Anatomy of the Nervous System
- PROSENCEPHALON = forebrain
forms from process of ventral induction (ie, 3 closely interconnected sequential events of formation + cleavage + midline development)
- cerebrum, lateral ventricles, choroid, thalami, cerebellum sonographically visible at 12 weeks MA
- Telencephalon = cerebrum
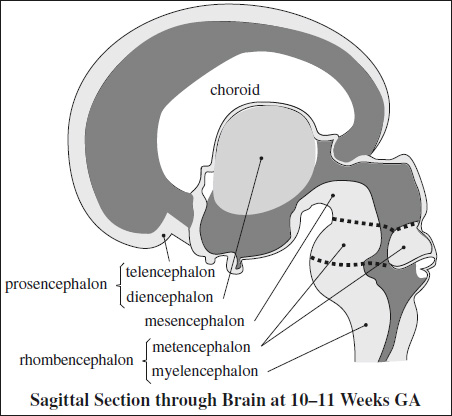
= cerebral hemispheres, putamen, caudate nucleus - Diencephalon
= thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus (= pineal gland + habenula), globus pallidus, optic vesicles
- MESENCEPHALON = midbrain
= short segment of brainstem above pons; traverses the hiatus in tentorium cerebelli; contains cerebral peduncles, tectum, colliculi (corpora quadrigemina) - RHOMBENCEPHALON = hindbrain
- posterior cystic space of 4th ventricle sonographically detectable between 8 and 10 weeks MA
- Metencephalon = cerebellar hemispheres, vermis
- Myelencephalon = medulla oblongata, pons
- BRAINSTEM = midbrain + pons + medulla contains
- cranial nerve nuclei
- sensory and motor tracts between thalamus, cerebral cortex, and spinal cord
- reticular formation controlling respiration, blood pressure, gastrointestinal function, centers for arousal and wakefulness
