= anterior displacement of one vertebra over another
Direction: anterolisthesis, retrolisthesis, lateral translation
Prevalence: 4% of general population
Causes (Newman classification):
- I congenital / dysplastic
- II isthmic / spondylytic
- III degenerative (disk disease)
- IV traumatic (fracture)
- V pathologic (bone tumor)
- VI postsurgical (removal of >50% of facet joint)
Grades I–IV (Meyerding method): each grade equals ¼ anterior subluxation of upper on lower vertebral body
Isthmic Spondylolisthesis = open-arch type
= pars interarticularis defect between superior + inferior articulating processes as weakest portion of spinal unit → separation of anterior part (vertebral body, pedicles, transverse processes, superior articular facet) slipping forward from posterior part (inferior facet, laminae, dorsal spinous process)
Cause: usually bilateral spondylolysis
Age: often <45 years
Location: L5-S1 (most common) or L4-5
- symptomatic if intervertebral disk + posterosuperior aspect of vertebral body encroaches on superior portion of neuroforamen causing nerve root compression:
- backache ± leg pain; sciatica ± backache
- elongation of spinal canal in anteroposterior diameter
- bilobed configuration of neuroforamen
- ratio of maximum anteroposterior diameter of spinal canal at any level divided by diameter at L1 >1.25
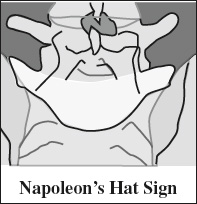
- inverted “Napoleon's hat” sign (on AP view) = severely subluxed L5 body (= dome of hat) that projects end-on overlapping the sacrum with transverse processes forming the hat's tapered brim
Degenerative Spondylolisthesis = closed-arch type
= PSEUDOSPONDYLOLISTHESIS
Cause: degenerative / inflammatory joint disease (eg, rheumatoid arthritis)
Pathophysiology: excess motion of facet joints allowing forward / posterior movement
Age: usually >60 years; M <F (at L4-5)
- commonly symptomatic ← spinal stenosis + narrowing of neuroforamen
- narrowing of spinal canal
- hypertrophy of facet joints
- ratio of maximum anteroposterior diameter of spinal canal at any level divided by diameter at L1 <1.25