Differential Diagnosis of Skull and Spine Disorders
Increased T1 Signal Intensity of Spinal Bone Marrow
= mostly benign
- FOCAL
- Hemangioma (11%)
- Modic type 2 endplate changes
- Lipoma
- Paget disease (later stage)
- Hemorrhage (with fracture)
- Melanoma
- DIFFUSE / MULTIFOCAL
- Normal variant
- S/P radiation treatment
- Osteoporosis
- Multiple hemangiomas
- Spondyloarthritis
- Anorexia nervosa
Decreased T1 Signal Intensity of Spinal Bone Marrow
= equal to / lower than SI of muscle
- CENTERED ON ENDPLATE
- Modic type 1 + 3 endplate changes
- Osteomyelitis
- Amyloid
- CENTERED IN VERTEBRAL BODY
- Malignancy (metastasis, lymphoma, plasma cell dyscrasia, solitary plasmacytoma, multiple myeloma)
- Fracture
- Hemangioma (rare presentation)
- Fibrous dysplasia
- CENTERED IN POSTERIOR ELEMENTS
metastases, myeloma, lymphoma, fracture, primary bone tumor - DIFFUSE / MULTIFOCAL
- Hematopoietic hyperplasia
- chronic anemia: sickle cell disease, thalassemia, hereditary spherocytosis
- chronic illness: HIV
- heavy smoking
- obesity
- drugs: granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor, erythropoietin
- Neoplasm
- avid enhancement
- Renal osteodystrophy
- Systemic inflammation: sarcoidosis, gout, spondyloarthropathy
- Hematologic malignancy: myelofibrosis. mastocytosis
- Hematopoietic hyperplasia
- NEOPLASM
- Metastasis
- Primary neoplasm: chordoma, chondrosarcoma, lymphoma, multiple myeloma
- INFECTION
- Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis
- Tuberculous spondylitis
- Brucellosis
- Fungal disease
- Echinococcosis
- Sarcoidosis
Granulomatous Spondylitis
- TB
- Brucellosis
- Sarcoidosis
- Osteonecrosis = Kümmell disease
- linear collection
- Osteomyelitis
- small gas bubbles ± extension into adjacent soft-tissues
- Intraosseous displacement of cartilaginous / Schmorl node
- branching gas pattern
- Malignancy
- Radiation therapy
during early childhood in excess of 1,000 rad - Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Location: cervical spine- atlantoaxial subluxation may be present
- vertebral fusion may occur
- Eosinophilic granuloma
Location: lumbar / lower thoracic spine- compression deformity / vertebra plana
- Gaucher disease
= deposits of glucocerebrosides within RES- compression deformity
- Platyspondyly generalisata
= flattened vertebral bodies associated with many hereditary systemic disorders: achondroplasia, spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda, mucopolysaccharidosis, osteopetrosis, neurofibromatosis, osteogenesis imperfecta, thanatophoric dwarfism- disk spaces of normal height
Vertebra Plana
mnemonic: FETISH
- Fracture (trauma, osteogenesis imperfecta)
- Eosinophilic granuloma (Langerhans cell histiocytosis)
- Tumor (metastatic neuroblastoma, myeloma, leukemia, aneurysmal bone cyst, Ewing sarcoma)
- Infection
- Steroids (avascular necrosis)
- Hemangioma
mnemonic: MELT
- Metastasis / Myeloma
- Eosinophilic granuloma
- Lymphoma
- Trauma / TB
Signs of Acute Vertebral Collapse on MR
- Osteoporosis
- retropulsion of posterior bone fragment
- Malignancy
- epidural soft-tissue mass
- no residual normal marrow signal intensity
- abnormal enhancement
- Paget disease
- “picture framing”; bone sclerosis
- Gigantism
- increase in height of body + disk
- Myositis ossificans progressiva
- bodies greater in height than width
- osteoporosis
- ossification of ligamentum nuchae
Enlarged Intervertebral Foramen
= NEUROFORAMINAL WIDENING = DUMBBELL-SHAPED / HOURGLASS LESION
- SOLID BENIGN
- Benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor (PNST):
- Neurofibroma
- Neurilemmoma = schwannoma
- Meningioma
- Extradural cavernous hemangioma
- Congenital absence / hypoplasia of pedicle
- Benign peripheral nerve sheath tumor (PNST):
- SOLID MALIGNANT
- Metastatic destruction of pedicle: neuroblastoma
- Malignant PNST
- Ewing sarcoma / primitive neuroectodermal tumor
- Solitary bone plasmacytoma
- Chondrosarcoma
- CYSTIC
