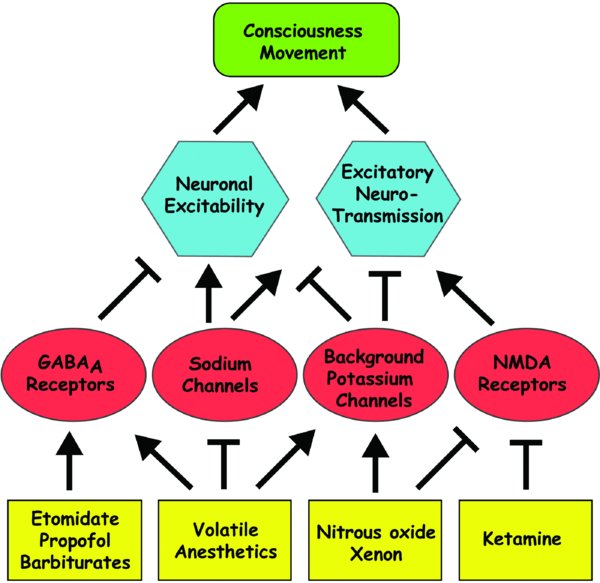
Anesthetics are grouped according to similarity of mechanism. Arrows indicate activation or potentiation, and Ts indicate inhibition or antagonism. The neurophysiologic effects of general anesthetics are lumped into neuronal excitability (the probability of a neuron firing and propagating an axon potential) and excitatory neurotransmission (synaptic activity at excitatory synapses such as glutamatergic). Neuronal excitability in this context is the sum of both intrinsic and extrinsic factors (GABAergic inhibition). GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; NMDA, N-methyl-d-aspartic acid.