprosencephaly → atelencephaly → alobar HPE → semilobar HPE → syntelencephaly → lobar HPE
Prevalence: 1÷10,000 in live and stillbirths; M÷F = 1÷1
- High rate of spontaneous abortions (50÷10,000)!
- Most common malformation of brain + face in humans
Classification (DeMyer):
- alobar = no hemispheric development
- semilobar = some hemispheric development
- lobar = frontal and temporal lobation + small monoventricle
Associated with:
polyhydramnios (60%), genital defects (24%), postaxial polydactyly (8%), vertebral defects (5%), limb reduction defects (4%), transposition of great arteries (4%), renal and cardiac anomalies; chromosomal anomalies (predominantly trisomy 13 + 18 in 24–45%)
Associated borderline syndromes←diencephalic malformation:
- Anophthalmia
- Microphthalmia
- Aplasia of pituitary gland
- Olfactogenital dysplasia
- Septooptic dysplasia
Prognosis: not uniformly lethal depending on severity of brain and facial malformations, presence of chromosomal abnormalities, involvement of other organs, and presence of multiple anomaly syndrome
DDx:
- Severe hydrocephalus (roughly symmetrically thinned cortex)
- Dandy-Walker cyst (normal supratentorial ventricular system)
- Hydranencephaly (frontal + parietal cortex most severely affected)
- Agenesis of corpus callosum with midline cyst (lateral ventricles widely separated with pointed superolateral margin)
= extreme form in which the prosencephalon does not divide
- minimal motor activity, little sensory response (ineffective brain function); seizures
- severe facial anomalies (“the face predicts the brain”):
- Normal face in 17%
- Cyclopia (= midline single orbit); may have proboscis (= fleshy supraorbital prominence)
+ absent nose [pro, Greek = forward; boscos, Greek = feed;proboskis, latinized = forward feeder, eg, elephant trunk]
Embryology: developmental interruption of single midline eye field into L + R eyes under signaling influence of prechordal plate - Ethmocephaly = 2 hypoteloric orbits + proboscis between eyes and absence of nasal structures
- Cebocephaly = 2 hypoteloric orbits + single nostril with small flattened nose + absent nasal septum
[kebos, Greek = monkey; kephale, Greek = head] - Median cleft lip + cleft palate + hypotelorism
- absent philtrum
- Others: micrognathia, trigonocephaly (early closure of metopic suture), microphthalmia, microcephaly
In alobar holoprosencephaly prosencephalic cleavage fails → single midline forebrain with primitive monoventricle often associated with a large dorsal cyst.
- crescent-shaped holoventricle = single large ventricle without occipital or temporal horns:
- “horseshoe” / “boomerang” configuration of brain
= peripheral rim of cerebral cortex displaced rostrally (coronal plane)- ball configuration (most common) = complete covering of monoventricle without dorsal cyst
- cup configuration = more cortex visible posteriorly
- pancake configuration = cortex covers monoventricle to edge of dorsal cyst
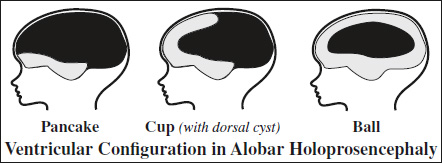
- cerebral mantle pachygyric
- “horseshoe” / “boomerang” configuration of brain
- absence of: anterior commissure, cavum septi pellucidi, falxcerebri, interhemispheric fissure, corpus callosum, fornix, optic tracts, olfactory bulb (= arrhinencephaly), internal cerebral veins, superior + inferior straight sagittal sinus, vein of Galen, tentorium, sylvian fissure, opercular cortex
- normal / fused / absent optic nerves
- fused thalami:
- protrusion of anteriorly placed fused hypothalamic and thalamic nuclei + basal ganglia into monoventricle resulting in absence of 3rd ventricle
- large dorsal cyst (in 92%) occupying most of calvarium widely communicating with single ventricle
Cause: fused thalami obstruct CSF flow → posterior ballooning of 3rd ventricle through suprapineal recess (= point of least resistance) - pancakelike cerebrum in posterior cranium
- ± single / azygos anterior cerebral artery:
- ± absence of middle + anterior cerebral arteries replaced by network of vessels arising from ICA + basilar vessels
- midbrain, brainstem, cerebellum structurally normal
- midline clefts in maxilla + palate
Prognosis: death within 1st year of life / stillborn
DDx: severe hydrocephalus, hydranencephaly (normal thalamic cleavage, partially visualized falx cerebri)
= intermediate form with incomplete cleavage of prosencephalon (more midline differentiation + beginning of sagittal separation) with >50%fusion of frontal lobes
- absent / mild facial anomalies: midline cleft lip + palate
- hypotelorism
- mental retardation
- single ventricular chamber with partially formed occipital horns + rudimentary temporal horns
- peripheral rim of brain tissue is several cm thick
- partially fused thalami anteriorly situated + abnormally rotated resulting in small 3rd ventricle:
- dorsal cyst (in 28%) → macrocephaly (if cyst large)
- absence of septum pellucidum + corpus callosum + olfactory bulb:
- part of corpus callosum may be present between posteriorly separated hemispheres
- rudimentary falx cerebri + interhemispheric fissure form posteriorly + caudally with partial separation of occipital lobes
- incomplete hippocampal formation
Prognosis: infants survive frequently into adulthood
= mildest form with formation of 3rd ventricle + some frontal horn + splenium and posterior body of corpus callosum
- May be part of septooptic dysplasia!
- usually not associated with facial anomalies except for hypotelorism, mild to severe mental retardation
- spasticity, athetoid movements
- interhemispheric fissure present along nearly entire midline
- separation into 2 cerebral hemispheres + 2 lateral ventricles
- closely apposed bodies of mildly dilated lateral ventricles
- distinct occipital + frontal horns
- colpocephaly
- dorsal cyst (in 9%)
- rudimentary unseparated frontal horns of angular squared shape + flat roof (on coronal images) ← dysplastic frontal lobes
- dysplastic anterior falx + interhemispheric fissure
- absence of septum pellucidum + sylvian fissures
- corpus callosum usually normal / incomplete
- hippocampal formation nearly normal
- basal ganglia + thalami completely / almost completely separated
- pachygyria (= abnormally wide + plump gyri), lissencephaly (= smooth gyri)
Prognosis: survival into adulthood
