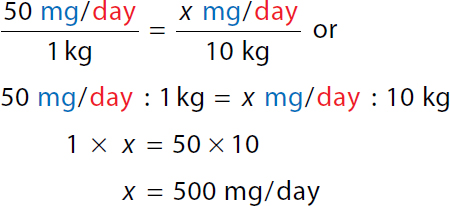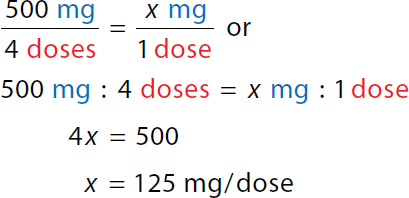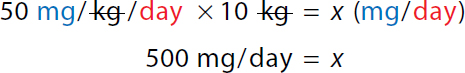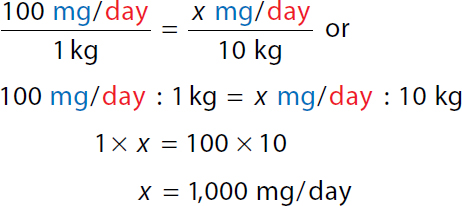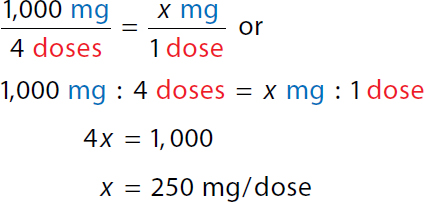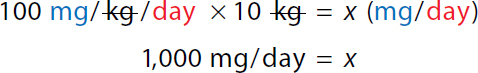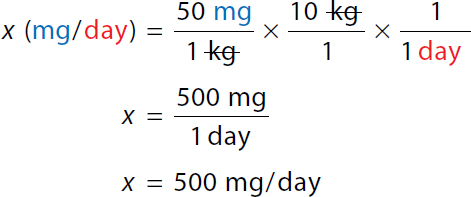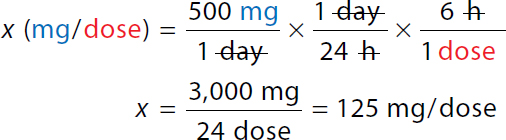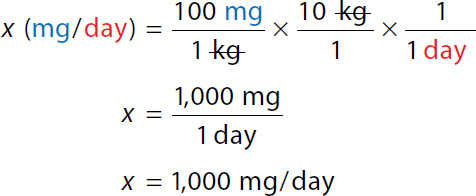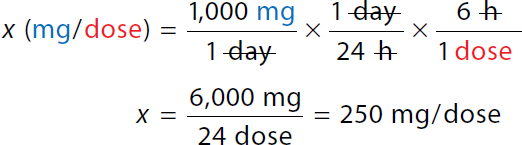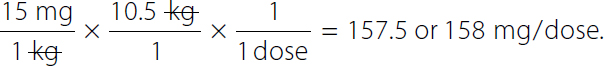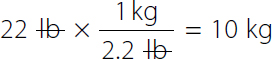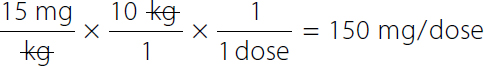Some daily medication safe doses are determined within a range, such as 10 to 20 mg/kg/day. In this case, the nurse will perform two calculations—the first to obtain the minimum safe dose and the second to obtain the maximum safe dose. After determining the safe daily dose range, if desired, the nurse may determine the minimum and maximum safe single doses by dividing both the minimum and maximum safe daily doses by the number of doses per day. Or, if using dimensional analysis, the nurse would multiply by the frequency factor and the conversion factor 1 day/24 h.
Example: Calculate the safe daily dose range and the safe single dose range of ampicillin for a 10 kg child. Regarding ampicillin, the drug reference recommends "50–100 mg/kg/day in divided doses q6h." For ratio-proportion and the formula method, the safe single dose range is calculated after determining the number of doses per day. Because q6h occurs 4 times per day, there are 4 doses per day.