- Dural ectasia (Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome)
- Synovial cyst
- Traumatic pseudomeningocele
- Arachnoid cyst
- Hydatid cyst
mnemonic: SPAR BIT
- Senile hypertrophic ankylosis (DISH)
- Psoriasis, Progressive myositis ossificans
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Reiter disease, Rheumatoid arthritis (juvenile)
- Block vertebra (Klippel-Feil)
- Infection (TB)
- Trauma
Straightening of Anterior Border
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Paget disease
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Reiter disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Normal variant
Anterior Scalloping of Vertebrae
- Aortic aneurysm
- Lymphadenopathy
- Tuberculosis
- Multiple myeloma (paravertebral soft-tissue mass)
Posterior Scalloping of Vertebrae
in conditions associated with dural ectasia
- INCREASED INTRASPINAL PRESSURE
- Communicating hydrocephalus
- Ependymoma
- MESENCHYMAL TISSUE LAXITY (dural ectasia)
- Neurofibromatosis
- Marfan syndrome
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Posterior meningocele
- BONE SOFTENING
- Mucopolysaccharidoses: Hurler, Morquio, Sanfilippo
- Achondroplasia
- Acromegaly (lumbar vertebrae)
- Ankylosing spondylitis (lax dura acting on osteoporotic vertebrae)
mnemonic: SALMON
- Spinal cord tumor
- AchondroPlasia
- Mucopolysaccharidosis
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Neurofibromatosis
mnemonic: DAMN MALE SHAME
- Dermoid
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Meningioma
- Neurofibromatosis
- Marfan syndrome
- Acromegaly
- Lipoma
- Ependymoma
- Syringohydromyelia
- Hydrocephalus
- Achondroplasia
- Mucopolysaccharidoses
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- CHILDHOOD
- Hurler syndrome = gargoylism
- rounded appearance of vertebral bodies
- mild kyphotic curve with smaller vertebral body at apex of kyphosis displaying tonguelike beak at anterior half (usually at T12 / L1)
- “step-off” deformities along anterior margins
- Hunter syndrome
less severe changes than in Hurler syndrome - Morquio disease
- flattened + widened vertebral bodies
- anterior “tonguelike” elongation of central portion of vertebral bodies
- Hypothyroidism = cretinism
- small flat vertebral bodies
- anterior “tonguelike” deformity (in children only)
- widened disk spaces + irregular endplates
- Hurler syndrome = gargoylism
- ADULTS
- Spondylosis deformans
- osteophytosis along anterior + lateral aspects of endplates with horizontal + vertical course ← shearing of outer annular fibers (Sharpey fibers connecting annulus fibrosus to adjacent vertebral body)
- Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH)
- flowing calcifications + ossifications along anterolateral aspect of >4 contiguous thoracic vertebral bodies ± osteophytosis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- bilateral symmetric syndesmophytes (= ossification of annulus fibrosus)
- “bamboo spine”
- “diskal ballooning” = biconvex intervertebral disks ← osteoporotic deformity of endplates
- straightening of anterior margins of vertebral bodies ← erosions
- ossification of paraspinal ligaments
- Fluorosis
- vertebral osteophytosis + hyperostosis
- sclerotic vertebral bodies + kyphoscoliosis
- calcification of paraspinal ligaments
- Acromegaly
- increase in anteroposterior diameter of vertebrae + concavity on posterior portion
- enlargement of intervertebral disk
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Neuropathic arthropathy
- Sternoclavicular hyperostosis
- Spondylosis deformans
Spine Ossification
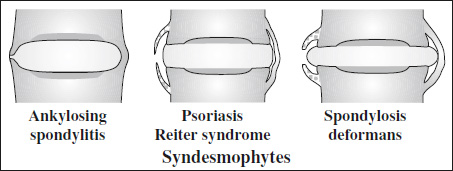
- Syndesmophyte = ossification of annulus fibrosus
- thin slender vertical outgrowth extending from margin of one vertebral body to next
Associated with: ankylosing spondylitis, ochronosis
- thin slender vertical outgrowth extending from margin of one vertebral body to next
- Osteophyte
= ossification of anterior longitudinal ligament- initially triangular outgrowth several millimeters from edge of vertebral body
