- PERIOSTEUM
= continuation of outer layer of cerebral dura mater - EPIDURAL SPACE
= space between dura mater + bone containing rich plexus of epidural veins, lymphatic channels, connective tissue, fat- cervical + thoracic spine: spacious posteriorly, potential space anteriorly
- normal thickness of epidural fat 3–6 mm at T7
- lower lumbar + sacral spine: may occupy more than half of cross-sectional area
- cervical + thoracic spine: spacious posteriorly, potential space anteriorly
- DURA
= continuation of meningeal / inner layer of cerebral dura mater; ends at 2nd sacral vertebra + forms coccygeal ligament around filum terminale; sends tubular extensions around spinal nerves; continuous with epineurium of peripheral nerves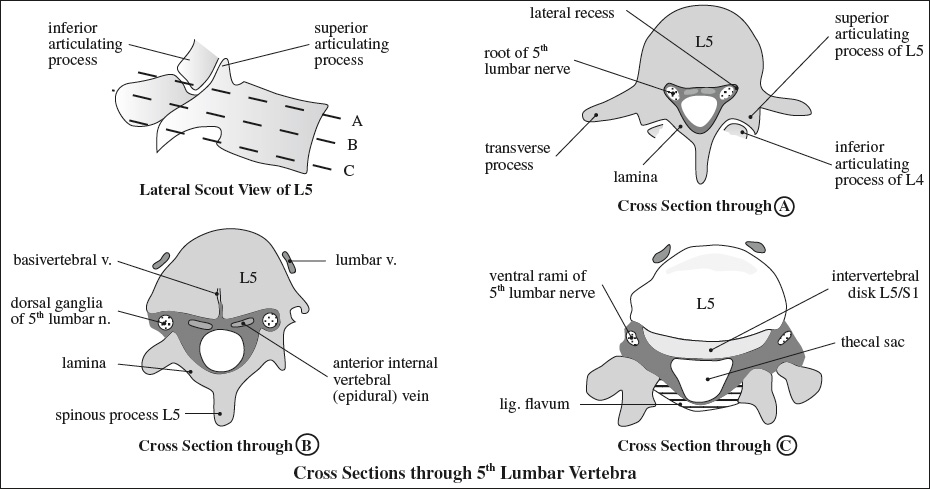
Attachment: at circumference of foramen magnum, bodies of 2nd + 3rd cervical vertebrae, posterior longitudinal ligament (by connective tissue strands) - SUBARACHNOID SPACE
= space between arachnoid and pia mater containing CSF, reaching as far lateral as spinal ganglia
dentate ligament partially divides CSF space into an anterior + posterior compartment extending from foramen magnum to 1st lumbar vertebra, is continuous with pia mater of cord medially + dura mater laterally (between exiting nerves)
dorsal subarachnoid septum connects the arachnoid to the pia mater (cribriform septum) - PIA MATER
= firm vascular membrane intimately adherent to spinal cord, blends with dura mater in intervertebral foramina around spinal ganglia, forms filum terminale, fuses with periosteum of 1st coccygeal segment
Artery of Adamkiewicz
[Albert Wojciech Adamkiewicz (1850–1921) Polish physician and chair of General and Experimental Pathology of Jagiellonian University in Kraków, Poland]
= GREAT ANTERIOR RADICULOMEDULLARY ARTERY
= most important feeder artery of thoracolumbar spinal cord
Diameter: 0.8–1.3 mm
Supply: lower ⅓ of spinal cord
Origin: left intercostal / lumbar artery (68–73%)
Level: 9–12th intercostal artery (62–75%)
Anatomy:
descending aorta →
intercostal / lumbar artery → division into
- anterior branch
- posterior branch→ subdivision into
- muscular branch
- dorsal somatic branch
- radiculomedullary artery→ subdivision into
- posterior radiculomedullary artery
- anterior radiculomedullary artery
Hairpin turn: at junction of artery of Adamkiewicz and anterior spinal artery ← increasing disparity between spinal segmental and vertebral levels during growth of spine
Visualization of hairpin: by MR angiography in 93% by CT angiography in 83% by selective angiography in 86%
Rx: paraplegia ← conventional selective angiography
DDx: anterior radiculomedullary vein (very similar shape and course as artery of Adamkiewicz)