Ratio-Proportion | Formula Method |
|---|---|
Minimum daily dose
To calculate the value of x. Calculation reads, 50 milligrams over day over 1 kilogram equals x milligrams over day all over 10 kilograms or. A ratio of 50 milligrams over day to 1 kilogram equals a ratio of x milligrams over day to 10 kilograms. 1 times x equals 50 times 10. x equals 500 milligrams over day. Minimum single dose
Calculation reads, 500 milligrams over 4 doses equals x milligrams over 1 dose or. A ratio of 500 milligrams to 4 doses equals a ratio of x milligrams to 1 dose. 4 x equals 500. x equals 125 milligrams over dose. | Minimum daily dose
50 milligram over kilogram over day times 10 kilogram equals x milligram over day. On the left-hand side, The numerator and denominator kilogram canceled each other. 500 milligrams over day equals x. Minimum single dose
500 milligrams over day divided by 4 doses over day equals milligrams over dose. On the left-hand side, The numerator and denominator day canceled each other. 125 milligrams over dose equals x. |
To calculate the maximum daily dose. 100 milligrams over day over 1 kilogram equals x milligrams over day over 10 kilograms or. A ratio of 100 milligrams over day to 1 kilogram equals a ratio of x milligrams over day to 10 kilograms. 1 times x equals 100 times 10. x equals 1000 milligrams over day. Maximum single dose
1000 milligram over 4 doses equals x milligram over 1 dose or. A ratio of 1000 milligrams to 4 doses equals a ratio of x milligrams to 1 dose. 4 x equals 1000. x equals 250 milligrams over dose. | Maximum daily dose
100 milligram over kilogram over day times 10 kilogram equals x milligram over day. 1000 milligrams over day equals x. Maximum single dose
1000 milligrams over day divided by 4 doses over day equals milligrams over dose. On the left-hand side, The numerator and denominator day canceled each other. 250 milligrams over dose equals x. |
Dimensional Analysis | |
Minimum daily dose
To calculate the minimum daily dose. x milligrams over day equals 50 milligrams over 1 kilogram times 10 kilograms over 1 time 1 over 1 day. On the right-hand side, The numerator and denominator kilogram canceled each other. x equals 500 milligrams over 1 day. x equals 500 milligrams over the day. Minimum single dose
To calculate the minimum single dose. x milligram over dose equals 500 milligrams over 1 day times 1 day over 24 hours times 6 hours over 1 dose. On the right-hand side, both numerator and denominator day and hour canceled each other. x equals 3000 milligrams over 24 dose equals 125 milligrams over dose. | |
Maximum daily dose
To calculate the maximum daily dose. x milligrams over day equals 100 milligrams over 1 kilogram times 10 kilograms over 1 times 1 over 1 day. On the right-hand side, The numerator and denominator kilogram canceled each other. x equals 1000 milligrams over 1 day. x equals 1000 milligrams over day. Maximum single dose
To calculate the maximum single dose. x milligram over dose equals 1000 milligrams over 1 day times 1 day over 24 hours times 6 hours over 1 dose. On the right-hand side, both numerator and denominator day and hour canceled each other. x equals 6000 milligrams over 24 doses equals 250 milligrams over dose. | |
- The minimum daily dose of ampicillin for a 10 kg child is 500 mg per day.
- The maximum daily dose of ampicillin for a 10 kg child is 1,000 mg per day.
- The safe daily dose range of ampicillin for a 10 kg child is 500 to 1,000 mg per day.
- The minimum single dose of ampicillin for a 10 kg child is 125 mg per dose.
- The maximum single dose of ampicillin for a 10 kg child is 250 mg per dose.
- The safe single dose range of ampicillin for a 10 kg child is 125 to 250 mg per dose.
The safe dose and safe dose range of medications that are typically ordered on a scheduled basis are usually determined per day rather than per dose. For example, because antibiotics and cardiac medications are scheduled around the clock, drug references usually provide information regarding the safe daily dose/dose range of these drugs. From this information, the nurse will calculate the safe daily dose/dose range and:
|
LEARNING ACTIVITY 12-3 The recommended dose of amoxicillin is 20 to 40 mg/kg/day in divided doses q12h. Convert the weight of a 12 lb 4 oz infant to kg, then calculate the:
1. Minimum daily dose
2. Maximum daily dose
3. Minimum single dose
4. Maximum single dose
Clinical CLUE 12-4Weight-based medications require accurate weights to be recorded in charts. In the interest of time, a prescriber may order medications based on a reported weight instead of an actual weight. This may cause a discrepancy in the safe dose calculation obtained by the nurse and the prescriber. Consider the following scenario:
15 milligrams over 1 kilogram times 10.5 kilograms over 1 times 1 over 1 dose equals 157.5 or 158 milligrams over dose. On the left-hand side The numerator and denominator kilogram canceled each other.
22-pound times 1 kilogram over 2.2 pounds equals 10 kilograms. On the left-hand side. Both the numerator and denominator pound canceled each other.
15 milligrams over kilogram times 10 kilograms over 1 time 1 over 1 dose equals 150 milligrams over 1 dose. On the left-hand side, The numerator and denominator kilogram canceled each other. Because of the discrepancy between the dose ordered and the safe dose calculation, the nurse questions the order. This discrepancy can be avoided if patient weights are promptly obtained and recorded (Figure 12-2). Accurate weights are needed for weight-based medication doses.
A photo of a newborn on the tray of a neonatal weighing machine. © Francois Etienne du Plessis/Shutterstock. |