Associated with: osteoarthritis
- initially triangular outgrowth several millimeters from edge of vertebral body
- Flowing anterior ossification
= ossification of disk, anterior longitudinal ligament, paravertebral soft tissues
Associated with: DISH - Paravertebral ossification
- initially irregular / poorly defined paravertebral ossification eventually merging with vertebral body
Associated with: psoriatic arthritis, Reiter syndrome
- initially irregular / poorly defined paravertebral ossification eventually merging with vertebral body
Vertebral Endplate Abnormality
- Cupid's bow vertebra
Cause: ? (normal variant)
Location: 3rd–5th lumbar vertebra- two parasagittal posterior concavities on inferior aspect of vertebral body (best viewed on AP)
- Osteoporosis (senile / steroid-induced)
- “fish vertebra / fish-mouth vertebra”
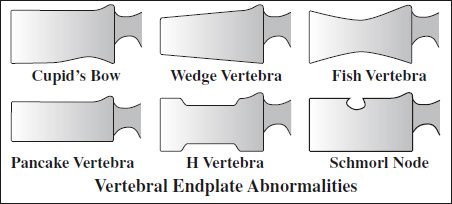
Cause: osteoporosis, osteomalacia, Paget disease, osteogenesis imperfecta, multiple myeloma, hyperparathyroidism, Gaucher disease- biconcave vertebra
- bone sclerosis along endplates
- wedge-shaped vertebra
- anterior border height reduced by >4 mm compared to posterior border height
- “pancake” vertebra
- overall flattening of vertebra
- “fish vertebra / fish-mouth vertebra”
- “H-vertebra”
= compression of central portions ← subchondral infarcts
Cause: sickle cell + other anemias, Gaucher disease - Schmorl / cartilaginous node
= intraosseous herniation of nucleus pulposus at center of weakened endplate
Cause: Scheuermann disease, trauma, hyperparathyroidism, osteochondrosis - Butterfly vertebra
Cause: congenital defect - Limbus vertebrae
= intraosseous herniation of disk material at junction of vertebral bony rim of centra + endplate (anterosuperior corner) - “Rugger-jersey spine”
Cause: hyperparathyroidism, myelofibrosis- horizontal sclerosis subjacent to vertebral endplates with intervening normal osseous density (resembling the stripes on rugby jerseys)
- “Sandwich” / “Hamburger” vertebra
Cause: osteopetrosis, myelofibrosis- sclerotic endplates alternate with radiolucent midportions of vertebral bodies
- “Ring” epiphysis
Ring Epiphysis
= normal small steplike recess at corner of anterior edge of developing vertebral body that calcifies ~ 6 years of age, ossifies ~ 13 years of age, and fuses with vertebral body ~ 17 years of age
- Severe osteoporosis
- Healing rickets
- Scurvy
mnemonic: HAM
- Hypothyroidism
- Achondroplasia
- Morquio syndrome
= “ghost vertebra” following stressful event during vertebral growth phase in childhood
- Stress line of unknown cause
- Leukemia
- Heavy metal poisoning
- Thorotrast injection, TB
- Rickets
- Scurvy
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypoparathyroidism
= increase in opacity of vertebral body retaining its size and contours
Cause: stimulation of osteoblasts, coarsening of trabeculae, reactive bone formation
- in adults: metastasis (prostate, breast), lymphoma (Hodgkin disease), Paget disease, osteosarcoma, carcinoid
- in children: Hodgkin disease >>osteosarcoma, metastatic neuroblastoma, medulloblastoma, osteoblastoma
mnemonic: LOST FROM CHOMP
- Lymphoma
- Osteopetrosis
- Sickle cell disease
- Trauma, Tuberculous spondylitis
- Fluorosis
- Renal osteodystrophy
- Osteoblastic metastasis
- Myelosclerosis
- Chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis, Chordoma
- Hemangioma
- Osteosarcoma
- Myeloma
- Paget disease
- Osteoid osteoma
- Unilateral spondylolysis
- Contralateral congenitally absent pedicle
- Increased T1 Signal Intensity of Spinal Bone Marrow
- Decreased T1 Signal Intensity of Spinal Bone Marrow
- Destruction of Vertebral Body
- Gas in Vertebral Body
- Small Vertebral Body
- Enlarged Vertebral Body
- Enlarged Intervertebral Foramen
- Cervical Spine Fusion
- Vertebral Border Abnormality
- Bony Outgrowths from Vertebra
- Vertebral Endplate Abnormality
- Bullet-shaped Vertebral Body
- Bone-within-bone Vertebra
- Ivory Vertebra
- Sclerotic Pedicle