= AARF = ATLANTOAXIAL ROTATORY SUBLUXATION (AARS) = ATLANTOAXIAL ROTATORY FIXATION (AARF) = SPONTANEOUS HYPEREMIC DISLOCATION = ATLANTOAXIAL ROTATORY / ROTARY DISLOCATION = DISTENTION LUXATION = NASOPHARYNGEAL TORTICOLLIS
= nontraumatic subluxation / rotational disorder of atlantoaxial joint leading to limited rotation / fixation of neck comprising many different entities
Cause: idiopathic spontaneous
- increased ligamentous laxity: rheumatoid arthritis, Marfan syndrome, Down syndrome, Morquio syndrome
- congenital abnormality: incomplete odontoid process, incomplete transverse ligament
- infection: sinusitis, otomastoiditis, otitis media, pharyngitis, adenotonsillitis, cervical / retropharyngeal / tonsillar abscess = Grisel syndrome
(= not associated with trauma or bone disease primarily in children) ← hyperemia + pathologic ligamentous relaxation
Predisposed: cervical dystonia, post surgery
May be associated with: ipsilateral contracted SCMM
- history of insignificant cervical spine trauma / upper respiratory tract infection
- limited painful neck motion = painful torticollis
- head held in “cock-robin” position = rotation + flexion + tilt of head contralateral to direction of rotation with inability to turn head that does not resolve within 5–7 days after injury
X-ray (Dx difficult to make):
- atlanto-odontoid asymmetry (open mouth odontoid view):
- decrease in atlanto-odontoid space + widening of lateral mass on side ipsilateral to rotation
- increase in atlanto-odontoid space + narrowing of lateral mass on side contralateral to rotation
- atlantoaxial asymmetry remains constant with head turned into neutral position
- posterior arch of C1 not identified in true lateral projection
- obscuration of craniovertebral junction in true lateral view
CT (dynamic with 3D reconstruction [a] with head in resting position [b] with maximal contralateral rotation):
- facet displacement in neutral head position
- asymmetrically fixed C1-C2 rotation
Rotation up to an average of 79° in adult volunteers, loss of contact of articular facets of C1 and C2 during rotation as high as 74–85% in physiologic conditions. Therefore, a diagnosis of subluxation of the atlanto-occipital joint should not be made based solely on the CT appearance of this joint.
MR:
- disruption of alar + transverse ligg.
- spinal cord compression (rare)
Types:
- I <3 mm anterior displacement of atlas on axis = rotatory fixation within normal range of movement (most common)
Injury: intact alar + transverse ligaments- pivot around dens, NO anterior displacement of atlas
- II 3–5 mm anterior displacement of atlas + unilateral displacement of lateral mass of atlas ← restraint by alar lig.
Injury: transverse ligament- center of rotation shifted to one of lateral masses
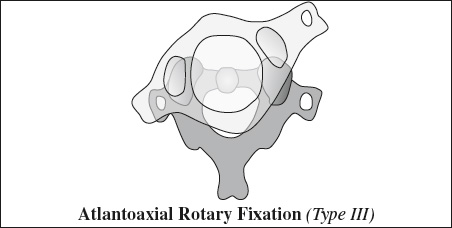
- III >5 mm anterior displacement of atlas + anterior displacement of both lateral masses
Injury: deficiency of both (alar + transverse) ligaments - IV posterior displacement of atlas on axis (rare)
Injury: deficiency of both (alar + transverse) ligaments
DDx: torticollis (atlantoaxial symmetry reverts to normal with head turned into neutral position)
Traumatic Rotatory Subluxation
Cause: injury of alar ligaments ← flexion + rotation forces
Age: more prevalent in children than in adults ← mostly flat articular facets allow ample movement in multiple directions